
TNU Journal of Science and Technology
229(14): 117 - 128
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 117 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
A COMPARISON OF LINEAR LOAD FLOW MODELS
FOR 39-BUS NEW ENGLAND TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
Nguyen Duy Duc, Vo Trong Sang, Pham Nang Van *
School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering - Hanoi University of Science and Technology
ARTICLE INFO
ABSTRACT
Received:
04/7/2024
Power flow equations are fundamental mathematical models that serve
as the foundation for planning and operating electrical systems. While
traditional alternating current power flow (ACPF) methodologies yield
accurate outcomes, their nonlinear characteristics, poor convergence,
and low efficiency in computation restrict their applications in power
systems. This paper compares two linear power flow methods for
electrical grids, namely the direct current power flow (DCPF) method
and the decoupled linear power flow (DLPF) method. These power
flow methods are applied to the 39-bus NewEngland transmission grid
to compute voltage magnitudes, voltage phase angles, and power flow
on branches. The computational results indicate that the decoupled
linear power flow (DLPF) method yields better results in terms of
nodal voltage magnitudes and phase angles compared to the direct
current power flow (DCPF) method. Nevertheless, the DLPF approach
exhibits inferior performance in terms of power flow on branches when
compared to the DCPF method.
Revised:
29/10/2024
Published:
29/10/2024
KEYWORDS
Power flow equations
39-bus NewEngland system
Linear power flow method
Direct current power flow
(DCPF)
Decoupled linearized power
flow (DLPF)
SO SÁNH CÁC PHƢƠNG PHÁP TUYẾN TÍNH ĐỂ PHÂN TÍCH CHẾ ĐỘ
XÁC LẬP CỦA LƢỚI ĐIỆN TRUYỀN TẢI 39 NÚT NEW ENGLAND
Nguyễn Duy Đức, Võ Trọng Sáng, Phạm Năng Văn*
Trường Điện – Điện tử - Đại học Bách khoa Hà Nội
THÔNG TIN BÀI BÁO
TÓM TẮT
Ngày nhận bài:
04/7/2024
Hệ phương trình trào lưu công suất có vai trò quan trọng trong các bài
toán quy hoạch và vận hành hệ thống điện. Các phương pháp phân tích
trào lưu công suất xoay chiều (ACPF) truyền thống cho kết quả chính
xác, nhưng do tính phi tuyến, khả năng hội tụ kém và hiệu suất tính toán
thấp nên ứng dụng trong hệ thống điện bị hạn chế. Bài báo này so sánh
hai phương pháp tuyến tính để phân tích chế độ xác lập của lưới điện,
bao gồm phương pháp dòng điện một chiều (DCPF) và phương pháp
trào lưu công suất tuyến tính tách biến (DLPF). Các phương pháp phân
tích chế độ xác lập này được so sánh sử dụng lưới điện truyền tải 39 nút
New England để tính toán mô-đun điện áp nút, góc pha điện áp nút và
dòng công suất tác dụng trên các nhánh. Các kết quả tính toán cho thấy
phương pháp trào lưu công suất tách biến (DLPF) cho kết quả tốt hơn
về mô-đun và góc pha điện áp nút so với phương pháp dòng điện một
chiều (DCPF), trong khi đó kết quả về dòng công suất tác dụng trên các
nhánh của phương pháp DLPF lại kém hơn so với phương pháp DCPF.
Ngày hoàn thiện:
29/10/2024
Ngày đăng:
29/10/2024
TỪ KHÓA
Hệ phương trình trào lưu công
suất
Hệ thống điện 39 nút
NewEngland
Mô hình trào lưu công suất
tuyến tính
Trào lưu công suất một chiều
(DCPF)
Trào lưu công suất tuyến tính
tách biến (DLPF)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.34238/tnu-jst.10704
* Corresponding author. Email: van.phamnang@hust.edu.vn

TNU Journal of Science and Technology
229(14): 117 - 128
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 118 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
1. Giới thiệu
Trong thời gian gần đây, lĩnh vực hệ thống điện trên thế giới đã chứng kiến những sự thay đổi
đáng kể và tiến bộ to lớn. Sự phát triển này có nguồn gốc từ nhiều yếu tố khác nhau, bao gồm sự
gia tăng của nguồn năng lượng tái tạo, sự tiến bộ trong công nghệ và quản lý hệ thống, cũng như
nhu cầu ngày càng tăng về một nền công nghiệp xanh và bền vững. Do đó, ngày càng có nhiều
thách thức liên quan đến việc điều khiển và tối ưu hệ thống điện. Trong đó, phân tích trào lưu
công suất là một công cụ cơ bản và là chìa khóa để giải quyết các vấn đề đó. Phân tích trào lưu
công suất mang ý nghĩa quan trọng trong việc tính toán sự cố [1], đánh giá độ tin cậy [2] và phân
tích trào lưu công suất xác suất (PLF) [3] một cách chính xác và hiệu quả.
Các phương trình trào lưu công suất tiêu chuẩn dựa trên một hệ phương trình phi tuyến yêu cầu
tính toán phức tạp do phải sử dụng các phép lặp. Bên cạnh sự phức tạp về mặt tính toán, tính phi
tuyến dẫn đến các nhược điểm sau: khó khăn khi tìm nghiệm (ví dụ các trường hợp giải kém);
không thể kết luận được rằng lời giải không tồn tại hoặc không thể đạt trong trường hợp thuật toán
không hội tụ và sự tồn tại nhiều nghiệm [4]. Nguyên nhân chính là do mối quan hệ phi tuyến giữa
mô-đun điện áp và góc pha. Chính mối quan hệ phi tuyến này đã thu hút nhiều nhà nghiên cứu đề
xuất các phương pháp khác nhau để tính trào lưu công suất. Do đó, việc tìm ra một mô hình trào lưu
công suất tuyến tính có tốc độ tính toán nhanh, độ chính xác và độ ổn định hợp lý cho tất cả các loại
lưới điện nhận được sự quan tâm rất lớn. Mô hình tuyến tính như vậy cũng có thể mang lại lợi ích
trong việc giải quyết các bài toán tối ưu hóa. Bằng cách sử dụng mô hình trào lưu công suất tuyến
tính, các bài toán tối ưu phi tuyến như định giá biên nút (LMP) [5] và lựa chọn tổ máy vận hành có
ràng buộc an toàn (SCUC) [6] có thể được chuyển thành các bài toán tối ưu tuyến tính.
Phương pháp dòng điện một chiều (DCPF) là một trong những mô hình trào lưu công suất
tuyến tính được áp dụng rộng rãi trong lĩnh vực hệ thống điện. Vì tính tuyến tính của nó, mô hình
này có tốc độ tính toán nhanh và không đòi hỏi việc sử dụng các phép lặp để đạt được độ chính
xác hợp lý trong tính toán dòng công suất tác dụng so với phương pháp dòng điện xoay chiều
(ACPF) [7]. Phương pháp dòng điện một chiều (DCPF) cổ điển được xây dựng dựa trên giả thiết
mô-đun điện áp các nút bằng 1 pu và bỏ qua tổn thất công suất tác dụng trên các nhánh [4]. Ngoài
ra, các nghiên cứu đã đề xuất các phiên bản tổng quát hơn của mô hình trào lưu công suất một
chiều (DCPF) bao gồm mô hình khởi động nóng (hot-start) và khởi động lạnh (cold-start) nhằm
mở rộng ứng dụng của mô hình [8]. Tuy nhiên, nhược điểm của phương pháp dòng điện một
chiều (DCPF) là không thể tính toán mô-đun điện áp nút.
Phương pháp trào lưu công suất tuyến tính tách biến (DLPF) [9] liên quan đến phân tách mô-
đun điện áp và góc pha giúp khắc phục những hạn chế do tính phi tuyến của phương pháp dòng
điện xoay chiều (ACPF) [10] và giả thiết mô-đun điện áp các nút bằng 1 pu của phương pháp
dòng điện một chiều (DCPF). Tương tự như phương pháp DCPF, việc xây dựng hệ phương trình
tuyến tính của phương pháp DLPF không đòi hỏi phải biết trước điểm làm việc ban đầu của hệ
thống điện. Nói cách khác, việc xây dựng hệ phương trình tuyến tính theo phương pháp DLPF
độc lập với trạng thái làm việc của hệ thống điện. Đây là sự khác biệt của phương pháp DLPF so
với phương pháp Newton-Raphson bởi vì hệ phương trình tuyến tính trong mỗi bước lặp của
phương pháp Newton-Raphson được xây dựng dựa trên điểm làm việc của hệ thống điện đã được
biết. Trong một nghiên cứu trước đây [11], một mô hình tuyến tính đã được đề xuất cho hệ thống
phân phối hình tia. Tuy nhiên, mô hình này chỉ áp dụng cho các hệ thống phân phối hình tia cụ
thể và không thể mở rộng cho các hệ thống điện truyền tải. Một tiến bộ quan trọng đã đạt được
trong nghiên cứu [8], khi các tác giả đã xây dựng hệ phương trình trào lưu công suất tuyến tính
có xét dòng công suất phản kháng. Mô hình này phản ánh cả sự cân bằng công suất tác dụng và
công suất phản kháng, liên quan đến bình phương của mô-đun điện áp U2 và góc pha được điều
chỉnh δ. Tuy nhiên, vì mô-đun điện áp và góc pha không thể phân tách nên các bài toán tối ưu có
dạng quy hoạch bậc hai. Do đó, nghiên cứu này đề xuất một mô hình trào lưu công suất tuyến
tính phân tách U ‒ δ nhằm nâng cao độ chính xác trong tính toán mô-đun điện áp nút.

TNU Journal of Science and Technology
229(14): 117 - 128
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 119 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
Mục đích của nghiên cứu này là so sánh kết quả tính toán chế độ xác lập cho lưới điện truyền
tải 39 nút New England sử dụng hai mô hình tuyến tính, bao gồm phương pháp dòng điện một
chiều (DCPF) và phương pháp trào lưu công suất tuyến tính tách biến (DLPF). Các đóng góp
chính của bài báo bao gồm: (1) Trình bày chi tiết hai phương pháp tuyến tính để tính toán chế độ
xác lập của lưới điện; (2) So sánh kết quả tính toán chế độ xác lập cho lưới điện truyền tải 39 nút
New England.
Bài báo gồm 4 phần. Mô hình toán học của hai phương pháp trào lưu công suất tuyến tính
được trình bày ở Phần 2. Sự áp dụng tính toán của hai mô hình tuyến tính cho lưới điện 39 nút
New England được mô tả trong Phần 3. Các kết luận và chủ đề nghiên cứu tương lai được trình
bày trong Phần 4.
2. Phƣơng pháp nghiên cứu
2.1. Hệ phương trình trào lưu công suất phi tuyến
Phân tích chế độ xác lập nhằm mục đích tính toán mô-đun và góc pha điện áp tại các nút; công
suất phát của các nguồn điện; dòng công suất tác dụng và phản kháng trên các đường dây và tổn
thất công suất trong lưới điện [12].
Xét hệ thống điện với
N
nút, và mạng lưới điện được mô tả bởi ma trận tổng dẫn nút Ybus.
Lưới điện trong chế độ xác lập được mô tả bởi hệ phương trình phi tuyến như sau:
1
cos sin ; 1,2,...,
N
i i k ik ik ik ik
k
P U U G B i N
(1)
1
sin cos ; 1,2,...,
N
i i k ik ik ik ik
k
Q U U G B i N
(2)
trong đó:
,
ii
PQ
tương ứng là công suất hữu công và vô công tại nút
;i
,
ik
UU
tương ứng là mô-đun điện áp tại các nút
và ;ik
,
ik ik
GB
tương ứng là phần thực và ảo của phần tử
ik
trong ma trận Ybus;
,
ik
tương ứng là góc pha điện áp tại các nút
và .ik
Phương pháp Newton-Rapson [13] thường được áp dụng để tìm nghiệm của hệ phương trình phi
tuyến (1)-(2). Theo phương pháp này, tại bước lặp thứ r, ta cần giải hệ phương trình tuyến tính:
r r r
ΔP H N Δδ
ΔQ M L ΔU / U
(3)
trong đó,
và H,N,M L
là các ma trận con của ma trận Jacobi.
D
T
T
1 2 1 1 2
, , , , , ,
NN
P P P Q Q Q
ΔP ΔQ
(4)
2.2. Phương pháp trào lưu công suất một chiều (DCPF)
Phương pháp trào lưu công suất một chiều (DCPF) được mô tả trong các tài liệu tham khảo
[7], [8], [14], [15] và được trình bày chi tiết như dưới đây. Phương pháp DCPF chỉ phù hợp để
tính toán chế độ xác lập của lưới điện có điện áp định mức từ 220 kV trở lên. Ngoài ra, hệ
phương trình trào lưu công suất theo phương pháp DCPF cũng được áp dụng rộng rãi trong các
bài toán tối ưu cho lưới điện 220 kV trở lên như phân bố tối ưu công suất (ED ‒ Economic
Dispatch), lập lịch vận hành cho các tổ máy phát (UC ‒ Unit Commitment) và tính giá biên nút
trong thị trường điện bán buôn.
Với lưới điện có điện áp định mức từ 220 kV trở lên, dòng công suất phản kháng trên các
đường dây thường nhỏ hơn nhiều dòng công suất tác dụng. Dựa trên đặc điểm này, phương pháp
TNU Journal of Science and Technology
229(14): 117 - 128
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 120 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
DCPF chỉ xét dòng công suất tác dụng và bỏ qua dòng công suất phản kháng, tức là chỉ tính toán
với (1) và bỏ qua (2).
Bên cạnh đó, các đường dây có điện áp từ 220 kV trở lên thường sử dụng dây dẫn với tiết diện
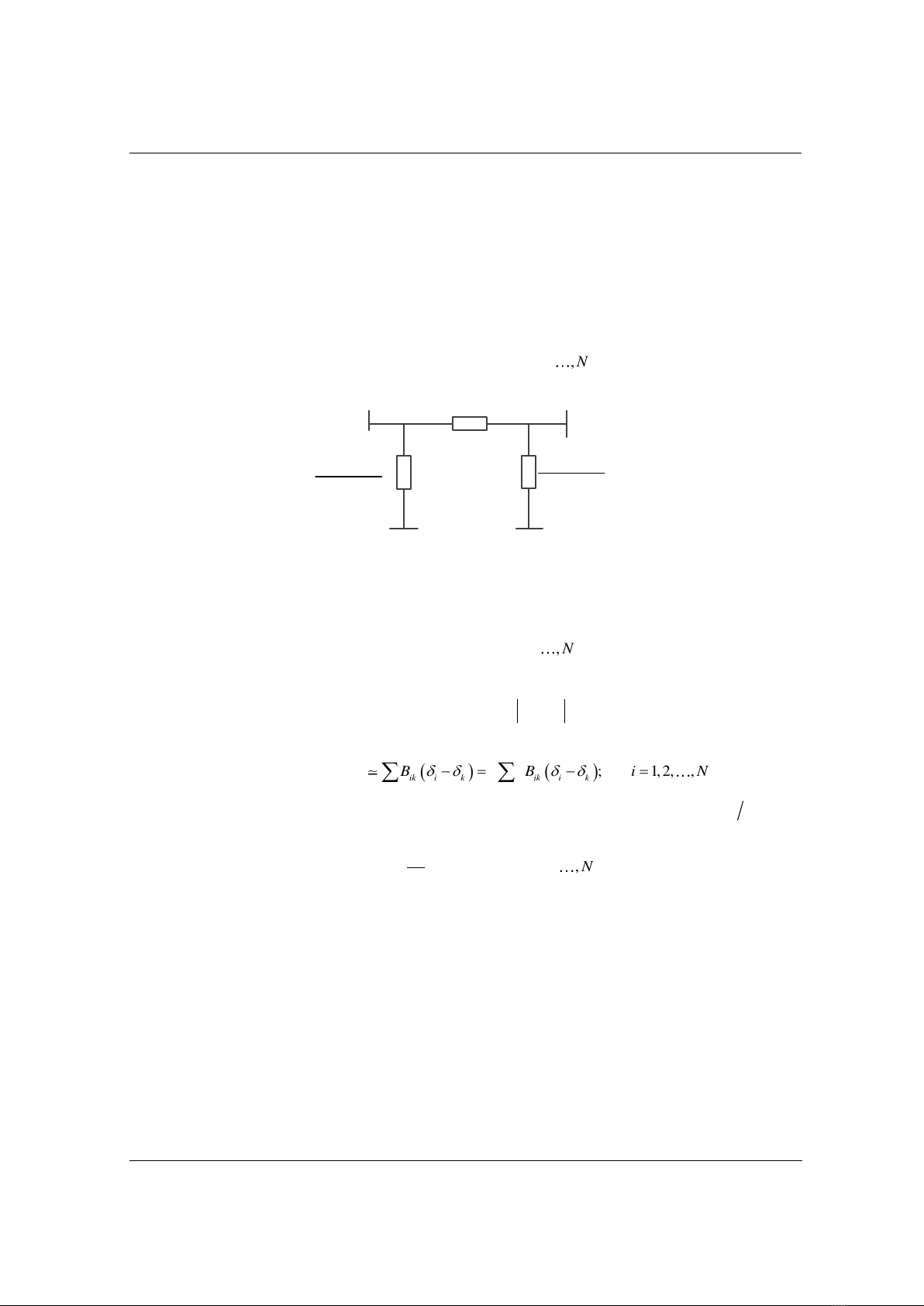
lớn và có phân pha. Đồng thời, khoảng cách giữa các pha của các đường dây này cũng lớn. Do
đó, trong sơ đồ thay thế của đường dây (xem Hình 1), trị số điện trở tác dụng (rik) nhỏ hơn nhiều
điện kháng (xik) và trị số điện dẫn tác dụng
sh
ik
g
nhỏ hơn nhiều dung dẫn
sh .
ik
b
Dựa trên đặc
điểm này, phương pháp DCPF coi trị số điện trở tác dụng và điện dẫn tác dụng bằng 0. Khi đó,
Gik = 0 và biểu thức (1) được viết lại như sau:
1
sin ; 1,2, ,
N
i i k ik ik
k
P U U B i N
(5)
ik
ik ik
r jx
sh sh
2
ik ik
g jb
sh sh
2
ik ik
g jb
Hình 1. Sơ đồ thay thế của đường dây
Ngoài ra, trong chế độ xác lập bình thường, mô-đun điện áp tại các nút của lưới điện thường
lệch không quá 5% so với điện áp định mức. Do đó, với phương pháp DCPF, mô-đun điện áp các
nút được giả sử bằng 1 pu. Khi đó, biểu thức (5) được xấp xỉ như sau:
1
sin ; 1,2, ,
N
i ik ik
k
P B i N
(6)
Đặc điểm tiếp theo của vận hành hệ thống điện trong chế độ xác lập bình thường là chênh lệch
góc pha điện áp giữa hai nút liền kề nhau thường nhỏ
o
5.
ik
Khi đó, biểu thức (6) được
xấp xỉ như sau:
1 1 1,
sin ; 1,2, ,
N N N
i ik i k ik i k ik i k
k k k k i
P B B B i N
(7)
Thành phần
,ik i k
B
bằng trừ của phần ảo của tổng dẫn dọc nhánh ik, tức là
,1.
ik i k ik
Bx
Khi
đó, biểu thức (7) được viết lại như sau:
1, ,
1; 1,2, ,
N
i i k
k k i ik
P i N
x
(8)
2.3. Phương pháp trào lưu công suất tuyến tính tách biến (DLPF)
Các xấp xỉ tuyến tính được áp dụng vào (1) để phân tách mô-đun điện áp và góc pha điện áp:
2
1, 1,
2
1, 1, 1,
2
1, 1,
cos sin
cos sin
cos sin
NN
i i ii i k ik ik i k ik ik
k k i k k i
N N N
i ii ik i k ik ik i k ik ik
k k i k k i k k i
NN
i ii i ik i k ik i k ik ik
k k i k k i
ii
P U G U U G U U B
U g g U U g U U b
U g U g U U U U b
Ug
1, 1, 1 1
N N N N
i ik i k ik i k ik k ik k
k k i k k i k k
g U U b G U B
(9)

TNU Journal of Science and Technology
229(14): 117 - 128
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 121 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
trong đó:
1, 1,
khi k khi k
;
khi k khi k
NN
ii ij ij
j j i j j i
ik ik ik ik ik ik
ik ik
y y i y i
Y G jB Y G jB
y i y i
,
ik ik
G B
lần lượt là phần thực và phần ảo của phần tử thuộc hàng
i
, cột
k
trong ma trận
tổng dẫn
;Y
,
ik ik
G B
lần lượt là phần thực và phần ảo của phần tử thuộc hàng
i
, cột
k
trong ma trận
tổng dẫn
Y
với sự bỏ qua thành phần ngang;
ik ik ik
y g jb
là tổng dẫn dọc của đường dây ik;
ii ii ii
y g jb
là tổng dẫn ngang của nút
.i
Tương tự, phương trình (2) cho công suất vô công của nút
i
được xấp xỉ như sau:
11
NN
i ik k ik k
kk
Q B U G
(10)
Lưu ý rằng, vì điện dẫn tác dụng có thể xem như không đáng kể so với điện dẫn phản kháng
trong tổng dẫn ngang
ii ii
gb
do đó
ik ik
GG
.
Dòng công suất vô công của nút
i
được xấp xỉ viết lại như sau:
11
NN
i ik k ik k
kk
Q B U G
(11)
Ta xét xấp xỉ trong biểu thức của dòng công suất tác dụng trên nhánh của phương pháp trào
lưu công suất tuyến tính tách biến (DLPF) như sau:
cos
ik i i k ik ik i k
g U U U g U U
(12)
Cơ sở lý thuyết giải thích cho phép xấp xỉ trên được đề xuất trong mô hình DLPF như sau:
cos 1
1 1
ik i i k ik ik i i k ik i i k
ik i k ik i k ik i k
g U U U g U U U g U U U
g U U g U U g U U
(13)
Lưu ý rằng,
i
U
và
k
U
lần lượt phân tách thành
1i
U
và
1k
U
, trong đó
i
U
và
k
U
thường nhỏ hơn
i
U
và
k
U
một bậc thập phân. Trong bước thứ hai của phương trình trên, có thể bỏ
qua
2
i
U
và
ik
UU
mà không gây ra sai số đáng kể vì chúng nhỏ hơn
i
U
và
k
U
hai bậc thập phân.
Biểu thức tuyến tính cho dòng công suất hữu công và dòng công suất vô công:
sh 2
ik ik i k ik i k
ik ik i k ik i k ik i
P g U U b
Q b U U g b U
(14)
trong đó,
sh
ik
b
là tổng dẫn ngang của nhánh
.ik
Lưu ý rằng, để đảm bảo tính tuyến tính, tổn thất công suất trên đường dây được bỏ qua. Do
đó,
ik ki
PP
, trong đó
ik
P
là dòng công suất hữu công từ nút
i
đến nút
.k
Phương trình (9) và (10) biểu thị công thức cơ bản của mô hình DLPF. Dạng ma trận của các
phương trình này được viết như sau:
P B G δ
Q G B U
(15)
trong đó:
P, Q
lần lượt là ma trận công suất hữu công và vô công;
G, B
lần lượt là phần thực và phần ảo của ma trận tổng dẫn;
























![Chương trình đào tạo cơ bản Năng lượng điện mặt trời mái nhà [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260126/cristianoronaldo02/135x160/21211769418986.jpg)

