
XỬ LÝ ẢNH TRONG CƠ ĐIỆN TỬ
Machine Vision
1
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC BÁCH KHOA HÀ NỘI
Giảng viên: TS. Nguyễn Thành Hùng
Đơn vị: Bộ môn Cơ điện tử, Viện Cơ khí
Hà Nội, 2021
2
Chapter 6. Image Segmentation
1. Fundamentals
2. Point, Line, and Edge Detection
3. Thresholding
4. Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods, “Digital image processing,” Pearson (2018).

3
1. Fundamentals
Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods, “Digital image processing,” Pearson (2018).
➢Let R represent the entire spatial region occupied by an image. We may view
image segmentation as a process that partitions R into n subregions, R1, R2, …,
Rn, such that:
where Q(Rk) is a logical predicate defined over the points in set Rkand is the null
set.

4
1. Fundamentals
Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods, “Digital image processing,” Pearson (2018).
➢Two regions Riand Rjare said to be adjacent if their union forms a connected
set.
➢The regions are said to disjoint If the set formed by the union of two regions is
not connected.
➢The fundamental problem in segmentation is to partition an image into regions
that satisfy the preceding conditions.
➢Segmentation algorithms for monochrome images generally are based on one
of two basic categories dealing with properties of intensity values: discontinuity
and similarity.
▪Edge-based segmentation
▪Region-base segmentation
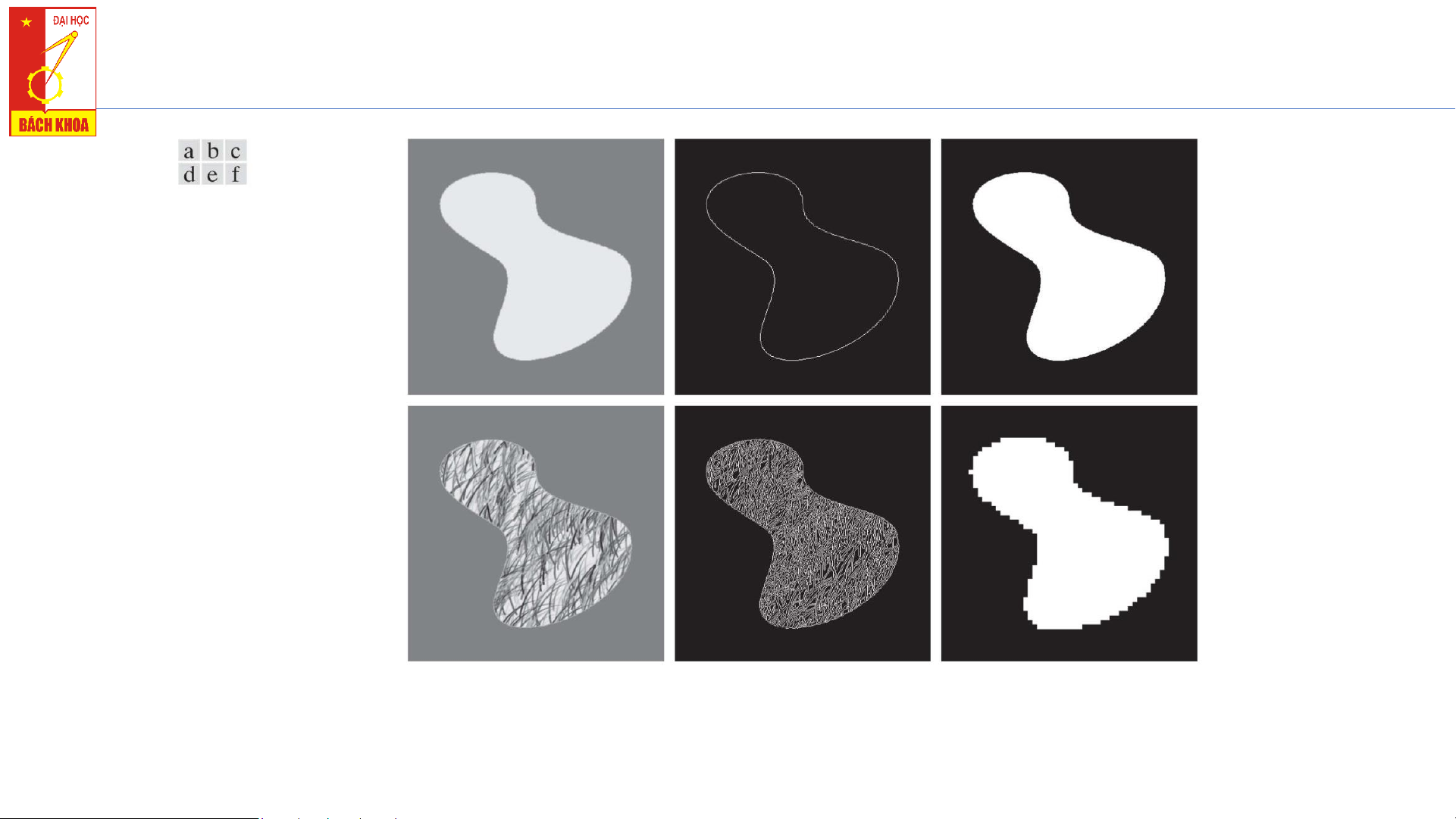
5
1. Fundamentals
Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods, “Digital image processing,” Pearson (2018).
(a) Image of a constant intensity region. (b) Boundary based on intensity discontinuities. (c) Result of
segmentation. (d) Image of a texture region. (e) Result of intensity discontinuity computations (note
the large number of small edges). (f) Result of segmentation based on region properties.









![Bài giảng Nguyên lý thị giác: Tổng quan [chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2020/20200824/trungtran87/135x160/6131598232982.jpg)
















