
Nhập môn Kỹ thuật Truyền thông
Phần 2: Các kỹ thuật điều chế số
(Digital Modulations)
Bài 11: Không gian tín hiệu 4-PSK và m-PSK
2
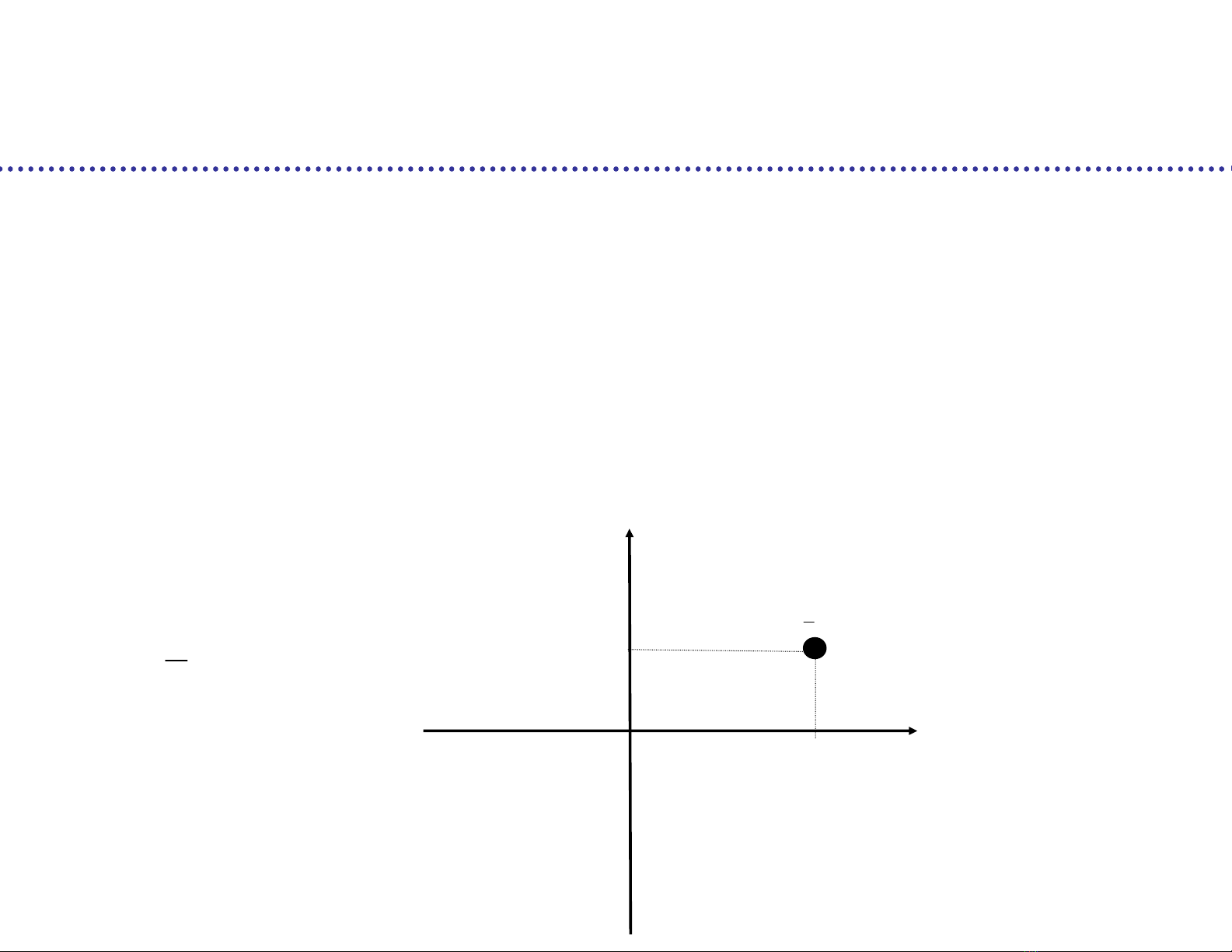
Consider a 2-D constellation, suppose that basis signals =cosine and sine
Quadrature modulation
Each constellation symbol corresponds to a vector with two real
components
1 0
( ) ( ) cos(2 )b t p t f t
2 0
( ) ( )sin(2 )b t p t f t
{ ( , )}
i i i
M s
0
( )b t
1
( )b t
i
s
i
i
1
( )b t
2
( )b t
3
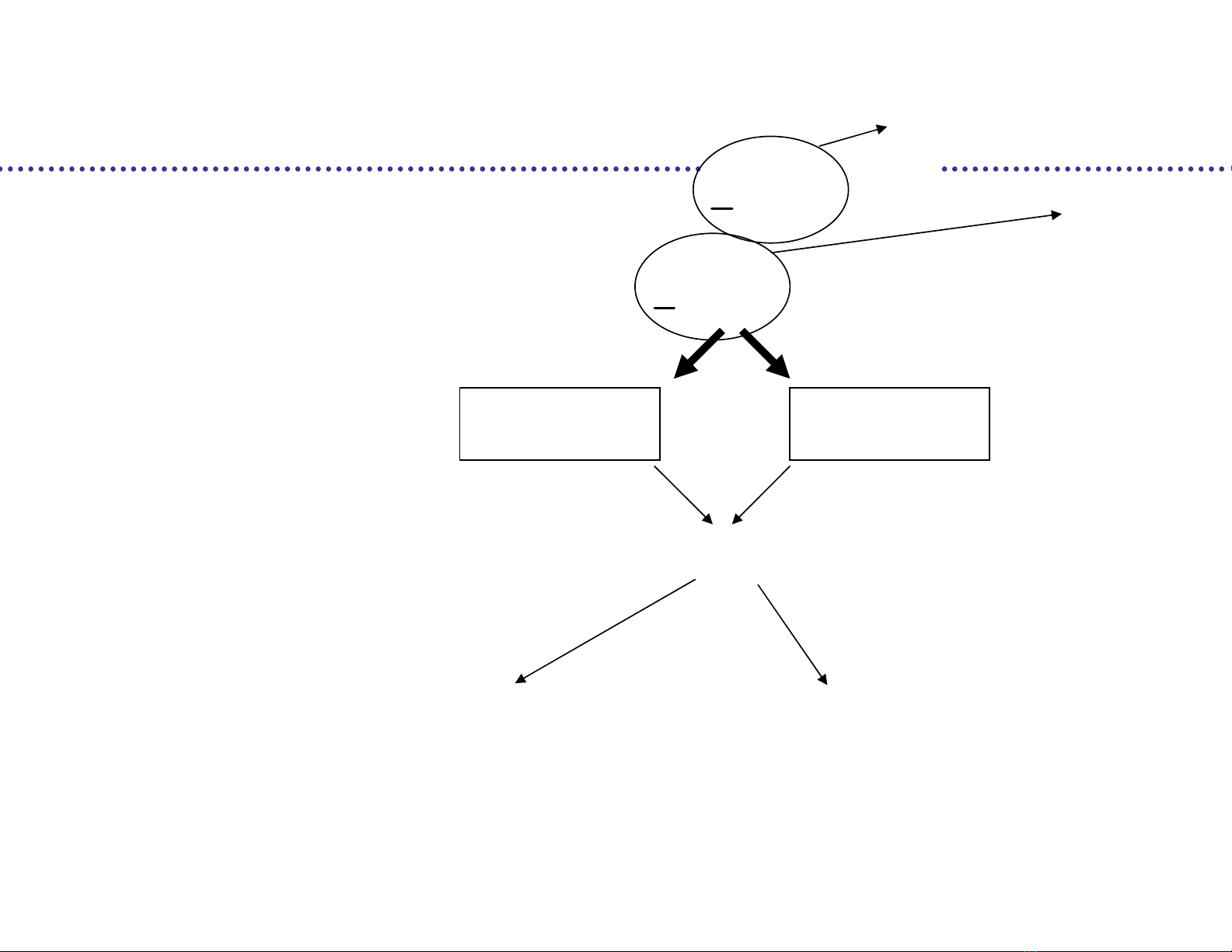
Binary information sequence
Quadrature modulation
Symbol sequence
Transmitted signal
[ ]
T k
v n H
1 2
( ) [ ] ( ) [ ] ( ) ( ) ( )
n n
s t n b t nT n b t nT a t b t
2
[ ]
T
s n M R
[ ]
n R
[ ]
n R
DURATION T
DURATION T
DURATION T
4
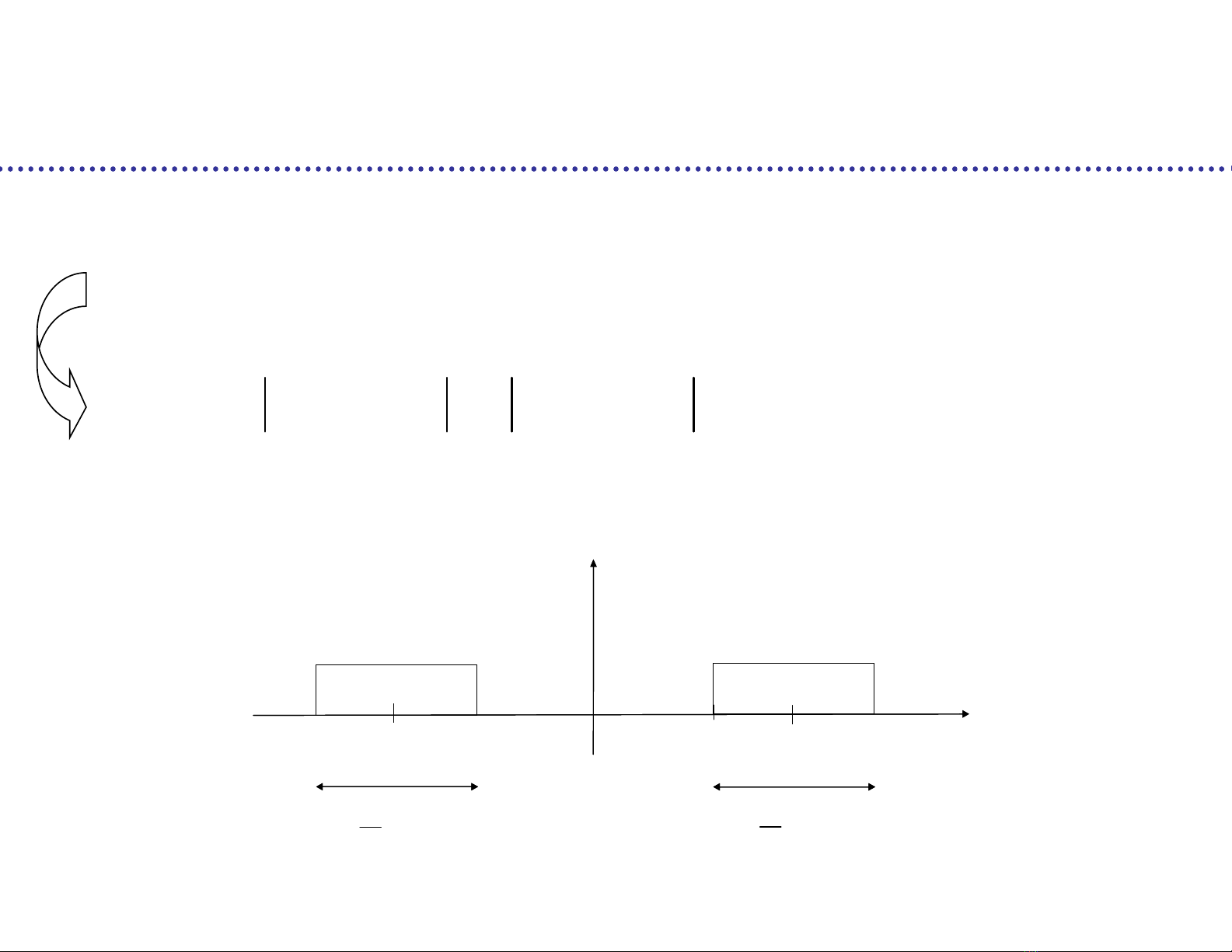
Spectrum of a(t):
Quadrature modulation
2 2
0 0
( ) ( )
a
G x P f f P f f x R
R
R
0
f
0
f
R
R
0
f
0
f
when p(t) = ideal low pass filter
1 0
( ) [ ] ( ) [ ] ( ) cos 2
n n
a t n b t nT n p t nT f t
1
R
T
1
R
T
5
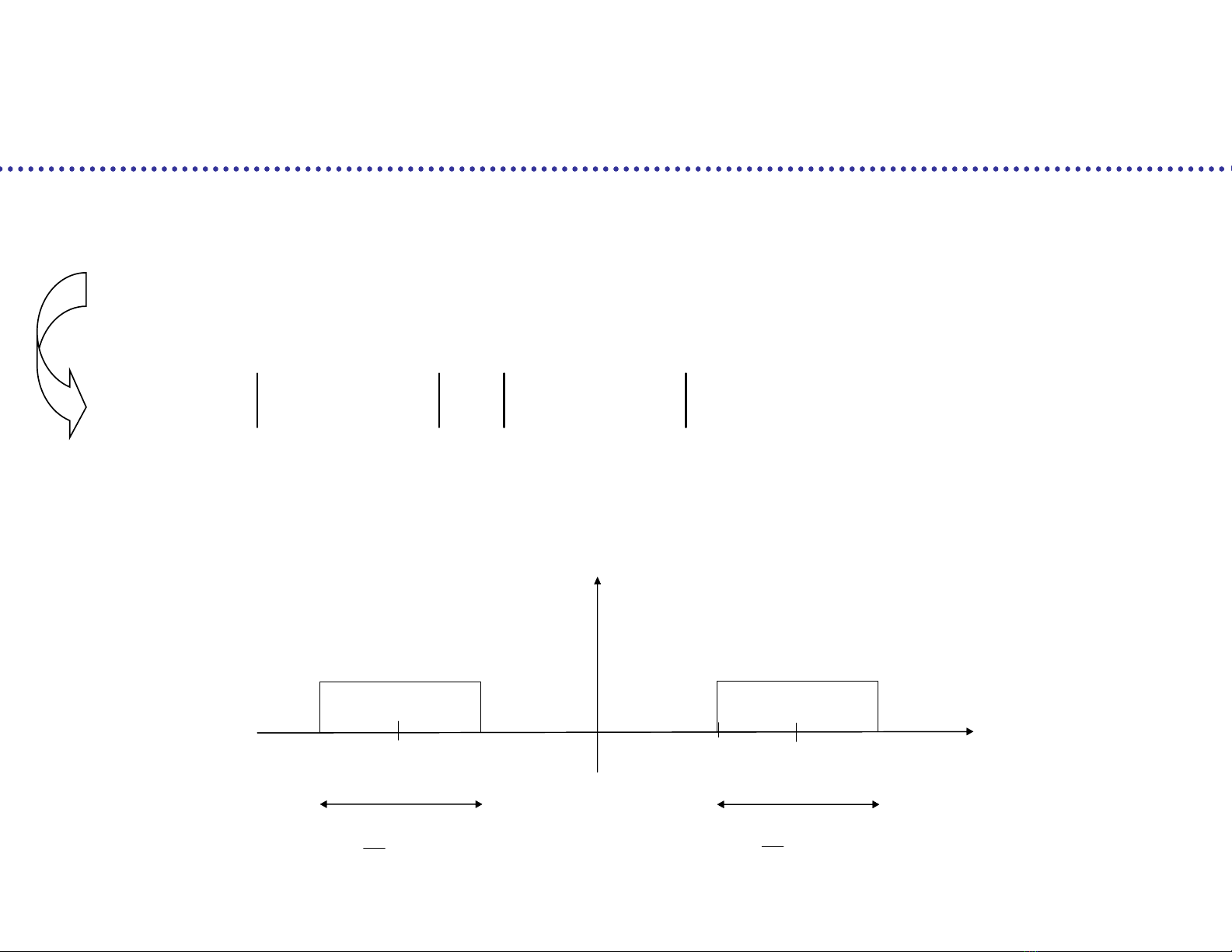
Spectrum of b(t):
Quadrature modulation
2 2
0 0
( ) ( )
b
G y P f f P f f y R
R
R
0
f
0
f
R
R
0
f
0
f
when p(t) = ideal low pass filter
1 0
( ) [ ] ( ) [ ] ( ) sin 2
n n
b t n b t nT n p t nT f t
1
R
T
1
R
T












![Bộ tài liệu Đào tạo nhân viên chăm sóc khách hàng tại đơn vị phân phối và bán lẻ điện [Chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251001/kimphuong1001/135x160/3921759294552.jpg)


![Ngân hàng câu hỏi thi giữa kì môn Truyền động điện [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250920/kimphuong1001/135x160/42601758354546.jpg)


![Câu hỏi ôn tập Quy trình an toàn điện có đáp án [kèm đáp án chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250920/kimphuong1001/135x160/18761758354548.jpg)
![Đề thi trắc nghiệm Kỹ thuật mạch điện tử: Tổng hợp [Năm]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250920/kimphuong1001/135x160/23481758356189.jpg)


![Tài liệu ôn tập Thông tin quang [năm] [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250917/anvunguyen0207@gmail.com/135x160/56551758168054.jpg)



