Suy tim với chức năng tâm thu
thất trái bảo tồn
Những vấn đề còn thách thức
TS.BS. Hong Văn Sỹ
Đại học Y Dược Tp. Hồ Chí Minh
Khoa Nội Tim mạch BV Chợ Rẫy
TP HCM 13/7/2019
Tần suất suy tim với EF bảo tồn (HFpEF)
In patients with clinical
HF, the prevalence of
HFpEF is estimated to be
approximately 50%1
Patients with HFpEF were
older and more likely to be
female than those with
HFrEF3a
The proportion of incident
cases of HFpEF increased
from 47.8% in 2000–2003 to
52.3% in 2008–20102
aThe GWTG-HF registry was merged with claims from the U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) from January 1,
2005, through December 30, 2009, with 5 years of follow-up through the end of December 2014
HF, heart failure; HFrEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
Vào 2020, ước đoán 65% suy tim nhập viện là suy tim EF bảo tồn4
Khoảng ½ bệnh nhân suy tim có triệu chứng l suy suy tim
EF bảo tồn
1. Yancy CW et al. Circulation. 2013;128:e240-e327; 2. Gerber Y et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(6):996-1004; 3. Shah KS et al. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 2017;70(20):2476-2486; 4. Oktay AA et al. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2013; 10(4): doi:10.1007/s11897-013-0155-7.
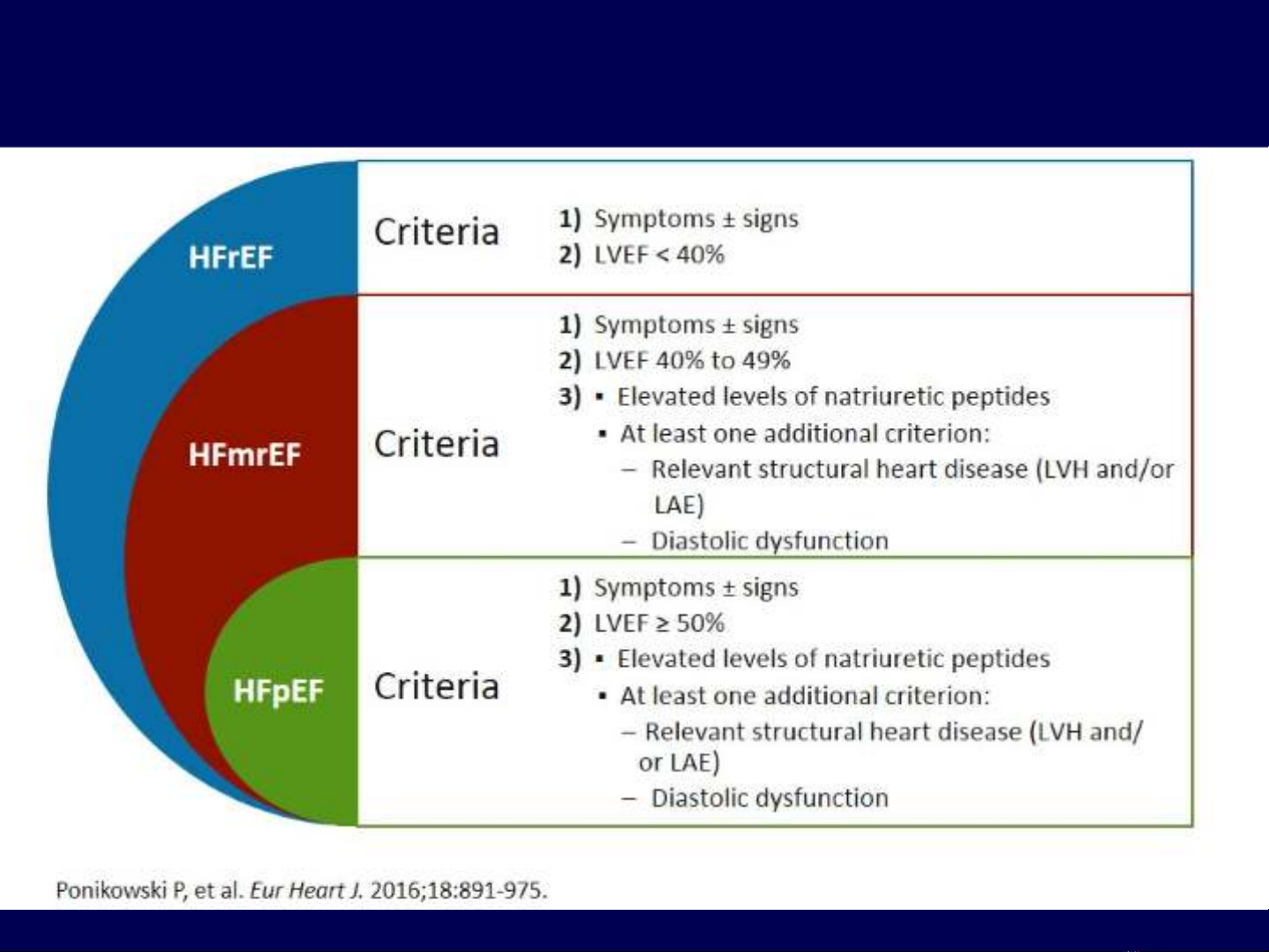
Định nghĩa các loại suy tim theo ESC
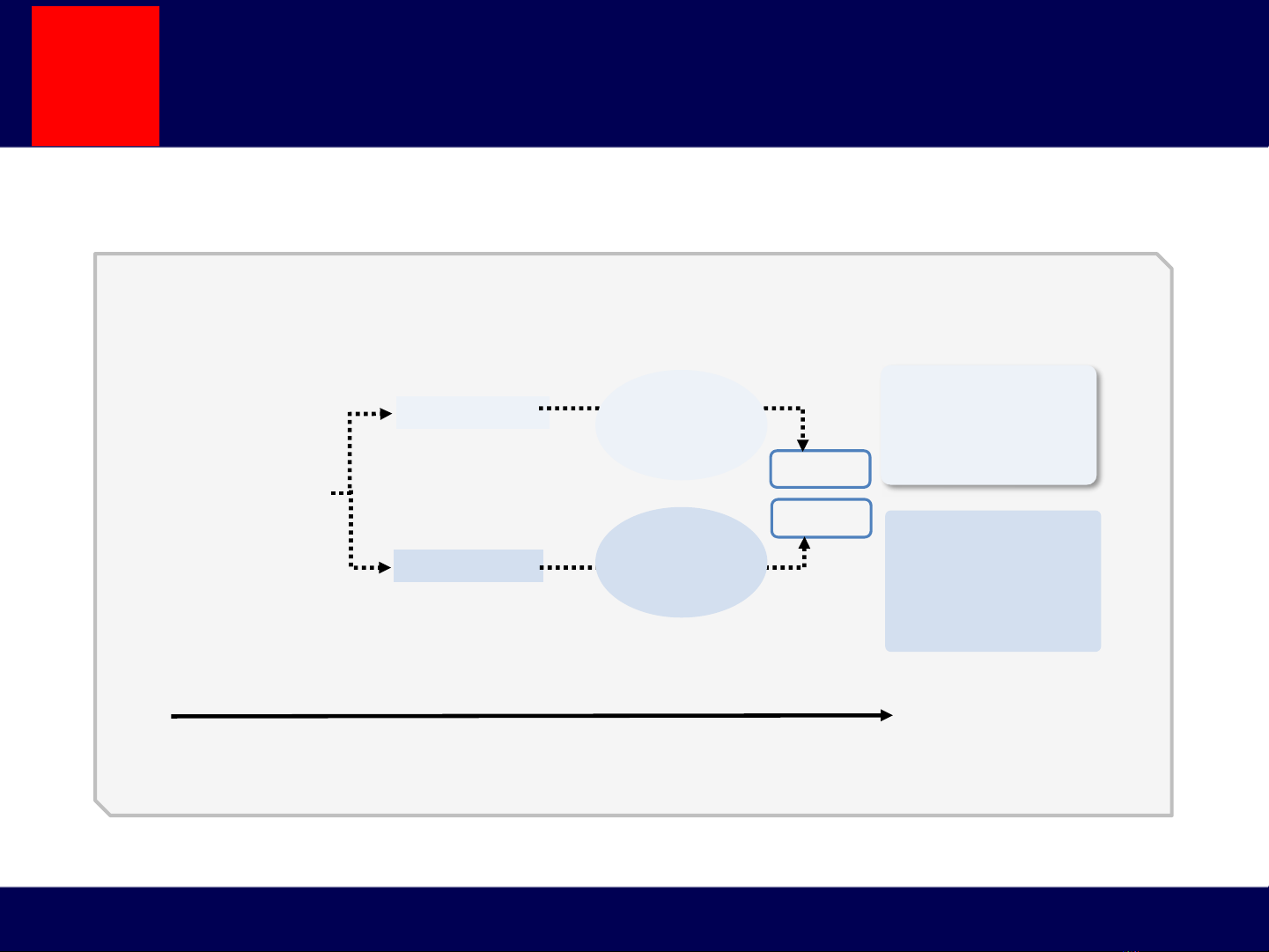
Cơ chế bệnh sinh còn chưa rõ ?
HFpEF
HFrEF
LV enlargement
LV hypertrophy
Clinical HF
Normal
LV structure
and function LV remodeling
Subclinical
LV dysfunction
Years/monthsYears
HFrEF is also called
systolic HF, although
patients may also
exhibit diastolic
abnormalities
HFpEF is also called
diastolic HF, although
most patients have
evidence of both
systolic and diastolic
dysfunction
Age
Smoking
Dyslipidemia
CAD/MI
Hypertension
Obesity
Diabetes
Systolic
dysfunction
Diastolic
dysfunction
CAD, coronary artery disease; HF, heart failure; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; LV,
left ventricular; MI, myocardial infarction.
Hypertension and coronary artery disease are major risk factors for
development of heart failure
Suy tim EF bảo tồn là biểu hiện của 1 bệnh ?
1. Krum H, Gilbert RE. Lancet 2003;362:147–58; 2. Borlaug BA, Paulus WJ. Eur Heart J.2011;32:670–679.
1
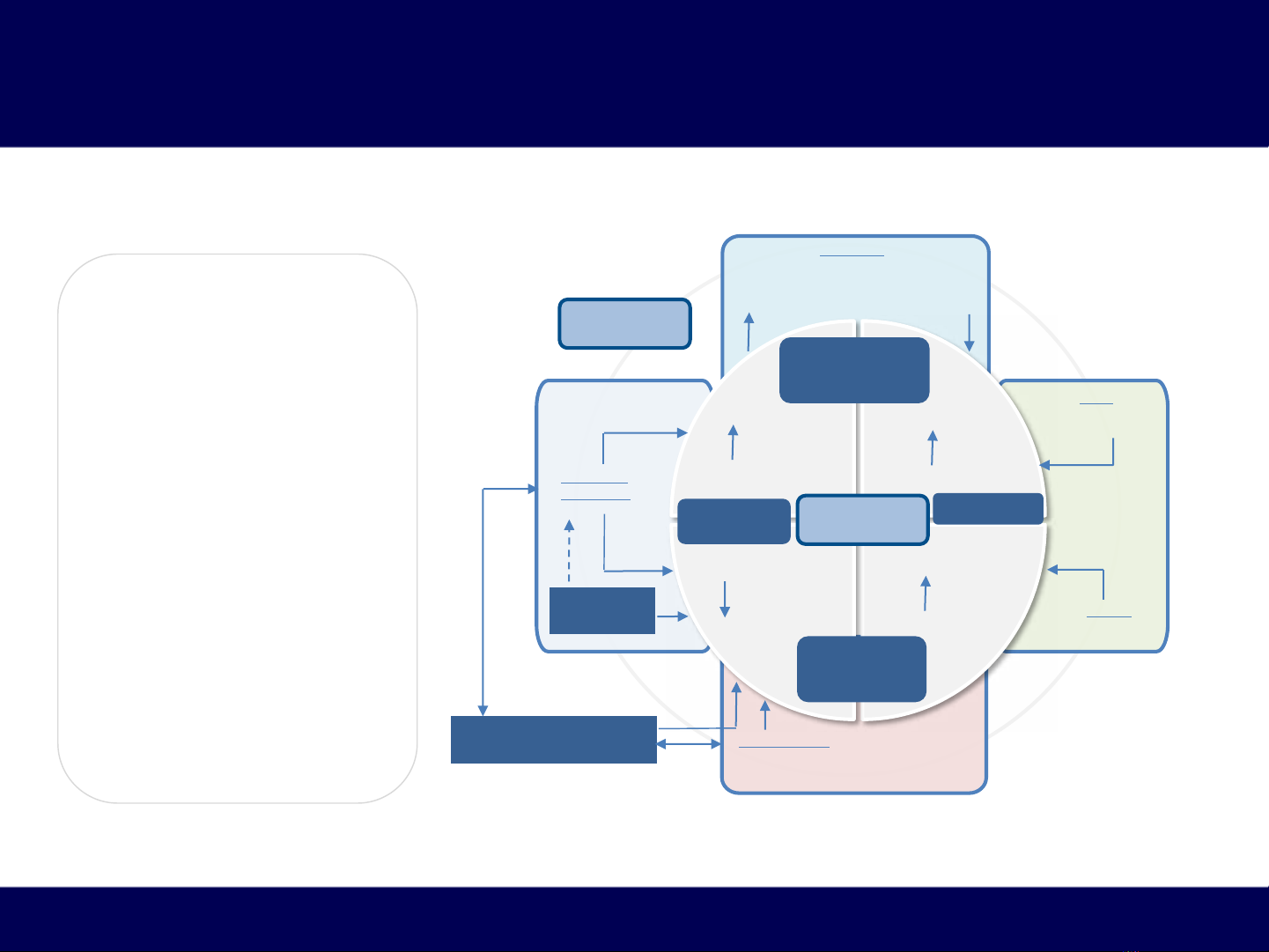
Sinh bệnh học của HFpEF
Các cơ chế SBH trung ương v ngoại vi
•Heterogeneity of patient
characteristics, organ-
system involvement and
number of
pathophysiological
abnormalities suggest a
multifactorial etiology
in patients with HFpEF
•Subphenotypes in HFpEF
are usually described
according to the most
dominant clinical
characteristics:
•HFpEF subphenotype
with PAH and RV
dysfunction has been
well characterized and
signifies advanced
stage HF
Central
Mechanisms
RV Dysfunction
AF and
LA Dysfunction
LV Systolic Stiffening
and Dysfunction
LV Diastolic
Stiffening and
Dysfunction
RV Filling
Pressures
Load
sensitivity
Exercise
tolerance
LV Filling
Pressures
Renal
Sodium retention
Arterial
Stiffening
Skeletal muscle
Myopathy
Endothelial
dysfunction
Autonomic
dysfunction
Coronary and systemic
microvascular rarefaction
Pulmonary
Pulmonary venous hypertension
±Impaired diffusion capacity
±‘Reactive’ arterial hypertension
Peripheral
Mechanisms
AF, atrial fibrillation, LA, left atria; LV, left ventricular; RV, right ventricular; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; PAH,
pulmonary arterial hypertension
Zakeri R and Cowie MR. Heart 2018;104(5):377-384
Suy tim EF bảo tồn là biểu hiện của nhiều bệnh ?