
CHẨN ĐOÁN TỔ CHỨC
(ORGANIZATIONAL DIAGNOSIS)
MBA 2013
Giảng viên: TS. Trương Thị Lan Anh
THAY ĐỔI VÀ PHÁT TRIỂN
TỔ CHỨC

NỘI DUNG CHÍNH
• Chẩn đoán tổ chức là gì?
•Hai cách tiếp cận trong chẩn đoán: cách
tiếp cận giải quyết vấn đề (problem solving
approach) và cách tiếp cận tích cực
(positive approach)
•Cách tiếp cận tích cực: Phương pháp Khai
thác điểm mạnh (Appreciative Inquiry
method)
Org diagnosis - Dr. Lan Anh 2
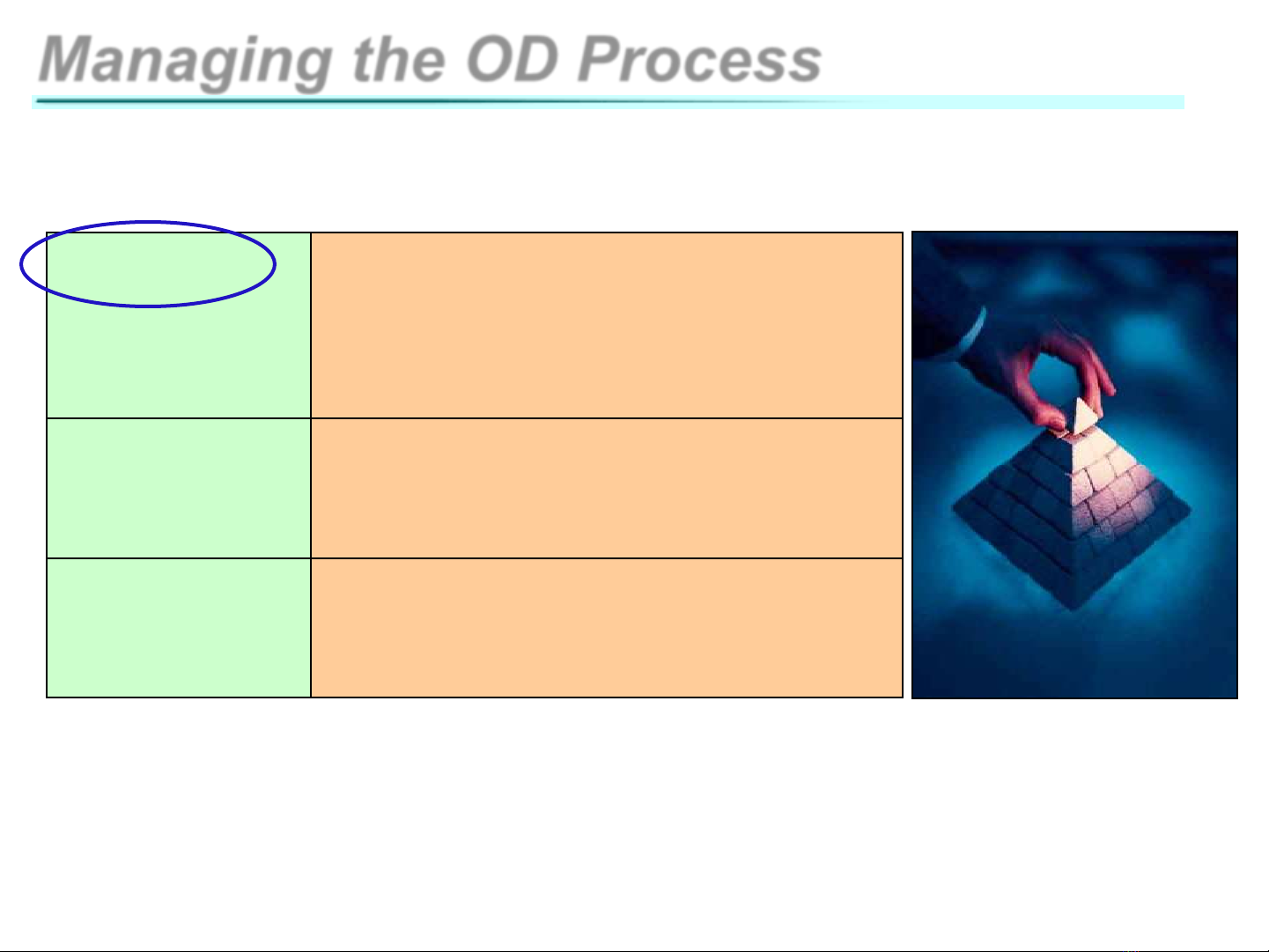
Managing the OD Process
Three basic components of OD programs:
Diagnosis Continuous collection of data
about total system, its
subunits, its processes, and
its culture
Action All activities and interventions
designed to improve the
organization’s functioning
Program
management
All activities designed to
ensure success of the
program
Org diagnosis - Dr. Lan Anh 3

CHẨN ĐOÁN TỔ CHỨC
•Là quá trình cộng tác giữa các thành viên của tổ
chức/nhóm có dự án OD với nhà tư vấn OD để
thu thập thông tin cần thiết, phân tích, xác định
mục tiêu thay đổi.
•Cung cấp thông tin đầu vào về những hiểu biết
về tổ chức phục vụ cho quá trình hoạch định kế
hoạch hành động cho các can thiệp OD
• Đây là đặc tính khác biệt và rõ ràng của một dự
án OD so với các dự án thay đổi ứng phó khác:
phải chẩn đoán tổ chức trước khi can thiệp
Thay đổi có hoạch định
Org diagnosis - Dr. Lan Anh 4

CHẨN ĐOÁN TỔ CHỨC
•Mục đích của chẩn đoán:
‒Problem-solving approach: Xác định các
nguyên nhân của những vấn đề cần giải quyết
Giống như bác sĩ chẩn đoán bệnh (Clinical
diagnosis)
‒Positive approach (AI): Xác định các thế mạnh
giúp vươn tới tầm nhìn của tổ chức
Org diagnosis - Dr. Lan Anh 5






![Bài giảng Quản lý chất lượng trong các tổ chức: Chương 3 - PGS.TS. Trương Đoàn Thể [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2023/20230303/bapnuong06/135x160/2101677835640.jpg)



















