
Stent Thrombosis
Cập nhật vai trò kháng tiểu cầu kép
TS.BS. NGUYỄN THƯỢNG NGHĨA
Trưởng khoa Tim mạch can thiệp
Phó Giám đốc Trung tâm tim mạch
BV. Chợ Rẫy
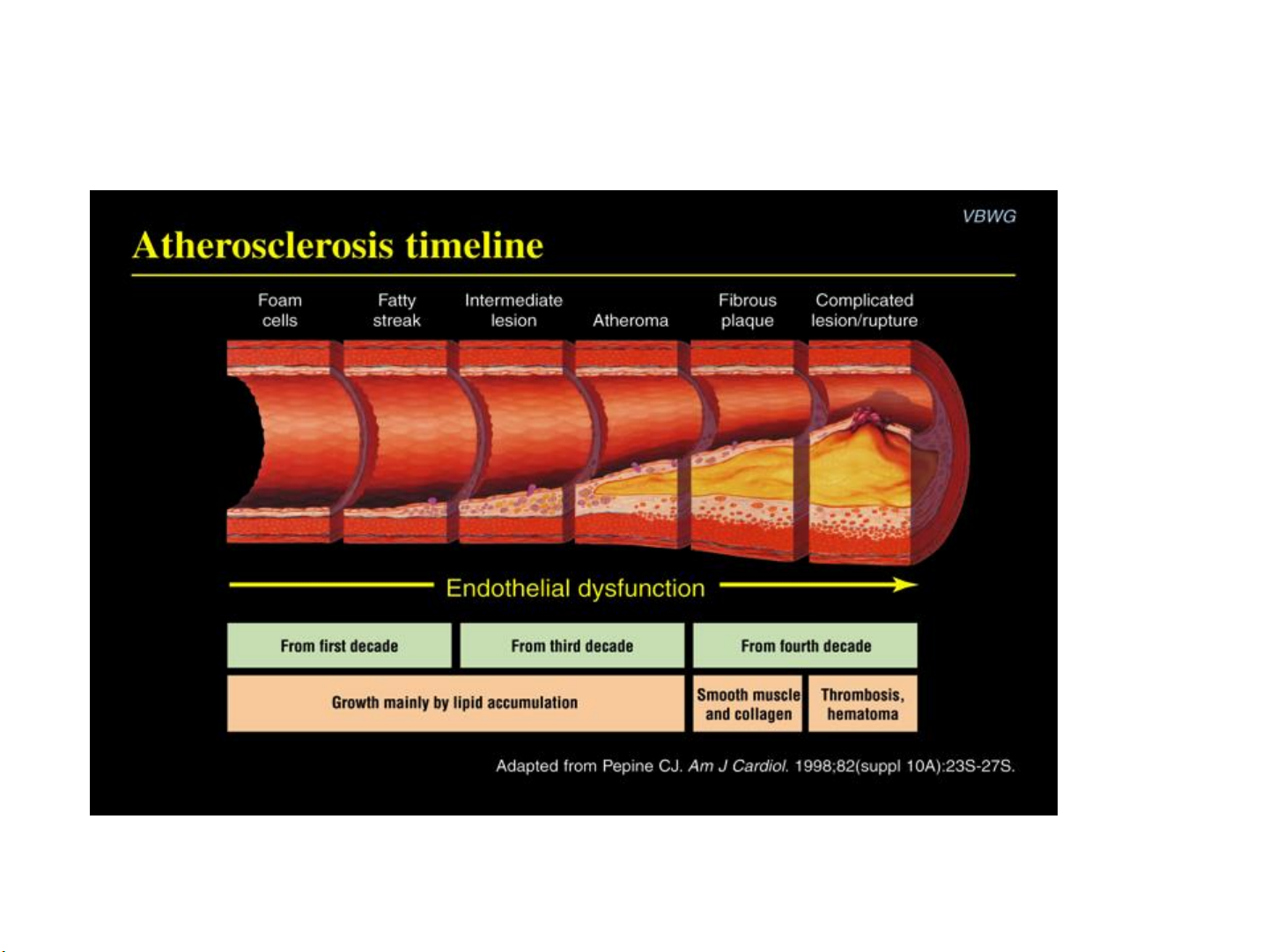
Let’s review the Arterial Disease Process
When the plaque ruptures, a blood clot can form that partially or completely blocks the artery.
Rupture of stable plaque is the initial pathologic event leading to 75% of all heart attacks
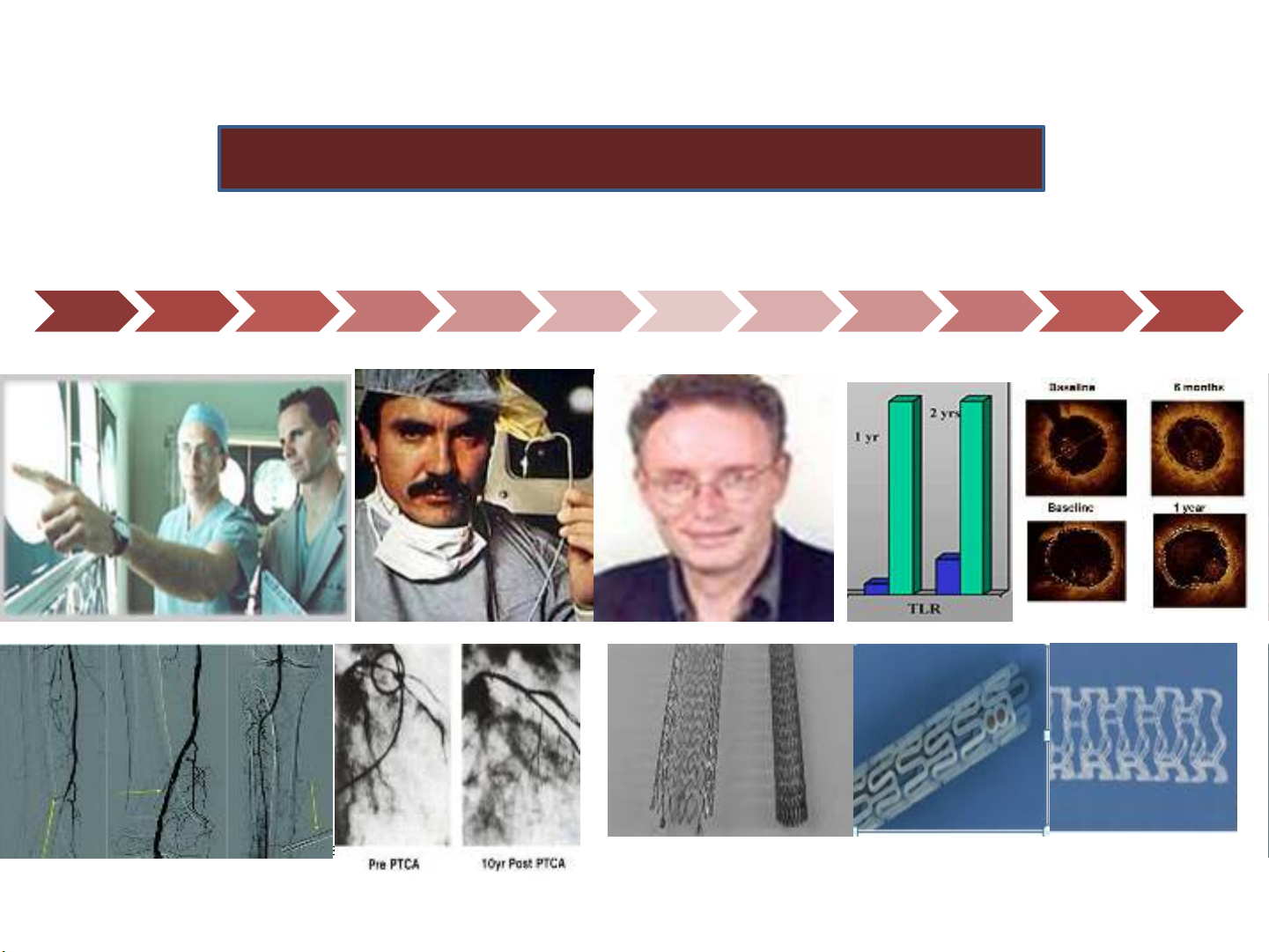
1964 1961 1974 1977 1987 1988 1989 2001 2003 2009
PTA BES
CCU
CABG PTCA
Coiled stent,
POBA PTCA
BMS
Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2006;116:41-53
Anesth Analg. 2008;107:552-69
Lancet. 1994;344:1383-1389
N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1665-1671
Historical Perspective of treatment cardiovascular diseases
Cypher
DES BVS
NC RAVEL
Hoa Ky hng năm 600.000 BN đt stent
Vit Nam hng năm: 2014 = 10455 Stent
Taxus Xience
Promus
What happens after stent implant?
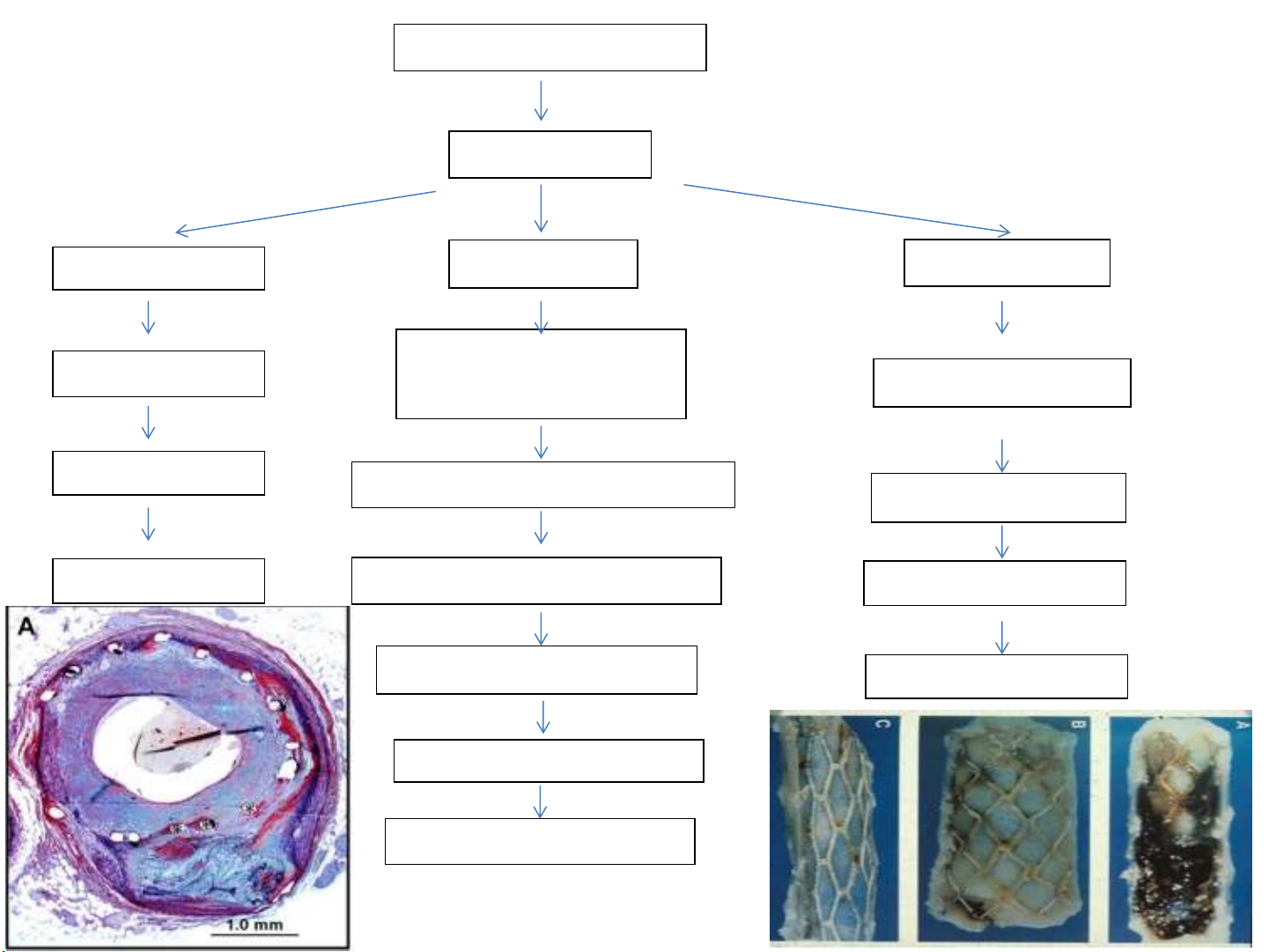
Intervention (POBA, stent)
Vessel Injury
Plaque Rupture
Inflammation
Endothelial damage
Vessel Stretch
Chemotactic Responses
(GF, CytoKines,…)
Platelet Activation
Acute Close Migration / Proliferation of SMC
Restenosis
Thrombus
Platelet Aggregation
Extracellular Matrix formation
Neointimal Hyperplasia
Remodelling
Restenosis
Elastic Recoil
- Plaque Rupture
- POBA disrupts endothelial injury to
arterial media
- Barotrauma from high-pressure balloon
inflation / angioplasty
- Stenting injure artery by acting as a
foreign body, tissue reaction
Thrombosis/Restenosis
Cascade
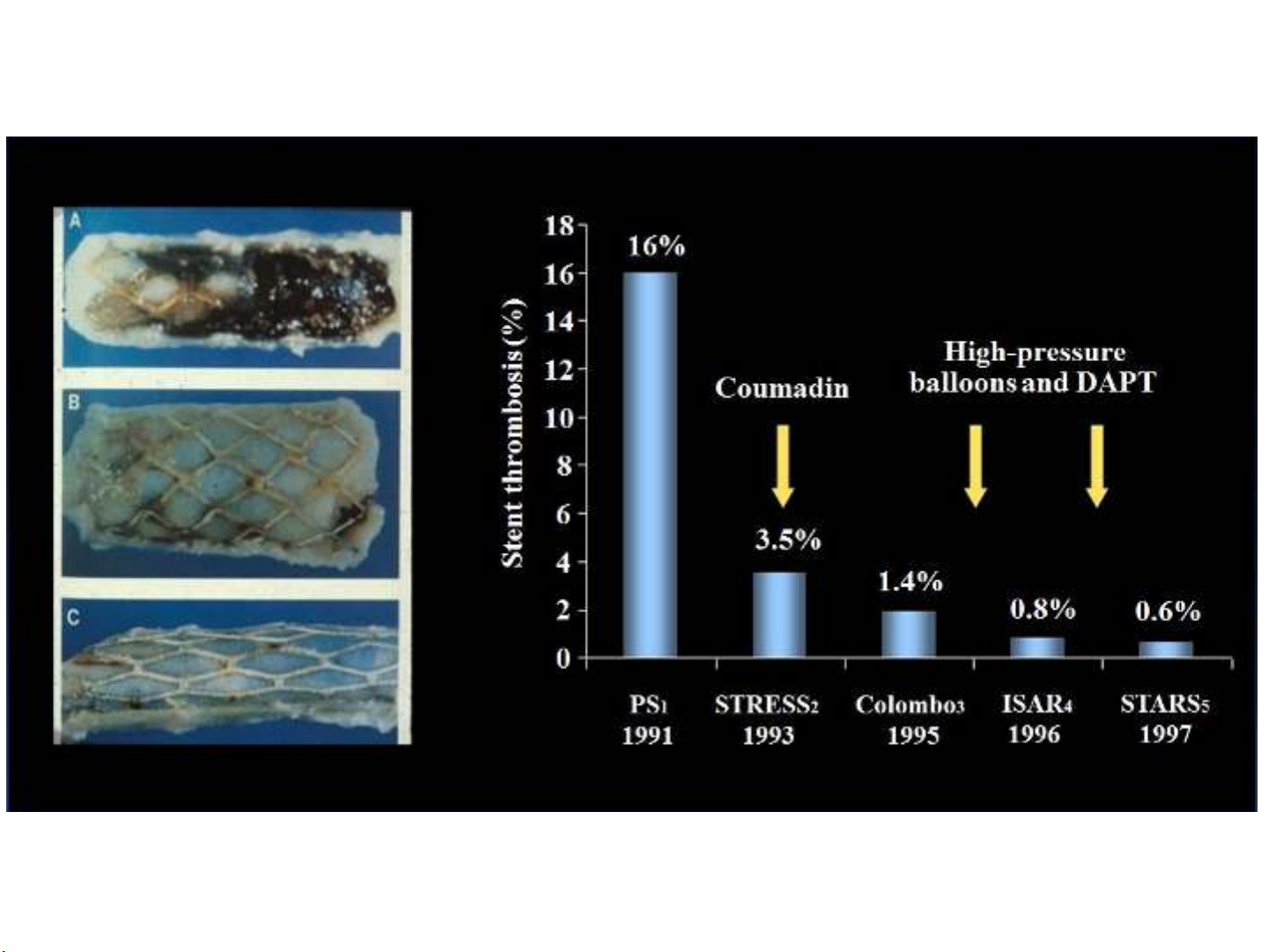
Stent Thrombosis: History & Histopathology
Schatz et al. Circulation.1991;83:148;
Fischman et al. N Engl J Med. 1994;331496;
Colombo et al. Circulation.1995;91:1676;
Schömig et al.Circulation.1994,90:2716;
Leon et al. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1665;
Joner et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:193.


























