TNU Journal of Science and Technology
230(05): 346 - 352
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 346 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
ASSESSMENT OF HEMOLYTIC TOXICITY OF
CHLORHEXIDINE DIGLUCONATE AND 1200 µg/mL CHLORHEXIDINE
DIGLUCONATE MOUTHWASH SOLUTION
Nguyen Khac Tiep, Nguyen Ngoc Anh, Nguyen Duc Thien*
Ha Noi University of Pharmacy
ARTICLE INFO
ABSTRACT
Received:
15/8/2024
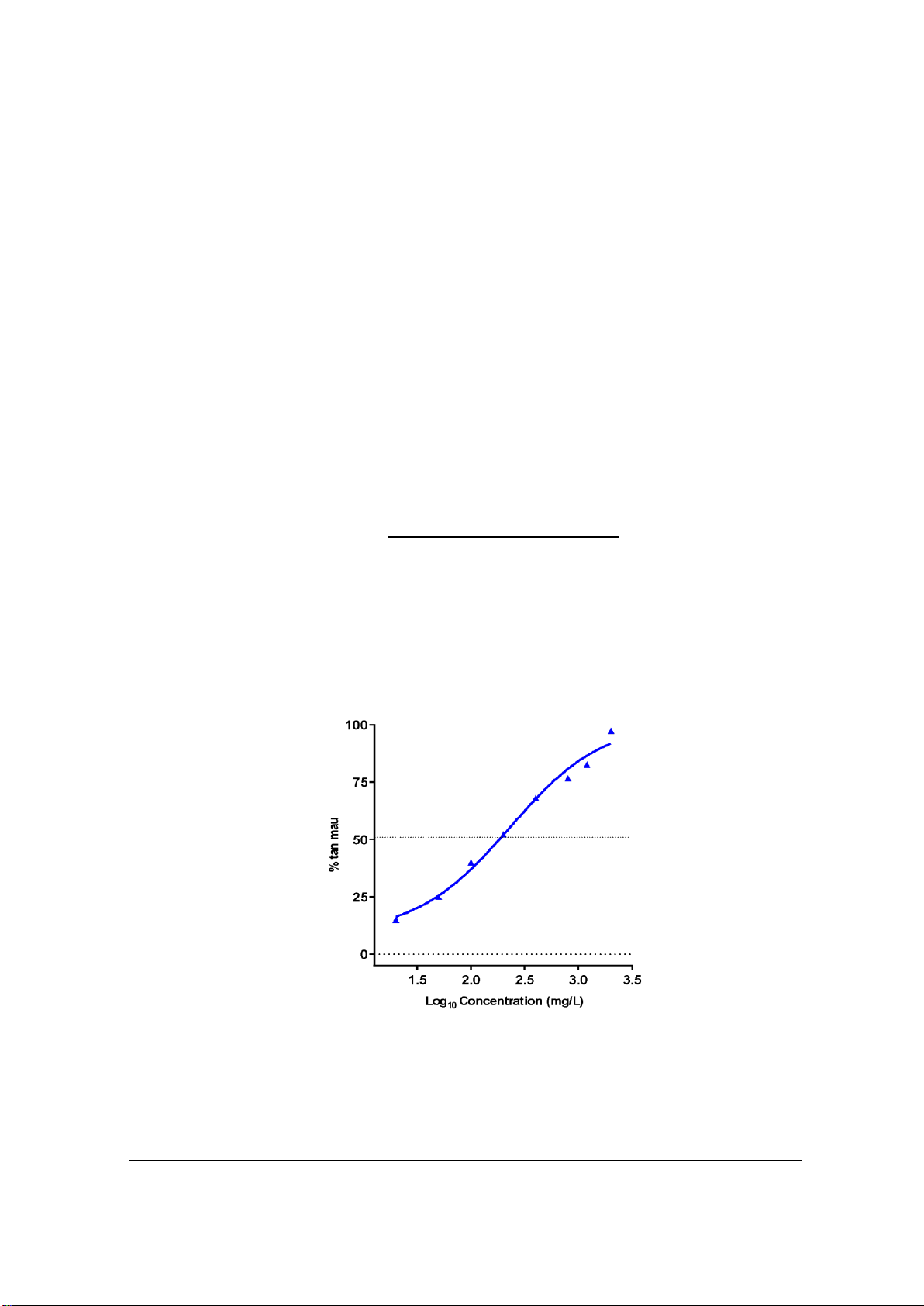
Chlorhexidine digluconate is an active ingredient that can kill many
strains of microorganisms, it can destroy red blood cells causing
hemolysis. The erythrocyte ability of chlorhexidine digluconate is
concentration-dependent, at a concentration of 20 µg/mL it is capable of
disrupting the red blood cell membrane. When chlorhexidine
digluconate solution was at a concentration of 1200 µg/mL, the
hemolysis rate increased to 84.7%, at 2000 µg/mL, the hemolysis rate
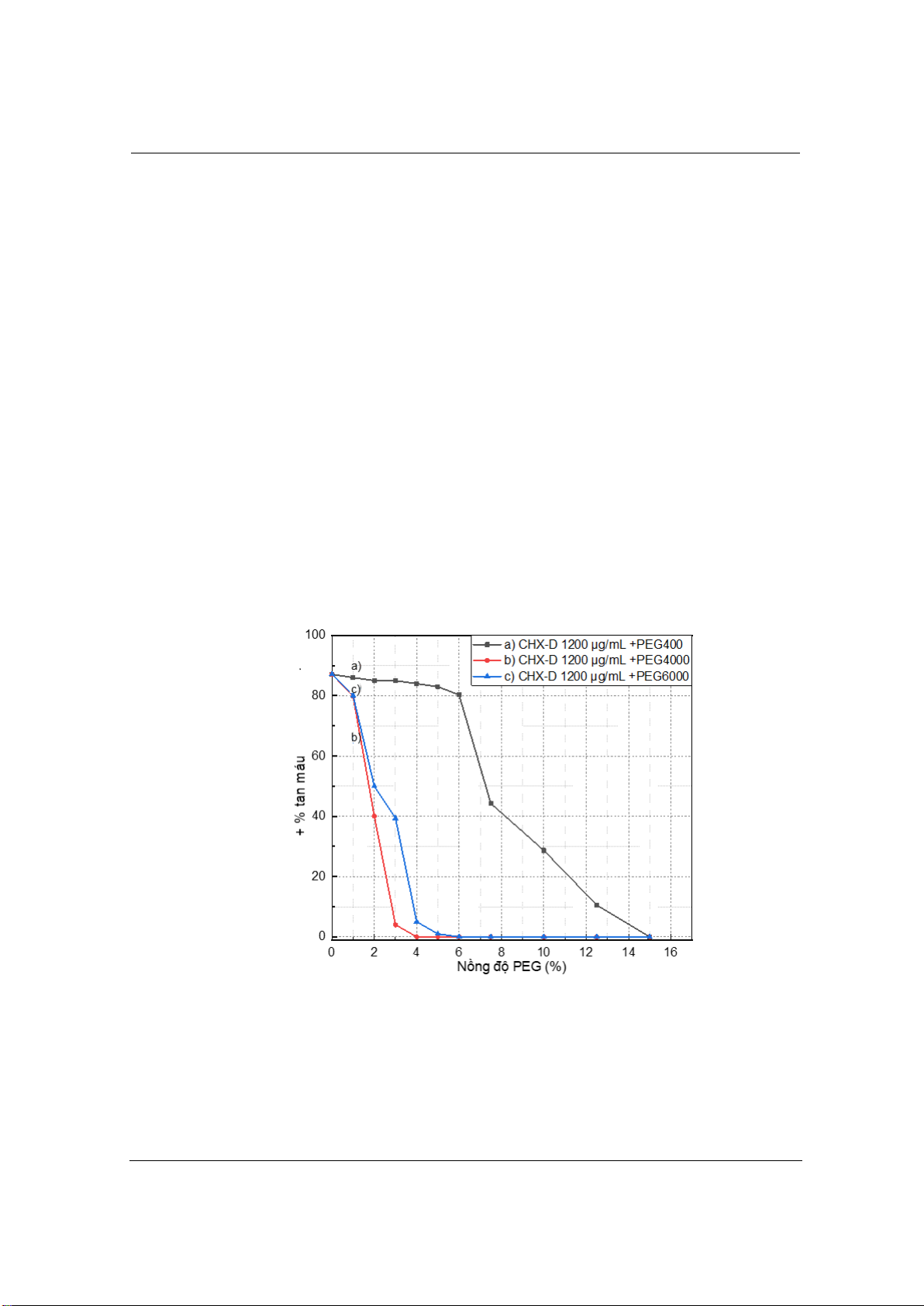
was 97.45%. Combining PEG400, PEG4000 and PEG6000 with a
sample solution containing chlorhexidine digluconate 1200 µg/mL, the
% of hemolysis decreases. The concentration of PEG400 is 15% in the
chlorhexidine digluconate 1200 µg/mL sample and does not cause
hemolysis. With PEG4000 at 3% concentration or PEG6000 at 4%
concentration in chlorhexidine digluconate solution at 1200 µg/mL, the
percentage of hemolysis was reduced to less than 5%, the test mixture
was less toxic to red blood cells. The excipients that create flavor, color
and taste in the mouthwash did not cause hemolysis and did not affect
the antibacterial and lytic properties of chlorhexidine digluconate. The
addition of PEG in mouthwashes using the antibacterial agent
chlorhexidine digluconate is necessary to reduce its hemolytic effect.
Revised:
06/02/2025
Published:
07/02/2025
KEYWORDS
Chlorhexidine
PEG
Mouthwash
Cytotoxicity
Hemolytic
KHẢO SÁT ĐỘC TÍNH ĐỐI VỚI MÀNG TẾ BÀO HỒNG CẦU CỦA
DUNG DỊCH CHLORHEXIDINE DIGLUCONATE VÀ
DUNG DỊCH NƯỚC SÚC MIỆNG CHLORHEXIDINE DIGLUCONATE 1200 µg/mL
Nguyễn Khắc Tiệp, Nguyễn Ngọc Ánh, Nguyễn Đức Thiện*
Trường Đại học Dược Hà Nội
THÔNG TIN BÀI BÁO
TÓM TẮT
Ngày nhận bài:
15/8/2024
Chlorhexidine digluconate là hoạt chất có khả năng diệt nhiều chủng vi sinh
vật, nó có thể phá hủy hồng cầu gây ra tan máu. Khả năng phá hủy hồng
cầu của chlorhexidine digluconate phụ thuộc vào nồng độ. Ở nồng độ 20
µg/mL nó đã có khả năng phá vỡ màng tế bào hồng cầu. Khi dung dịch
chlorhexidine digluconate ở nồng độ 1200 µg/mL thì tỷ lệ tan máu tăng lên
84,7%, ở 2000 µg/mL thì tỷ lệ tan máu là 97,45%. Phối hợp PEG400,
PEG4000 và PEG6000 với dung dịch mẫu thử chứa chlorhexidine
digluconate 1200 µg/mL thì tỷ lệ tan máu giảm. Nồng độ PEG400 là 15%
trong mẫu thử chlorhexidine digluconate 1200 µg/mL thì không gây ra tan
máu. Với PEG4000 nồng độ 3% hoặc PEG6000 nồng độ 4% trong dung
dịch chlorhexidine digluconate 1200 µg/mL thì tỷ lệ tan máu giảm xuống
dưới 5%, hỗn hợp thử ít gây độc tính lên tế bào hồng cầu. Các tá dược tạo
mùi, màu và vị trong nước súc miệng không gây tan máu và không ảnh
hưởng đến đặc tính kháng khuẩn và gây tan máu của chlorhexidine
digluconate. Việc bổ sung PEG trong nước súc miệng sử dụng chất kháng
khuẩn chlorhexidine digluconate là cần thiết để giảm khả năng tan máu.
Ngày hoàn thiện:
06/02/2025
Ngày đăng:
07/02/2025
TỪ KHÓA
Chlorhexidine
PEG
Nước súc miệng
Độc tính trên tế bào
Tan máu
DOI: https://doi.org/10.34238/tnu-jst.10947
* Corresponding author. Email: thiennd@hup.edu.vn