http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 265 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 7, Issue 7, November–December 2016, pp.265–270, Article ID: IJM_07_07_028
Available online at
http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=7&IType=7
Journal Impact Factor (2016): 8.1920 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
PERSONAL FINANCE IS MORE PERSONAL THAN IT
IS FINANCE: A STUDY ON FACTORS INFLUENCING
INVESTMENT CHOICE ON INVESTMENTS IN
TIRUCHIRAPPALLI CITY CORPORATION,
TAMIL NADU
Dr. I. Francis Gnanasekar
Associate Professor in Commerce, Former Vice-Principal & HOD
St. Joseph’s College (Autonomous), Tiruchirappalli, India
ABSTRACT
This study aims at to know the objectives of investments and also aims at to know the factors
that are considered before investments, i.e., factors influencing in selection of a particular type of
financial instruments and the behaviour of investors. The data has been collected through
structured questionnaire from the loyal, regular, serious, sincere investors. The data has been
tested by different statistical analysis namely; Frequency table, Percentage analysis, Chi-square
test, Descriptive statistics, Friedman rank test and so on. The findings of the study exposes that
regular income is the main objective of investments and investor considering safety as a principal
before investing. The Friedman rank test showed that not much difference between the top four
factors like capital appreciation, to gain a regular return, investment return, and reducing future
risk with regard to factors influence while selecting particular financial instruments.
Key words: Safety of principal, Descriptive statics and Friedman rank test
Cite this Article: Dr. I. Francis Gnanasekar, Personal Finance is more Personal than it is Finance:
A Study on Factors Influencing Investment Choice on Investments in Tiruchirappalli City
Corporation, Tamil Nadu. International Journal of Management, 7(7), 2016, pp. 265–270.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=7&IType=7
1. INTRODUCTION
Investment may be defined as an activity that commits funds in any financial/physical form in the present
with an expectation of receiving an additional return in the future. The expectation brings with it a
probability that the quantum of return may vary from a minimum to maximum. This possibility of
variation in the actual return is known as investment risk. Thus every investment involves a return and risk.
Investment is an activity that is undertaken by those who our savings. Savings can be defined as the excess
of income over expenditure. However, all savers need not be investors B S Bodla and Karam Pal (2016).
The basic objective of the investors minimizes the risk as well as maximizing the returns from the
investment. In the modern world investments are abundantly available viz., equity shares, preference
shares, debenture/bonds, mutual funds, real estate, postal savings, gold and so on. Similarly, several factors

Dr. I. Francis Gnanasekar
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 266 editor@iaeme.com
influencing the investors while selecting the particular type of financial interments viz., safety, liquidity,
capital appreciation, personal factors, family influence and so on. Hence, the study was carried out to know
the factors influencing the investors while selecting the financial instruments and behaviour of the
investors.
2. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
• to know the objectives of investments and find out the factors that investors consider before investing;
• to identify important factors influencing in selection of a particular type of financial instruments; and
• to study the responses and behaviour of the investors when company announce annual results.
3. HYPOTHESES
• There is no significant difference between age of the investor and their investment behaviour (Buy a Stock)
• There is no significant difference between age of the investor and their investment behaviour (Hold a Stock)
• There is no significant difference between age of the investor and their investment behaviour (Sella Stock)
4. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Dhiraj Jains and Nakul Dashora (2012) analyzed the rationality of the investors of Udaipur during different
market expectations, dividend and bonus announcements, the impact of age, income levels and other
market-related information on investment decisions of investors from Udaipur. The study exposed that,
investors prefer ‘A wait and watch policy’ for taking their decisions, and are very cautious and their
decisions are influenced by various psychological factors and behavioral dimensions.
Syed Tabassum Sultana and S Pardhasaradhi (2012), examined the factors influencing Indian
individual equity investors. The empirical findings of factor analysis exposed that all the 40 attributes are
reduced to the following ten factors Individual Eccentric, Wealth Maximization, Risk Minimization, Brand
Perception, Social Responsibility, Financial Expectation, Accounting information, Government & Media,
Economic Expectation and Advocate recommendation factors.
Francis Gnanasekar and Arul (2014), has stated that investors are of different categories. In this study,
the researchers found out various types of investors like a conservative, moderately conservative,
Aggressive and moderately aggressive. Moreover, investor’s risk tolerance varies on the basis of age, sex,
income; financial goals and so on.
Khoa Cuong Phan and Jian Zhou (2014), examined that factors influencing individuals’ investment
behavioral intention in the Vietnamese stock market. The empirical findings of the study exposed that
existence of psychological factors which supports the hypothesis that four psychological factors
(overconfidence, excessive optimism, a psychology of risk and herd behavior) do have a significant impact
on the individuals' attitude towards investment. Concurrently, the study has also brought out that gender
has a strong moderation affect in the relations between the psychological factors and the attitude towards
investments, between the attitude and behavioral intention, between subjective norms and behavioral
intention as well as between perceived behavioral control and behavioral intention of Vietnamese
individual investors.
Francis Gnanasekar and Arul (2015), Portfolio investment covers a range of securities, such as stocks
and bonds, as well as other types of investment vehicles. A diversified portfolio helps spread the risk of
possible loss due to the below-expectations performance of one or a few of them. They are categorized in
two major parts foreign institutional investment and investments by non-residents.
Personal Finance is more Personal than it is Finance: A Study on Factors Influencing Investment Choice on
Investments in Tiruchirappalli City Corporation, Tamil Nadu
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 267 editor@iaeme.com
5. METHODOLOGY
5.1. DATA
The researcher attempts to collect the information regarding investment detail and investment pattern of
the investors. For this purpose, the researcher identifies a number of stock broking agencies through survey
and internet. By referring to the addresses of the stock broking agencies, it is found that most of them
mainly in Thillainagar, Railway Junction area, Chattram Bus Stand, Palakarai, Woraiyur and Thennur.
From these areas, there are 23 stock broking agencies exist. Among 23 stock broking agencies, six agents
are not permited to collect the data from their clients; three stock broking agencies are closed due to some
reasons. Rests of the 14 stock broking agencies are allowed to collect data. The researcher contacted the
branch managers of 14 branches through phone and got the appointment for discussion. The researcher had
several rounds of talks, discussion with the branch managers. The researcher collected the names and
address of the regular customers of the stock broking agencies. The branch managers of the stock broking
agencies selected 50 loyal, regular, serious, sincerely investors. The stock broking branch managers felt
that only the above selected 50 respondents have been selected from each broking agencies. From the 14
agencies, 50 respondents were selected. Thus, 700 questionnaires were distributed and collected back.
Then, the researcher conducted data validity test viz., Chrona Alpha Test. The test reveals 0.809. i.e., 80.9
per cent as its result.
5.2. Tools and Techniques Used for this Study
The researcher collected primary data through a questionnaire from the loyal investors in Tiruchirappalli
city area and used Statistical Packages for Social Sciences (SPSS) with appropriate coding for the drawing
inferences. Tools are used in this study namely; Frequency table, Percentage analysis, Cross table,
Friedman rank test and Chi-Square test are applied to analyze the data.
6. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
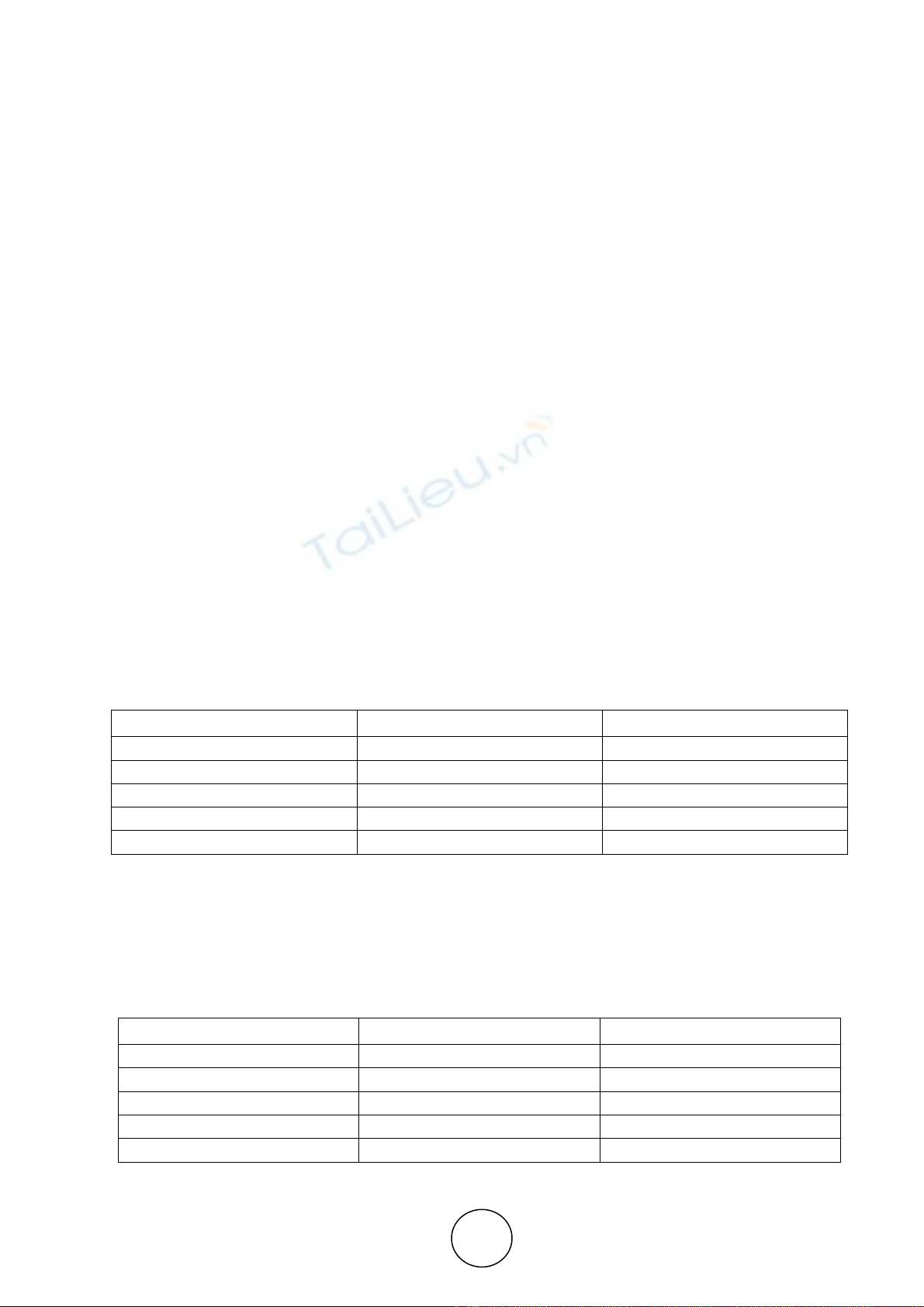
Table 1
Objectives of Investment
Objectives No. of the Respondents Per cent
High Returns 176 25.1
Tax benefits 94 13.4
Regular Income 313 44.7
Capital appreciation 117 16.7
Total 700 100.0
Source: primary data
It is clear that from the table 1, among the 700 respondents, 176 respondents say High returns are their
main investment objective, 94 respondents say Tax benefits are their investment objective, 313
respondents say Regular income is their investment objective and 117 respondents say Capital appreciation
is their investment objective.
Table 2
Factor to be considered before Investments
Factor No. of the Respondents Percent
Safety principal 234 33.4
Low risk 216 30.9
High returns 226 32.3
Maturity period 24 3.4
Total 700 100.0
Source: primary data
Dr. I. Francis Gnanasekar
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 268 editor@iaeme.com
It is clear that from the table 2, among the 700 respondents, 234 respondents consider the ‘safety
principal’ is the factor to be considered before their investment plan, 216 respondents felt that ‘Low risk’ is
the factor to be considered before their investment plan, 226 respondents considered ‘High returns’ is the
factor to be considered before their investment plan and 24 respondents planned Maturity period is the
factor to be considered before their investment plan.
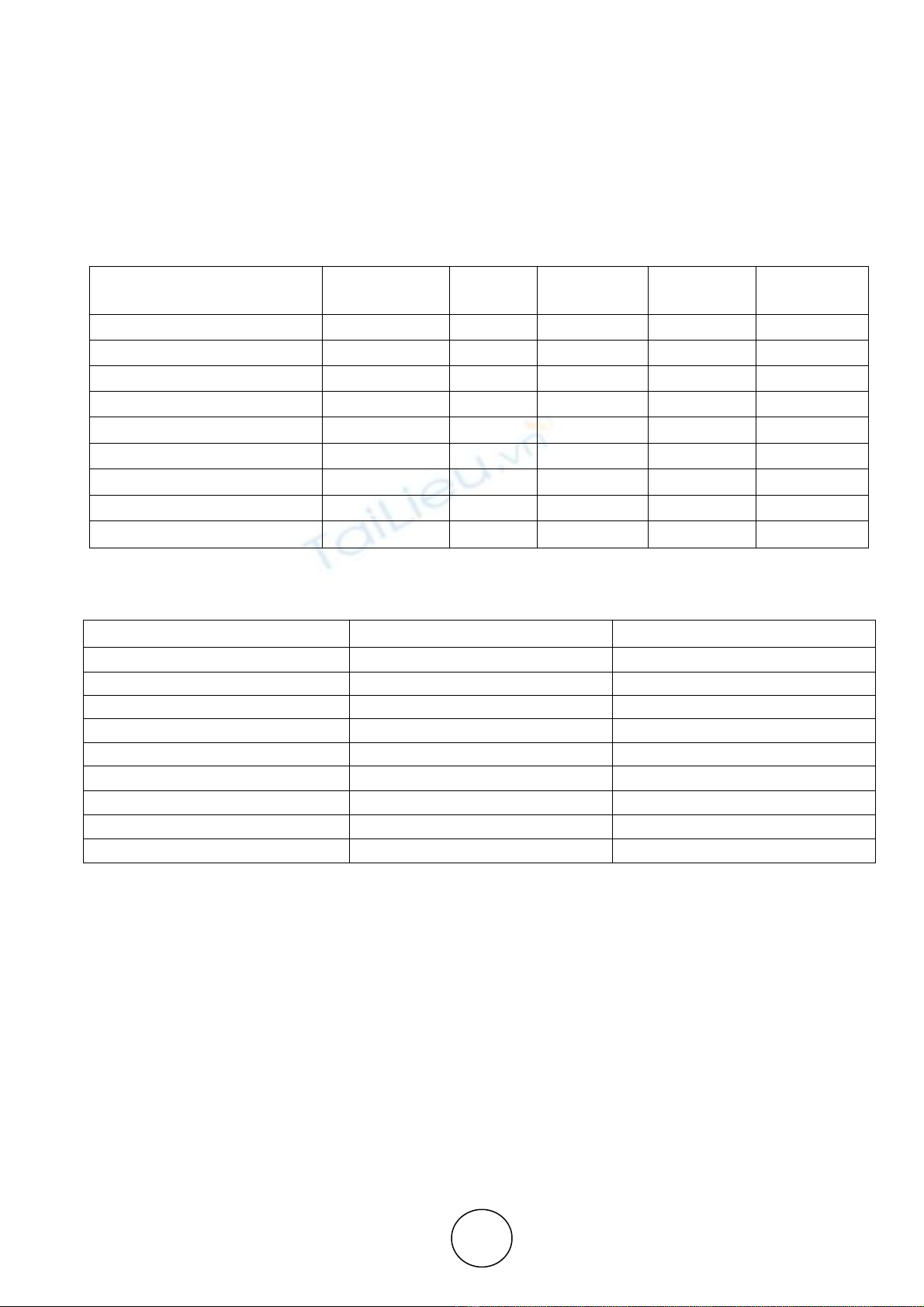
Table 3 Descriptive Statistics
Factors No of
respondents Mean Std.
Deviation Minimum Maximum
Tax benefits 700 4.77 2.889 1 9
To gain Regular returns 700 3.90 2.296 1 9
Reducing Future Risk 700 4.53 2.305 1 9
Capital appreciation 700 3.48 2.183 1 9
Reputations of the firm 700 5.68 2.164 1 9
Investment return 700 4.03 2.306 1 9
Time horizon 700 6.17 2.188 1 9
Investment goals 700 5.51 2.559 1 9
Risk tolerance 700 6.92 2.126 1 9
Source: primary data
Table 3 (A) Friedman Rank Test
Factors Mean value Rank
Tax benefits 4.77 5
To gain Regular returns 3.90 2
Reducing Future Risk 4.53 4
Capital appreciation 3.48 1
Reputations of the firm 5.68 7
Investment return 4.03 3
Time horizon 6.17 8
Investment goals 5.51 6
Risk tolerance 6.92 9
Source: primary data
In order to study the important factors influencing in selection of a particular type of financial
instrument by the investors, an attempt have been made to compute their mean influencing factors. The
mean influencing factors reflect the overall influenced factors for the investors while selecting financial
instruments. The lower mean value represents higher influenced factors and vice-versa. The table 3 shows
that among the nine importance factors capital appreciation is ahead of others in factors influencing. It is
closely followed by to gain a regular return. The investment return is the third important factors
influencing the investors. The important factors influence depends upon the type of financial instruments.
In order to verify the above-mentioned fact, Friedman Rank test is used. The result of the test furnished
in the Table 3 (A). It is understood that capital appreciation stands first rank and it is the most important
factors influencing the investors. The second influencing factor is to gain regular returns and it is closely
followed by investment return. The least influencing factor is a risk tolerance. From the above analysis it is
clear that the basic factors influencing the investors, is the capital appreciation from their financial
instruments, followed by gain as a regular return.
Personal Finance is more Personal than it is Finance: A Study on Factors Influencing Investment Choice on
Investments in Tiruchirappalli City Corporation, Tamil Nadu
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 269 editor@iaeme.com
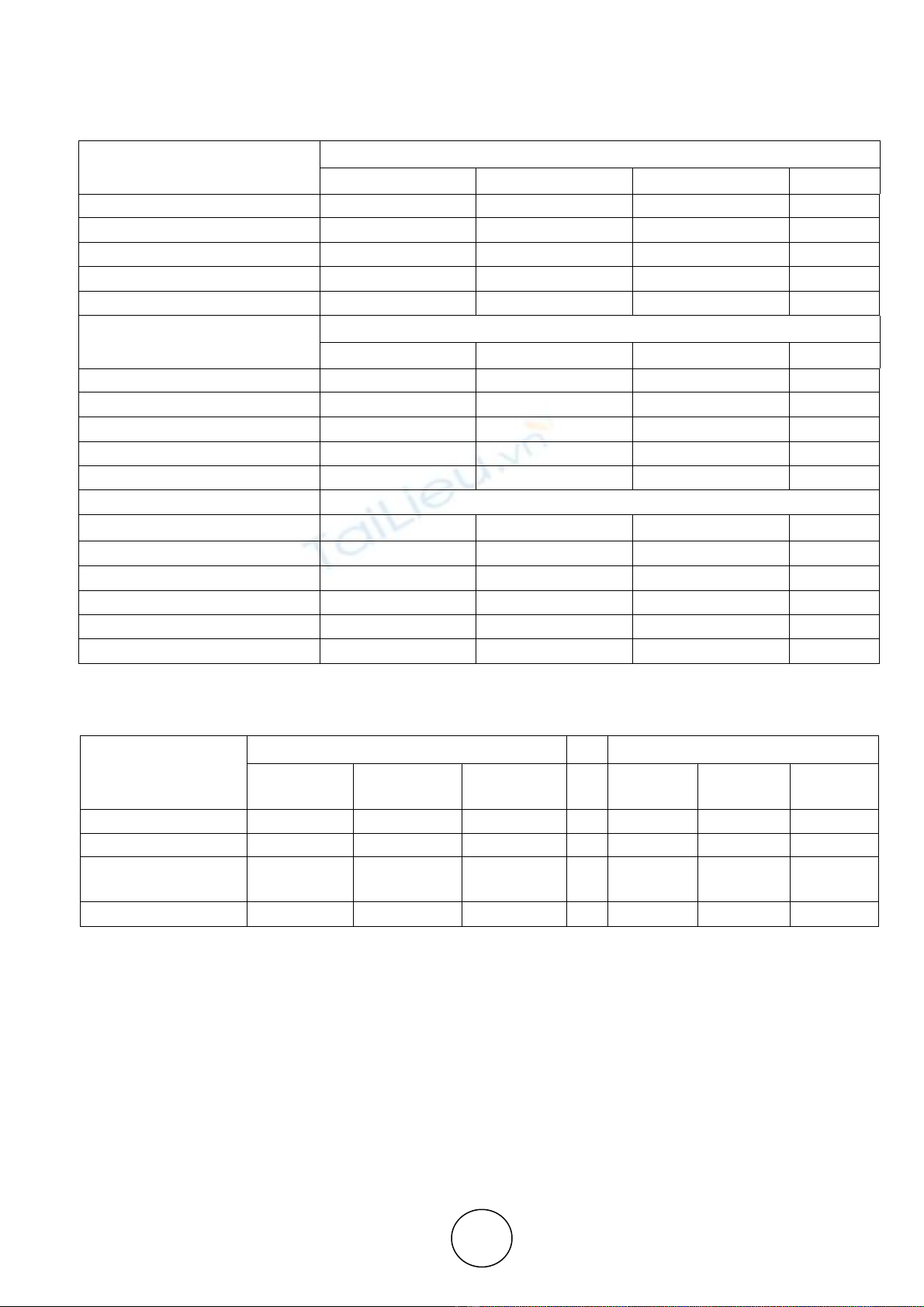
Table 4 Cross Table of Relationship between Age of the Investors and their Investment Behavior
Age Buy a Stock
Above expectation As per expectation Below expectation Total
Up to 30 180 69 31 280
31- 40 119 55 13 187
41-50 79 17 18 114
51 and above 63 34 22 119
Total 441 175 84 700
Age Hold a Stock
Above expectation As per expectation Below expectation Total
Up to 30 50 217 13 280
31- 40 39 131 17 187
41-50 4 96 14 114
51 and above 34 73 12 119
Total 127 517 56 700
Sell a Stock
Age Above expectation As per expectation Below expectation Total
Up to 30 65 66 149 280
31- 40 50 30 107 187
41-50 22 10 82 114
51 and above 57 12 50 119
Total 194 118 388 700
Source: primary data
Table 4 (A) Chi-Square Test
Value d.f Asymp. Sig. (2-sided)
Buy the
stock
Hold the
stock
Sell the
stock Buy the
stock
Hold the
stock
Sell the
stock
Pearson Chi-Square 19.142
a
33.888
a
47.557
a
6 .004 .000 .000
Likelihood Ratio 19.915 39.903 45.408 6 .003 .000 .000
Linear-by-Linear
Association 4.312 .489 5.152 1 .038 .484 .023
N of Valid Cases 700 700 700
Source: primary data
The table 4 exhibits the correlation between age of the investors and their investment behaviour. The
behaviour of the investors namely ‘Buy a Stock’, ‘Hold a Stock’ and ‘Sell a Stock’ when the companies
announce the annual results. The ‘F’ test carried out to know the association between age of the investors
and their behaviour.From the table 4 observed that F Pearson chi-square has the probability of 0.004 which
is lower than 0.05 (0.00 <0.05), here null hypothesis is rejected and research hypothesis is accepted, so it is
clear that there is a strong relationship between age of the investor and their investment behaviour (Buy the
Stock).From the table 4 observed that F Pearson chi-square has the probability of 0.000 which is lower
than 0.05 (0.00 <0.05), here null hypothesis is rejected and research hypothesis is accepted, so it is clear
that there is a strong relationship between age of the investor and their investment behaviour (Hold the
Stock).From the table 4 observed that F Pearson chi-square has the probability of 0.000 which is lower
than 0.05 (0.00 <0.05), here null hypothesis is rejected and research hypothesis is accepted, so it is clear



















![Câu hỏi ôn tập Tài chính tiền tệ: Tổng hợp [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251230/phuongnguyen2005/135x160/49071768806381.jpg)



![Câu hỏi ôn tập Tài chính Tiền tệ: Tổng hợp [mới nhất/chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251015/khanhchi0906/135x160/49491768553584.jpg)


