4/2/2013
1
ĐI HC QUC GIA TP.H CHÍ MINH
TRƯNG ĐI HC BÁCH KHOA
KHOA ĐINĐIN T
B MÔN K THU!T ĐIN T
TP.H" Chí Minh 01/2013
X LÝ TÍN HiU S V1I FPGA
Chaper 4: Retiming
(Tái đ?nh thì)
GV: Hoàng Trang
Email: hoangtrang@hcmut.edu.vn
mr.hoangtrang@gmail.com
Thank to: thLy H" Trung MN
Slide: from text book of Parhi
11
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013
Thut ng!
English Vietnamses
Pipelining t#o đư'ng (ng
Cutset tp c+t
Transposed SFG SFG chuy.n v0
Data broadcast truy2n d! liu kh+p nơi, phát tán d! liu
Parallel processing x lý song song
block processing x lý kh(i
communication bound gi:i h#n truy2n thông
th'i gian tr< truy2n thông
2
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com
4/2/2013
2
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013
Outline
•Retiming Introduction
•Preliminaries
– Quantitative Description
– Properties of Retiming
– Solving systems of inequalities
•Special Cases
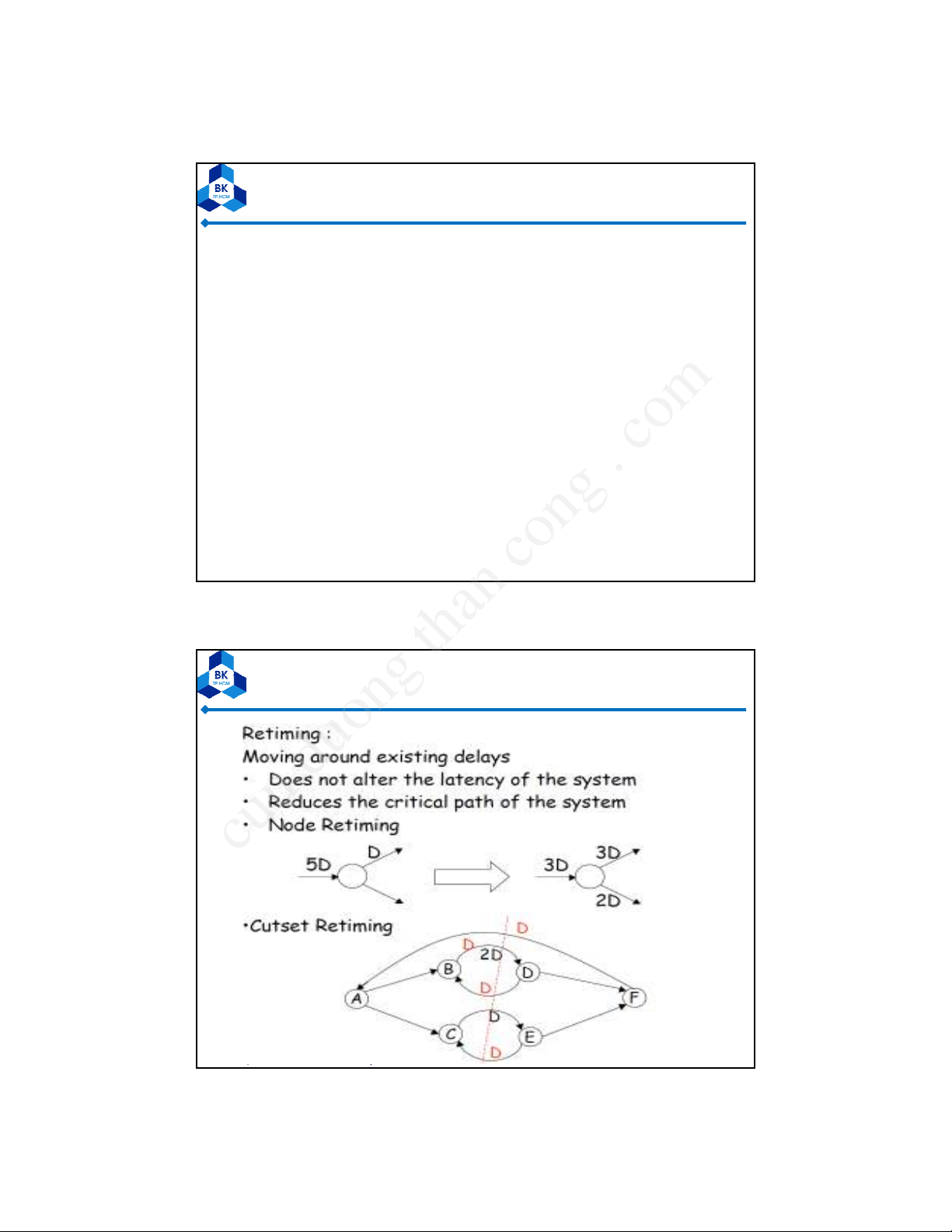
– Cutset Retiming
– Pipelining
•Uses of Retiming
– Retiming for Clock Period Minimization
– Retiming for Register Minimization
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013
4.1 INTRODUCTION
•Retiming is a transformation technique used to
change the locations of delay elements in a circuit
without affecting the input/output characteristics of
the circuit.
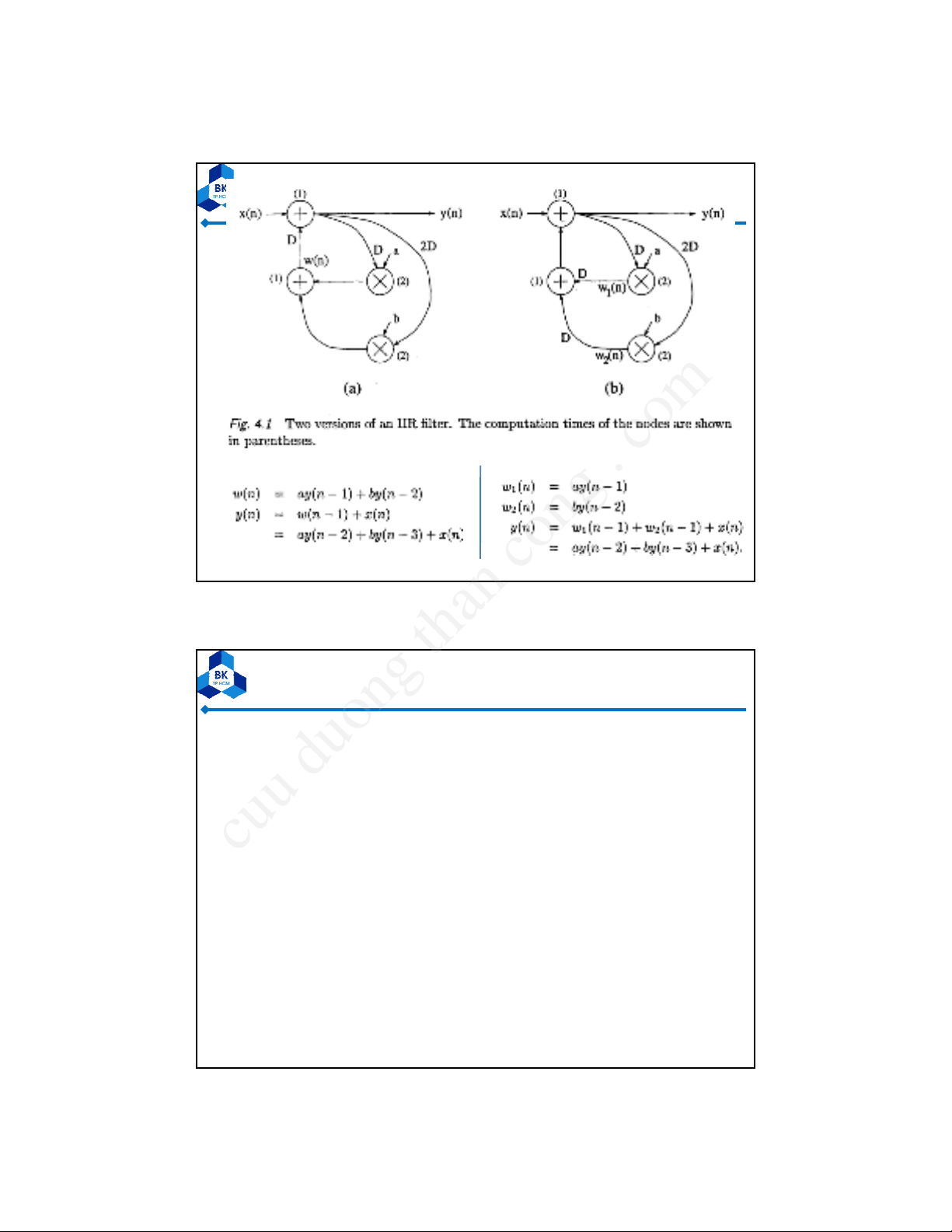
•For example, consider the IIR filters in Fig. 4.1(a) &
(b). Although the filters in Fig. 4.1(a) and Fig. 4.1(b)
have delays at different locations, these filters have
the same input/output characteristics. These 2
filters can be derived from one another using
retiming.
4
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com
4/2/2013
3
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013 5
The filter in Fig. 4.1(b) is described byThe filter in Fig. 4.1(a) is described by
Example:
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013
Applications of Retiming
•Retiming has many applications in synchronous circuit
design. These applications include
–reducing the clock period of the circuit,
–reducing the number of registers in the circuit,
– reducing the power consumption of the circuit, and
– logic synthesis
6
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com
4/2/2013
4
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013
Applications of Retiming (cont’d)
•Retiming can be used to increase the clock rate of a circuit by
reducing the computation time of the critical path.
•For example:
– The critical path of the filter in Fig. 4.1(a) = TM+TA= 3 u.t. => this
filter cannot be clocked with a clock period of less than 3 u.t.
– The retimed filter in Fig. 4.1(b) = TA+TA= 2 u.t. => this filter can be
clocked with a clock period of 2 u.t.
– By retiming the filter in Fig. 4.1(a) to obtain the filter in Fig. 4.1(b), the
clock period has been reduced from 3 u.t. to 2 u.t., or by 33%.
•Retiming can be used to decrease the number of registers in a
circuit. The filter in Fig. 4.1 (a) uses 4 registers while the filter in
Fig. 4.1 (b) uses 5 registers.
•Since retiming can affect the clock period and the number of
registers, it is sometimes desirable to take both of these
parameters into account. 7
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013 8
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com
4/2/2013
5
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013
Example:
9
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter4 01/2013
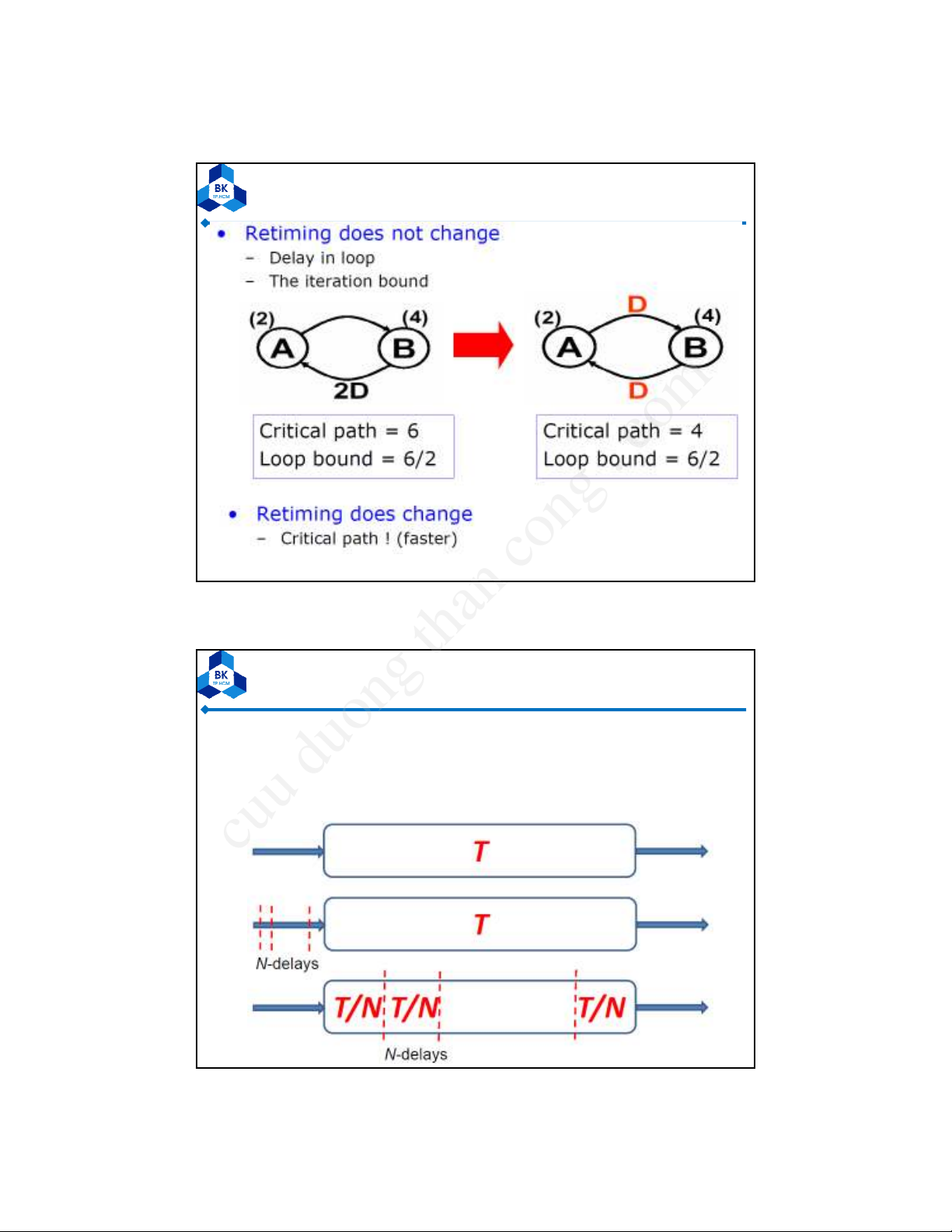
Retiming
•Generalization of Pipelining
•Pipelining is Equivalent to Introducing Many
delays at the Input followed by Retiming
10
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com












![Trắc nghiệm Mạch điện: Tổng hợp câu hỏi và bài tập [năm hiện tại]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251118/trungkiendt9/135x160/61371763448593.jpg)













