
Improvement of Vehicle/ Fuel
Efficiency through the
Introduction of Eco-Drive
Management System (EMS)
ALMEC CORPORATION
under MOEJ/GEC
26 February 2013
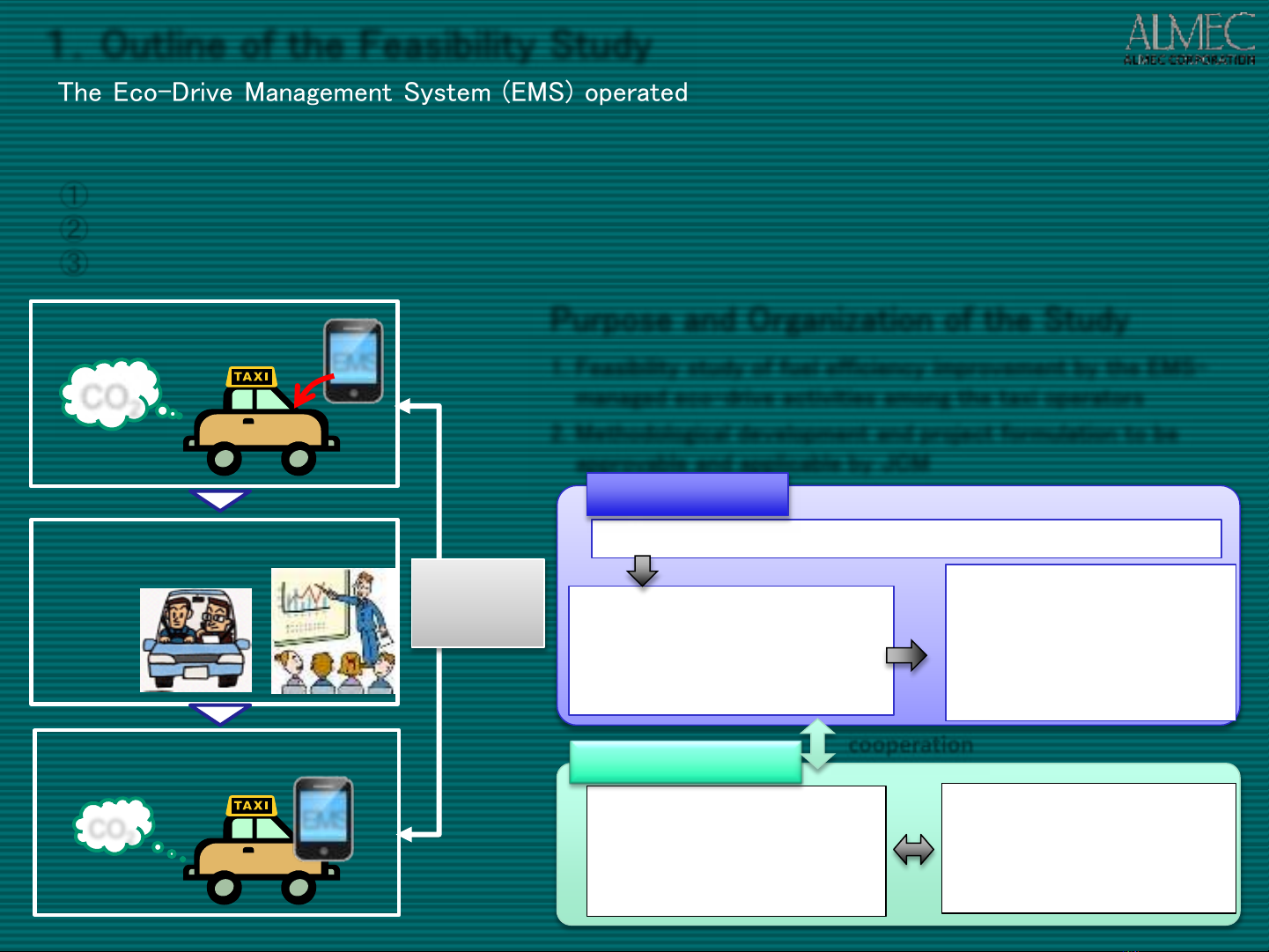
The Eco-Drive Management System (EMS) operated with the smart phone application, developed
in Japan, is to be introduced to the taxi operation in Hanoi. EMS equipment is installed in 10 taxis
during the Study.
① Collection and analysis of the taxi operation data before the EMS introduction
② Eco-Drive Training Program based on the Japanese knowhow
③ Verification of the emission reductions realized by the EMS introduction
1.Outline of the Feasibility Study
Comparison
of Fuel
Efficiency
CO2
EMS
CO2
① EMS Installation
② Eco-Drive Training
Program
EMS
③ Trial Run
Purpose and Organization of the Study
1. Feasibility study of fuel efficiency improvement by the EMS-
managed eco-drive activities among the taxi operators
2. Methodological development and project formulation to be
approvable and applicable by JCM
Energy Conservation Center,
Japan
Dispatching eco-drive
instructors
Ishida R&D, Ltd.
Installing and managing EMS
Almec, Ltd.
Managing FS implementation,
collecting and analyzing
relevant data
Developing MRV methodology
Global Environment Centre Foundation (GEC)
JCM FS commission
Japanese Side
Institute of Planning and
Transportation Engineering
Coordinating activities
Collecting data
(Counterpart)
Hanoi Taxi Group
Introducing EMS and engaging
in fuel efficiency
improvement
Vietnamese side cooperation

2.Outline of EMS
Eco-Drive Training Program
Low-cost and effective support of eco drive promotion and management by using the smartphone application
capable of recording real-time taxi operation and providing on-board diagnoses
Real-time records of operation are wirelessly transmitted to the smartphone by means of commercially
available Bluetooth connected to the OBD2 scanner (on-board diagnostics) installed in each taxi (55
types of data are recorded, including instant-by-instant records of fuel efficiency and operating speed
and GPS coordinates)
EMS (Smartphone)
wireless
OBD2 Scanner
■ Three-day course in September 2012 for 22 participants
・A designated course is cruised twice by taxis, once in the normal manner
(without project activity) and once in the eco drive mode. The records
are collated for comparative analysis.
■ Eco-Drive Training (two courses to be provided)
・Suburban course: Cruising without interruptions of traffic congestion
・Inner city course: Cruising in traffic congestion mixed with other
automobiles and motor cycles
Suburban Course (Uncongested Traffic)
・No. of participants: 16 taxi drivers
・Driving experiences: average of 4.5 years
・Fuel efficiency improvement: average of
5.6% (a range of-3%~23%)
Average 5.6%
Inner City Course (Congested Traffic)
・ No. of participants: 6 taxi drivers
・ Driving experiences: average of 5.4years
・ Fuel efficiency improvement: average of
6.6% (a range of -17% ~ 17%)
Aaverage 6.6%
※ Incidences of negative improvement
are excluded from the chart.
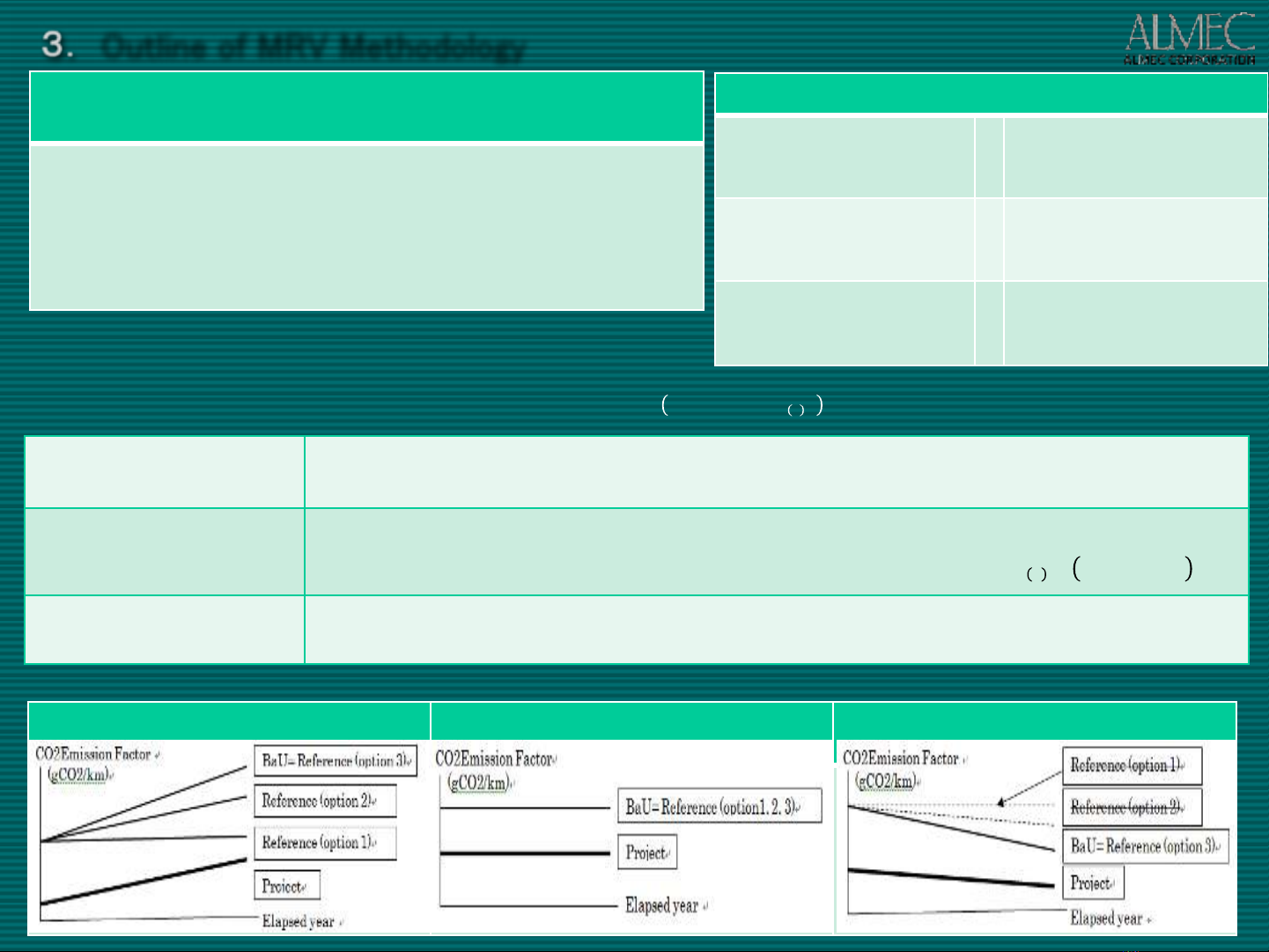
3. Outline of MRV Methodology
𝑬𝑹𝑽𝑬,𝒚 =
𝑫𝑫𝒊,𝒚
𝒊×𝑹𝑭𝑪𝒊(𝒙) −𝑷𝑭𝑪𝒊𝒙 ,𝒚 ×𝑵𝑪𝑽𝒙×𝑬𝑭𝑪𝑶𝟐,𝒙
Increasing Emission Factor per km
Constant Emission Factor per km Decreasing Emission Factor per km
Op.1 Measurement of
target taxis
The reference efficiency is obtained by the measurement before the eco drive
introduction and used throughout the project duration. 𝑹𝑭𝑪𝒊(𝒙) = 𝑪𝒐𝒏𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕
Op.2 Rate of improvement
The reference rate of efficiency𝑷𝑽𝑬,𝒊(𝒙) is calculated from the field test of with and
without situations before the eco drive introduction. 𝑹𝑭𝑪𝒊(𝒙)=𝑷𝑭𝑪𝒊𝒙 ,𝒚/𝟏−𝑷𝑽𝑬,𝒊(𝒙)
Op.3 Measurement of a
control group of taxis
A control group of taxis are designated and the reference efficiency is calculated by
measuring them throughout the project duration.
Eligibility Requirements of the Project Activities
for Applying MRV Methodology
•Composite program of activities that could contribute to the
fuel efficiency improvement of the taxi operation.
•Operated distance, occupancy rate and fuel consumption of the
taxi fleet are to be closely managed.
•The proposed activities are supported by Japanese technology,
experts and finance.
Calculation Options
1) Activities for
vehicle/fuel efficiency
improvement
Op.1 Measurement of
target taxies
2) Activities for
transport efficiency
improvement
×
Op.2 Rate of
improvement
3) Composite activities Op.3 Measurement of
target taxis and a
control group of taxis
Formula for calculating emission reductions:
Comments on Reference Efficiency Used per Calculation Option
Selection from Calculation Options by Alternative Emission Factor per Km
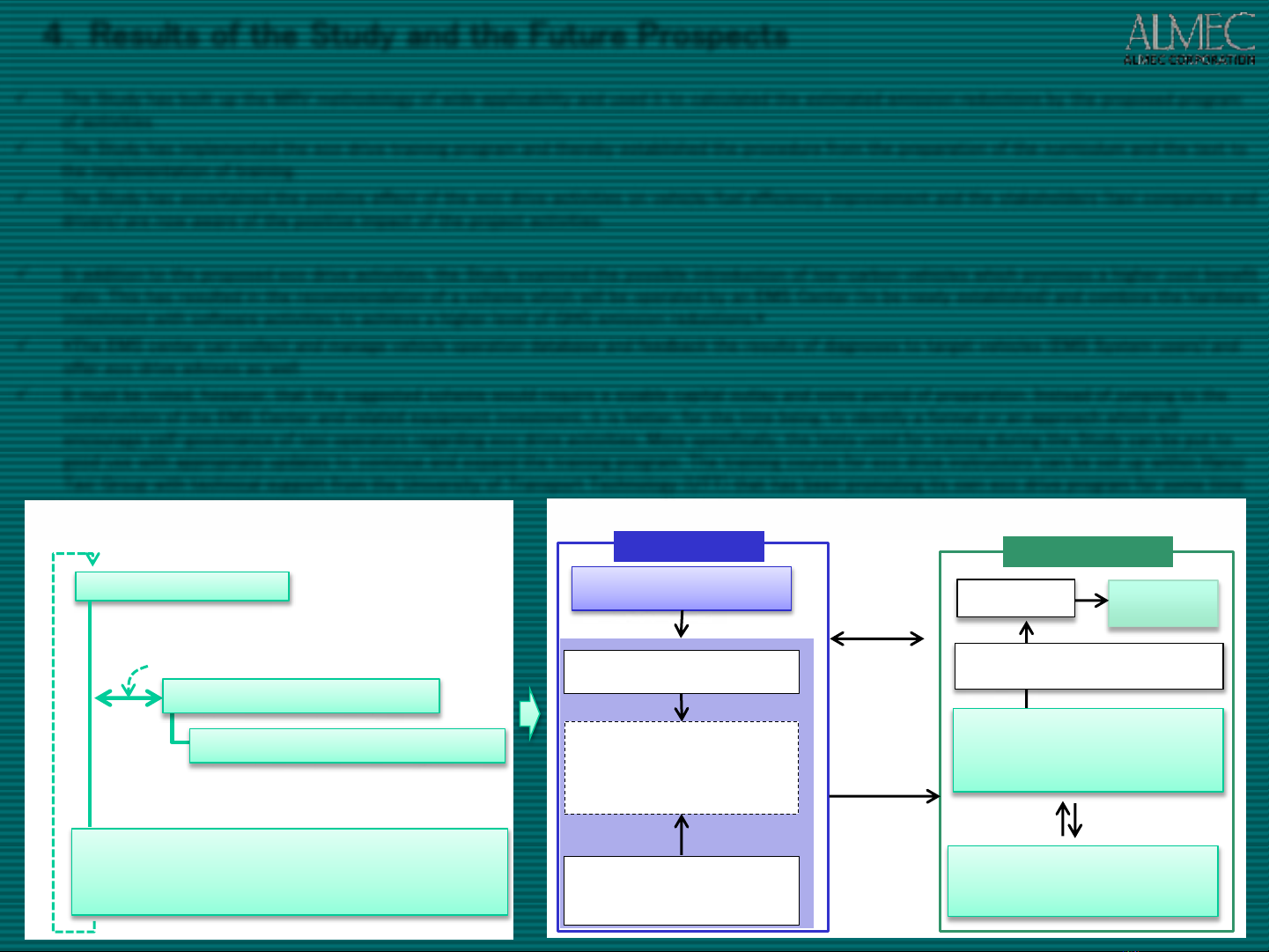
4.Results of the Study and the Future Prospects
Results of the Study
The Study has built up the MRV methodology of wide applicability and used it to calculated the estimated emission reductions by the proposed program
of activities.
The Study has implemented the eco drive training program and thereby established the procedure from the preparation of the curriculum and the text to
the implementation of training.
The Study has ascertained the positive effect of the eco drive activities on vehicle/fuel efficiency improvement and the stakeholders (taxi companies and
drivers) are now aware of the positive impact of the project activities.
Future Prospects
In addition to the proposed eco drive activities, the Study examined the possible introduction of low-carbon vehicles which promises a higher cost benefit
ratio. This has resulted in the recommendation of a scheme which will be operated by an EMS Center (to be newly established) and combine the hardware
investment with software activities to achieve a higher level of GHG emission reductions.*
*The EMS center can collect and manage vehicle operation database and feedback the results of diagnoses to target vehicles (EMS System users) and
offer eco drive advices as well.
It must be noted, however, that the suggested scheme would require a sizable capital outlay and some period of preparation. Instead of jumping to the
construction of the EMS Center and related equipment investment, it is better, for the time being, to identify a format or an approach which will
encourage self-governance of taxi operators regarding eco drive activities. More specifically, the texts used for training during the Study can be put to
good use with appropriate updates to continue and expand the training program. The training course for eco drive instructors can be set up within Hanoi
Taxi Group with technical support from the University of Transport Technology (UTT) that has been promoting its own eco drive program for some time.
Japanese Side
Gov’t of Viet
Nam
Vietnamese side
Bilateral Credit
Monitoring Reports on GHG Emission
Reductions
Gov’t of Japan
(model projects, etc)
Technical Support (Hardware &
Software)
・Eco drive promotion & diffusion
・Introduction of low-carbon
vehicles
Assistanc
Technical
Support
[Cooperation]Energy Conservation
Center, Japan
Automobile manufacturers
[Technical Support / Study &
Planning] ALMEC Corporation
Host Party of the Project & Monitoring
EMS Center (tentative)
Server PC & EMS management system
[Target Beneficiaries]
Taxi operators
(EMS System users)
Utilization of
EMS Services
EMS Database & Eco
Drive Advices
Suggested Institutional Development with EMS Center for GHG Emission
Reductions
Bilateral
Agreemen
Construction
& Equipment,
Analysis &
Advice,
Technical
Education
Self-Governance of Taxi Operations / Sustainable Eco
Drive Activities
Database of Taxi Operation
・Checking average vehicle efficiency from the monthly
reports
・Identifying low performance drivers
Eco Drive Education & Training
Univ. of Transportation Technology (UTT)
・Training and assignment of eco drive instructors
・Technical support to the training courses
Cooperation
To be repeated
Annual Performance Review of Fuel Efficiency Improvement
・Evaluation of participants after eco drive training
・Good performance awards

![Bài giảng bảo dưỡng kim phun nhiên liệu động cơ diesel [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2023/20230711/phuong5901/135x160/4001689050569.jpg)







![Bài giảng Bơm xăng cơ khí SC-BD: Tổng hợp kiến thức [Chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2014/20140908/hoanglinh0808/135x160/9551410189280.jpg)

![Bài giảng Kỹ thuật điện - điện tử ô tô [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260121/hoatrami2026/135x160/37681769069450.jpg)








![Câu hỏi ôn tập Truyền động điện [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250613/laphong0906/135x160/88301768293691.jpg)
![Giáo trình Kết cấu Động cơ đốt trong – Đoàn Duy Đồng (chủ biên) [Phần B]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251120/oursky02/135x160/71451768238417.jpg)




