
6/12/141 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
Iterator - Comparable - Comparator
Nguy n Xuân Vinhễ
nguyenxuanvinh@hcmuaf.ed
u.vn
C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ
DATA STRUCTURES
[214331]
6/12/142 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
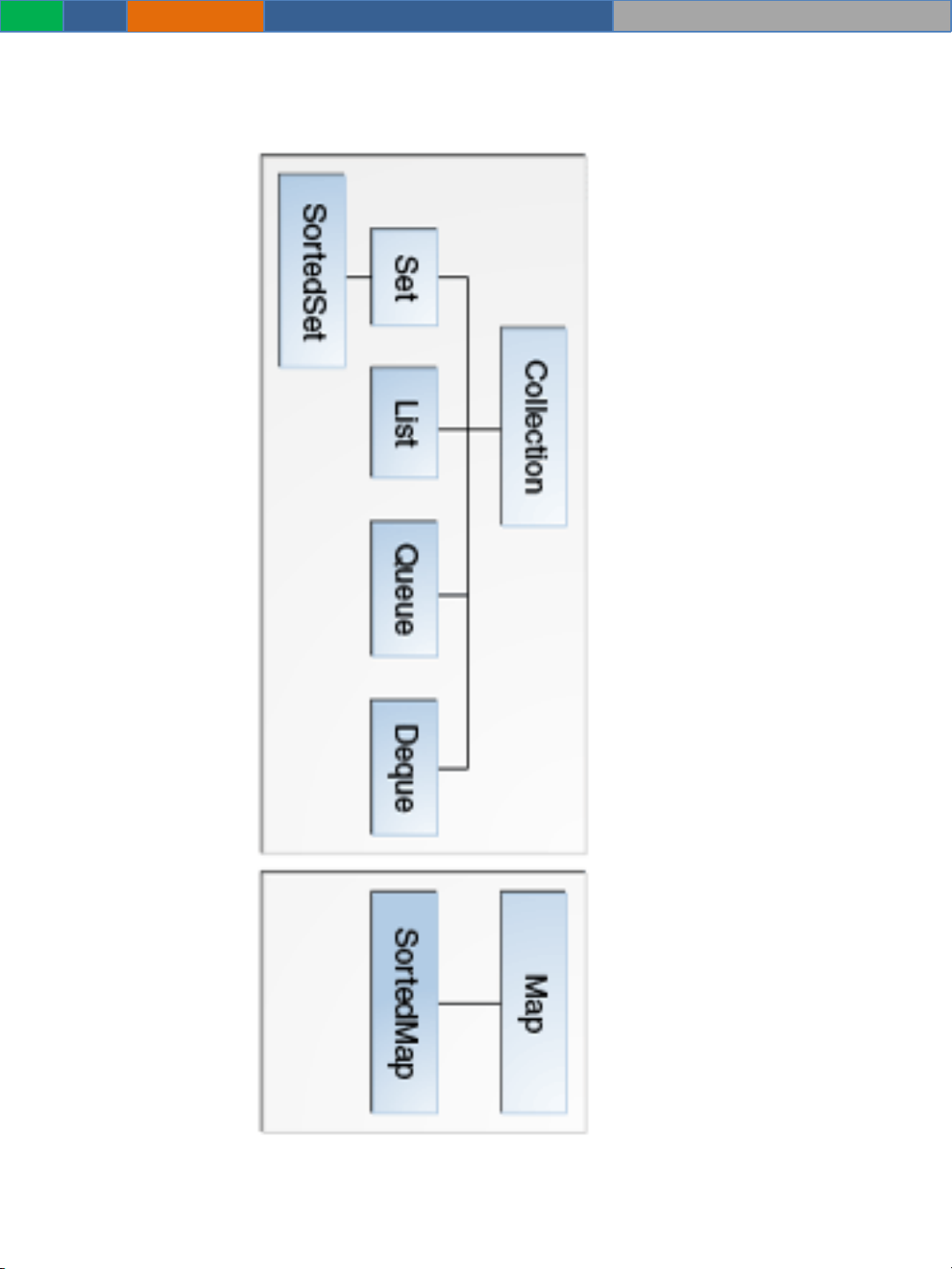
Java Collection Architecture
6/12/143 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
The Differences!!!
•How to browse element?
–Elements of List are indexed.
int value = list[0];
–Elements of LinkedList, Sets and
Maps can't be accessed by
index
•How to remove element?
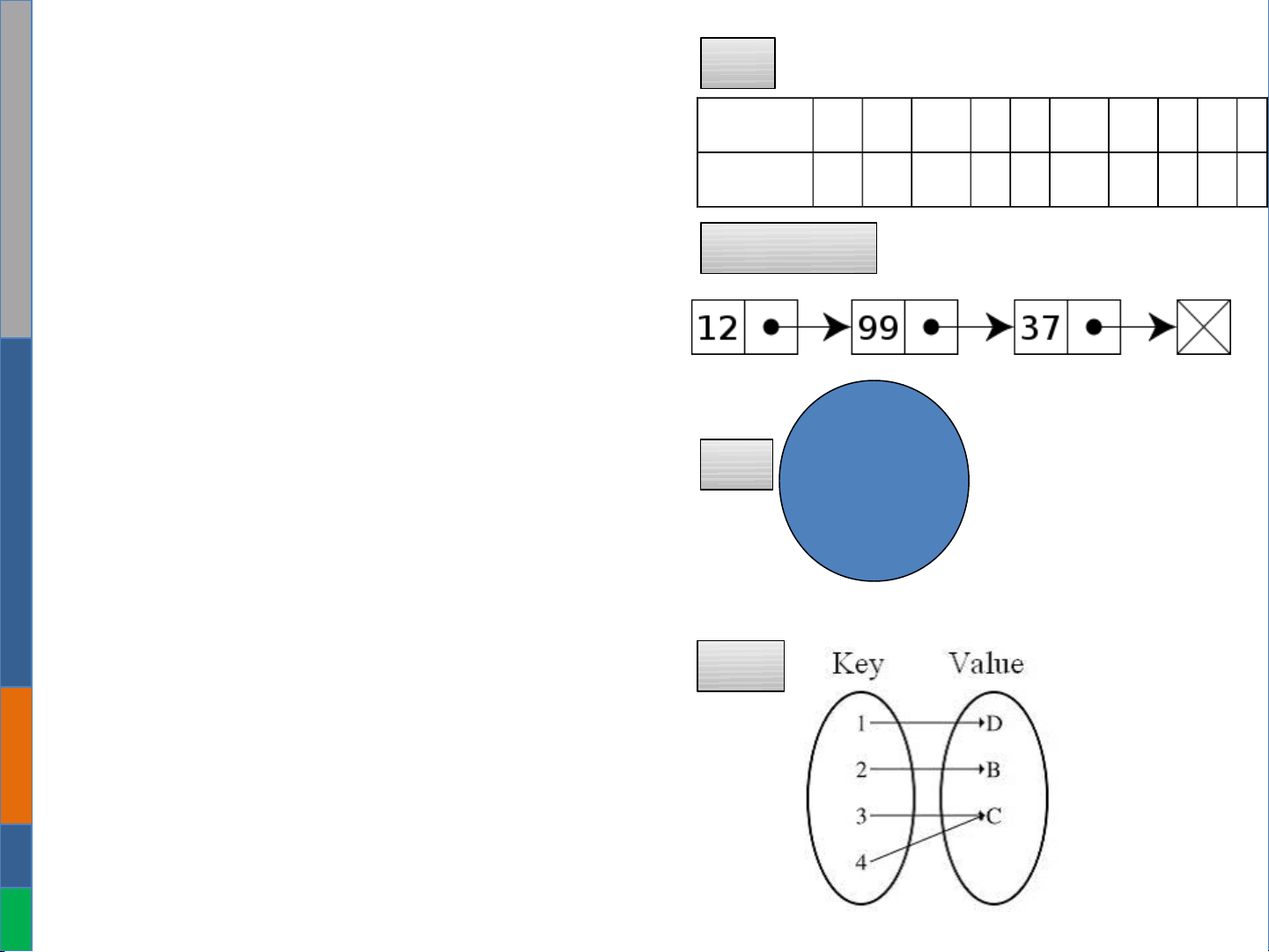
index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
value 3 8 9 7 5 12 0 0 0 0
List
Set
"the"
"to"
"from"
"we"
Linked List
Map

6/12/144 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
Examining sets and maps
•elements of Java Sets and Maps can't be accessed by index
–must use a "foreach" loop:
Set<Integer> scores = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int score : scores) {
System.out.println("The score is " + score);
}
–Problem: foreach is read-only; cannot modify set while looping
for (int score : scores) {
if (score < 60) {
// throws a ConcurrentModificationException
scores.remove(score);
}
}
6/12/145 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
Iterators (11.1)
•iterator: An object that allows a client to traverse the elements of
any collection, regardless of its implementation.
–Remembers a position within a collection, and allows you to:
•get the element at that position
•advance to the next position
•(possibly) remove or change the element at that position
–Benefit: A common way to examine any collection's elements.
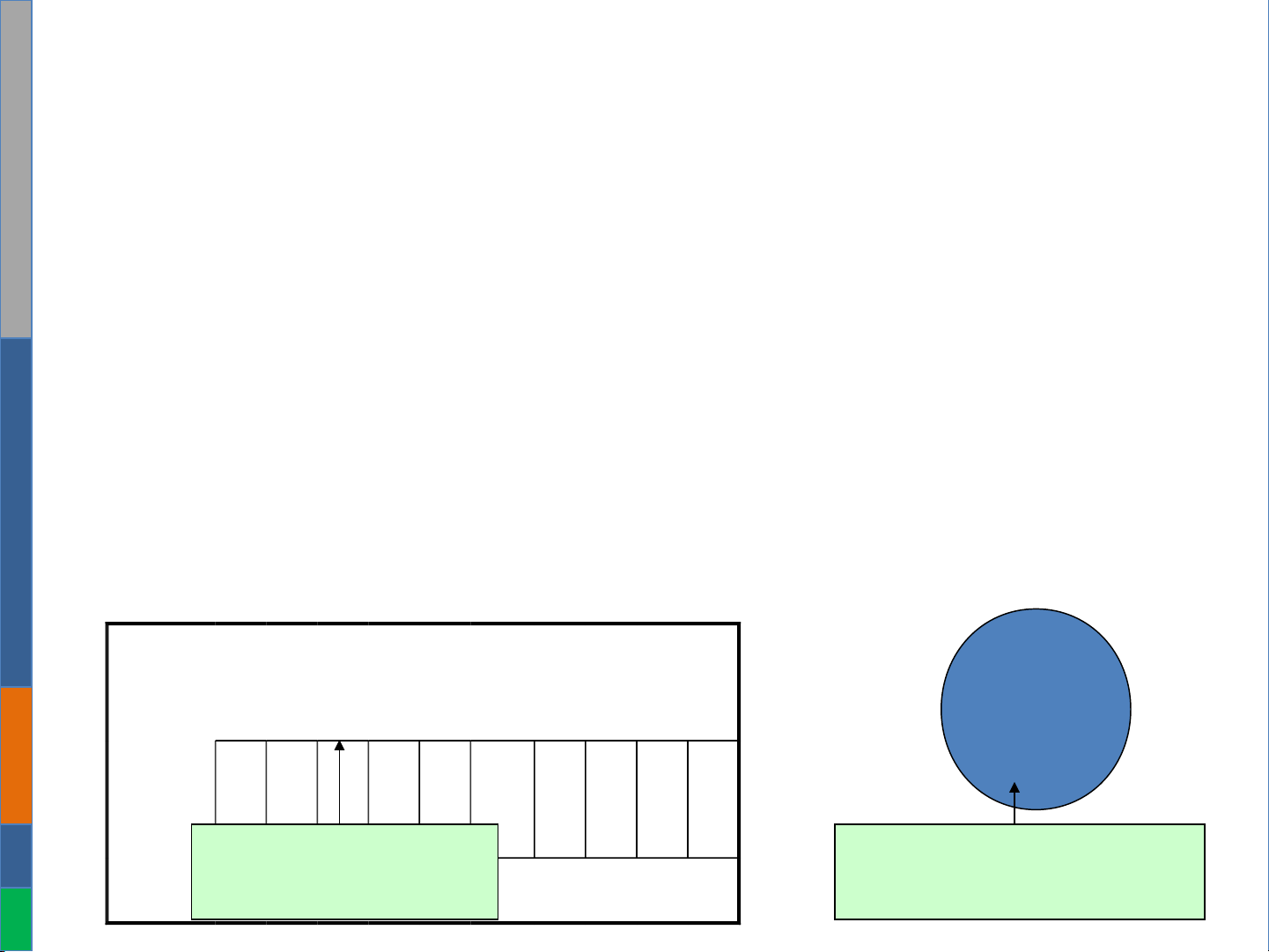
inde
x
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
valu
e
3 8 9 7 5 12 0 0 0 0
size 6
list
current element: 9
current index: 2
iterator
set
"the"
"to"
"from"
"we"
current element: "from"
next element:"the"
iterator

![Bài giảng Thực hành cơ sở dữ liệu Trường ĐH Công Nghệ [năm] mới nhất](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251120/oursky02/135x160/14661768233842.jpg)
























