http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 89 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 7, Issue 6, September–October 2016, pp.89–94, Article ID: IJM_07_06_010
Available online at
http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=7&IType=6
Journal Impact Factor (2016): 8.1920 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF LONG RUN EQUILIBRIUM
BETWEEN EXCHANGE RATE AND FOREIGN
EXCHANGE RESERVE – AN INDIAN PERSPECTIVE
Dr. Pritpal Singh Bhullar
Assistant Professor - Department of Humanities & Management Studies,
Giani Zail Singh Campus College of Engineering & Technology, India.
Manika Dhameja
CA (Final), ICAI New Delhi, India
ABSTRACT
The present study makes an effort to find the long run equilibrium between Exchange Rate and
Foreign Exchange Reserve. Fifteen years data of these variables has been extracted from the
official website of Reserve Bank of India and has been analyzed by devising statistical software E –
Views. Regression analysis has been applied through SPSS to evaluate the relationship between
foreign exchange reserve and exchange rate. The statistical output of present research supports the
previous research documents and shows the existence of long run equilibrium between these
foreign exchange reserve and exchange rate. It also supports the influence of foreign exchange
reserve on the exchange rate of country.
Key words: Foreign exchange Reserve, Exchange Rate, Regression. Cointegration Test and Unit
Root Test.
Cite this Article: Dr. Pritpal Singh Bhullar and Manika Dhameja, Empirical Analysis of Long Run
Equilibrium between Exchange Rate and Foreign Exchange Reserve – An Indian Perspective.
International Journal of Management, 7(6), 2016, pp. 89–94.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=7&IType=6
1. INTRODUCTION
Capital flow acts as the blood in veins of the economy. High capital flow boosts the chances of growth of
economy. The positive global macroeconomic signs are true symbolic representation of rise of capital flow
in any economy. With globalization, the interdependence of economies has been increased. The global
events have significant impact on the capital flow of the economies. The financial recession of 2008 dent
the capital inflow in all the major economies across the globe. With globalization, the financial flow has
been inclined developed countries to developing countries and under developed countries. The manifold
rise has been reported in capital flows in many developing economies. Kohli (2203) supports the fact that
increase in capital flow to any economy boost its liquidity, stock market growth and growth prospects of
corporate. Carderelli et al (2010) analyzed that capital flow has significant effect upon the economic
sectors like real estate, financial sector and manufacturing sectors. Dua and Sen (2013) documents the

Dr. Pritpal Singh Bhullar and Manika Dhameja
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 90 editor@iaeme.com
dependency between capital flow and several macro economic variables like current account deficit,
liquidity, inflation and money supply. Since last one decade, India has been emerged as a global
destination for investment. Major global investors have been attracted to India for their bulk investment as
Indian market has sent positive sentiments to the global investors. The countries maintain their foreign
exchange reserves to meet their international short term and long term payment obligations. These
obligations consists of sovereign debt, import financing, commercial debt, for intervention in the foreign
currency markets during periods of volatility, besides helping to boost the confidence of the market in the
ability of a country to meet its external obligations and to absorb any unforseen external shocks,
contingencies or unexpected capital movements. Foreign exchange reserve comprises of Foreign Currency
Assets, Gold and SDR (Special Drawing Rights) and Reserve Tranch Position in which each member is
allocated a special quota by IMF. These include sovereign bonds, treasury bills and short-term deposits in
top-rated global banks besides cash accounts. with the change in the patterns of global trade and other
developments including several currency crises. Foreign exchange reserves acts as catalyst in maintaining
stability of macro-economy. The accumulation of foreign exchange reserve build the strong platform for
enhancing the control of economy of any country, rise in efficiency in currency intervention and also
avoids the probability of occurring financial crisis and national and international level. The rapid
fluctuations in foreign exchange reserve indicates the weak foreign trade activities and economic policies.
Reza, Ostry and Sheehy (2011) quote that foreign exchange reserve acts as external assets that assists in
maintaining Balance of Payments (BOP) and controlling exchange rate with other countries. The exchange
rate intervention also have significant effect upon the foreign exchange reserve of any country. Kasman
and Ayman (2008) examines short term and long term unidirectional flow of causality from foreign
exchange rate to real exchange rate as well as from nominal exchange rate to foreign exchange reserve.
2. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Emmanuel (2013) study the effect of foreign exchange reserve on exchange rate in Nigeria and finds that
foreign exchange reserve has significant effect upon the exchange rate of Nigeria. Hoshikawa (2012)
analyzed the existence of long term rerelationship between foreign exchange reserve and exchange rate.
Romero (2011) perform a comparative analysis of factors affecting foreign exchange reserve on India and
China and find that an inverse relationship between exchange rate and foreign reserve. They find that with
rise in exchange rate the foreign exchange reserve falls down. Prasad and Raju (2010) find an inverse
relationship between foreign exchange international reserve and exchange rate. They explore that an
inverse relation between foreign exchange reserve and exchange rate when the currency of home country
depreciates. Kasman and Ayan (2008) study the relationship between foreign exchange reserve and
exchange rate in Turkey and finds that long run relationship exist between them. Elhiraika and Ndikumana
(2007) examine that countries maintain foreign exchange reserve to lower the inflation and foreign
exchange rate in home country. Bachhante et al. (2006) confirms the harmful effect of volatile exchange
rate and foreign exchange reserve on the economic growth of any economy. Dua and Sen (2006) analyse
empirically from financial year 1993 to financial year 2004 and finds that Cointegration exist between
capital flow level, volatility in capital flow and real exchange rate. Aizenman and Lee (2005) confirms that
countries reserve foreign exchange reserve to maintain low exchange rate and enhance economic growth
3. OBJECTIVES OF STUDY
The present study is aimed at fulfil the following objectives from Indian prospective:
• To analyze the existence of long run equilibrium between foreign exchange reserve and exchange rate
• To analyze the existence of causal relationship between foreign exchange reserve and exchange ratio
4. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
To achieve the objectives stated in the present research paper, statistical techniques have been devised.
Causal relationship between foreign exchange reserve and exchange reserve has been measured by Unit
Empirical Analysis of Long Run Equilibrium between Exchange Rate and Foreign Exchange Reserve – An
Indian Perspective
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 91 editor@iaeme.com
Root Test, Johansson Co -integration Test and Vector Auto Regression (VAR) test. E-views Statistical
software has been used to devised these tests for the statistical interference. Foreign exchange reserve data
and exchange rate have been used as the variables. The data of Indian foreign exchange reserve and
exchange rate from FY 2005 to FY 2016 has been collected from the official website of Reserve Bank of
India. The influence of foreign exchange reserve and exchange rate has been examined by the regression
analysis by applying SPSS software.
5. HYPOTHESIS
• Hypothesis I – A long run relationship does not exist between foreign exchange reserve and foreign
exchange rate
• Hypothesis II – Foreign Exchange Reserve has no significant affect on Exchange rate.
6. DATA ANALYSIS
6.1. Unit Root Test at Levels (Augmented Dickey - Fuller Test)
Unit Root Test has been performed to analyze whether the data is stationary of not.
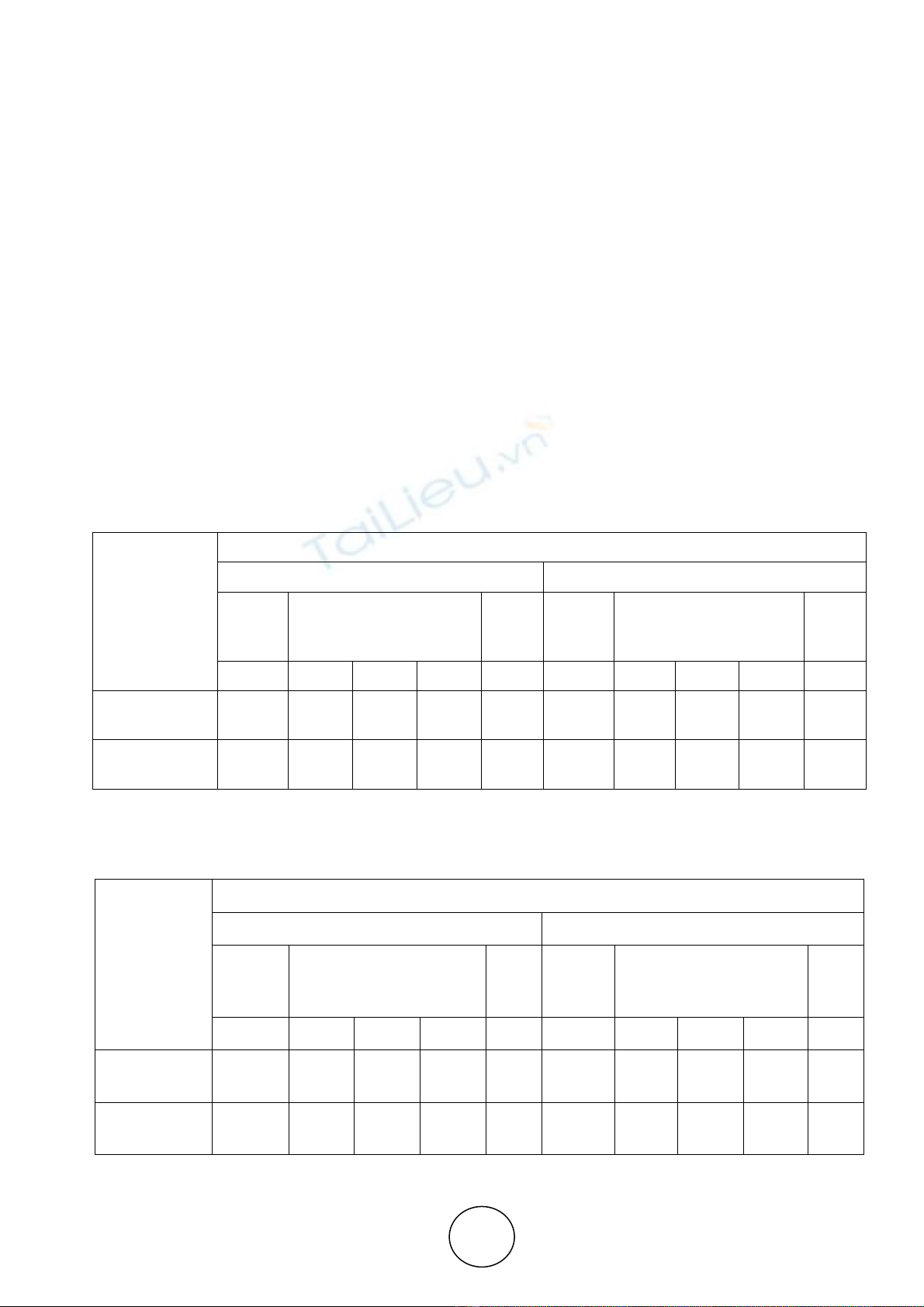
Table 1 Unit Root Test at Level
Variables
Level
No Trend With Trend
t –
statisti
c
Critical Values p
value
t-
statisti
c
Critical Values p
value
1% 5% 10%
1% 5% 10%
LNEXRATE -2.221 -3.438 -2.865 -2.568 0.199
1 -1.66 -
3.969 -3.415 -3.130 0.767
3
LNFRXCRAT
E 3.000 -3.438 -2.865 -2.568 1.000 -0.201 -
3.969 -3.415 -3.130 0.993
6.2. Unit Root Test at First Difference (Augmented Dickey - Fuller Test)
Table 2 Unit Root Test at First Difference
Variables
First Difference
No Trend With Trend
t -
statistic Critical Values
p
valu
e
t-
statisti
c
Critical Values
p
valu
e
1% 5% 10%
1% 5% 10%
LNEXRATE -
23.7980 -3.438 -2.865 -2.568 0.000 -23.861 -3.969 -3.415 -3.130 0.000
LNFRXRAT
E -10.893 -3.438 -2.865 -2.568 0.000 -11.500 -3.969 -3.415 -3.130 0.000
Dr. Pritpal Singh Bhullar and Manika Dhameja
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 92 editor@iaeme.com
The above statistics shows that series is not stationary in both the cases but it become stationary after
taking first difference. The p value for both the variables becomes lower than 0.05 that shows the
stationarity of series.
6.3. Johansen Juselius (J-J) Cointegration Test
Johansen and Juselius Cointegration test (1990) has been performed to analyze the long run relationship
between variables
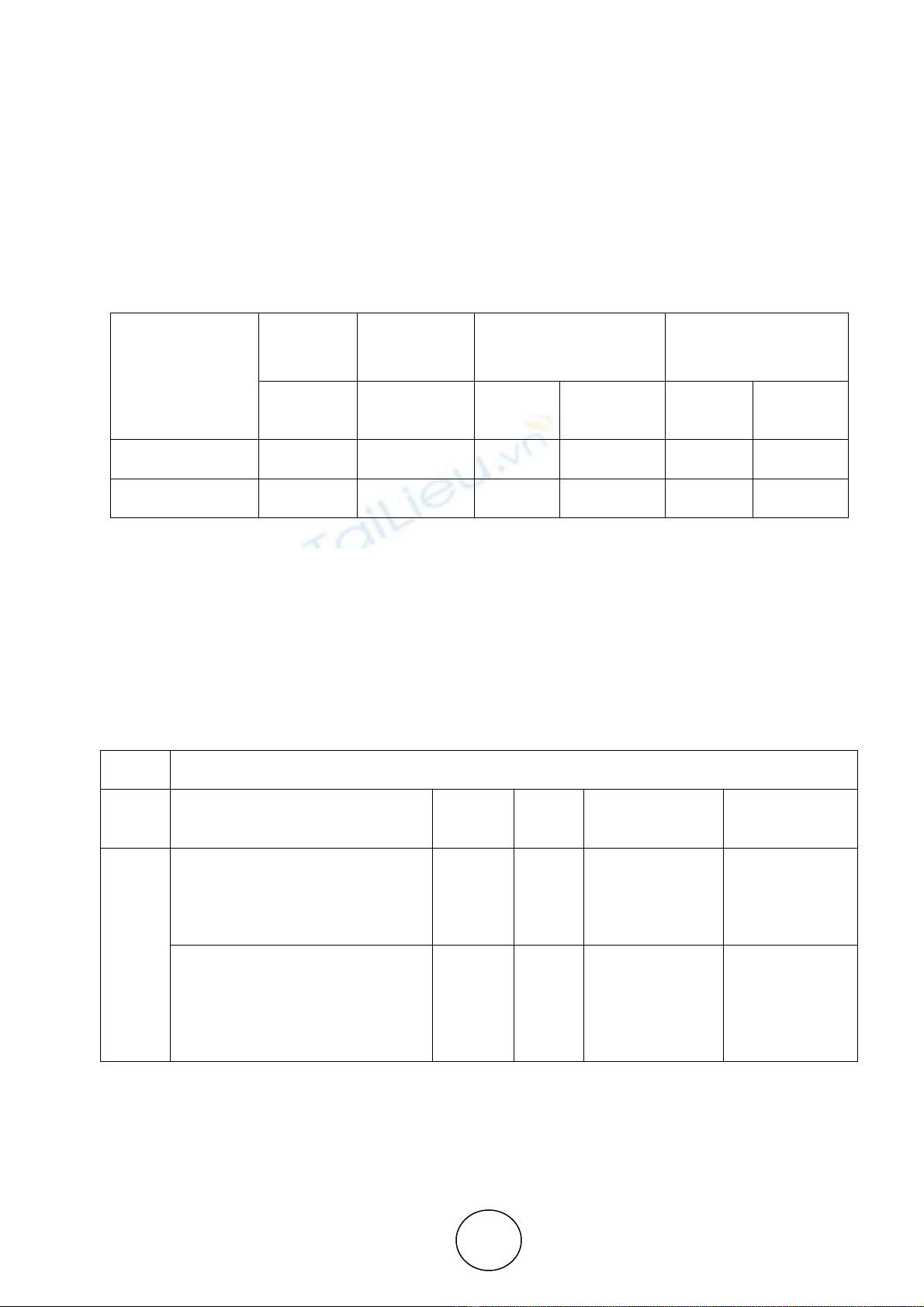
Table 3 J-J Cointegration Test
Hypothesized No.
of CEs
Trace Max-Eigen Critical Values (5% )
p - Values
Statistics Statistics Trace Max-Eigen Trace Max -
Eigen
r = 0 13.30554 11.79033 15.49471 14.26460 0.1041 0.1188
r ≤ 1 1.515210 1.515210 3.841466 3.841466 0.2183 0.2183
The above Trace test statistics and Max – Eigen statistics shows that no Cointegration exists between
the variables as the p values in both the cases is higher than 0.05. Higher the p – values more than its
significant vale (5%) leads to rejection of null hypothesis at this level. The non - existence of Cointegration
supports the existence of long run equilibrium in both the variables.
6.4. Pairwise Granger - Casuality Test
The Granger Causality test indicates a causality run from foreign exchange reserve to exchange rate
Table 4 Granger Causality Test
Null Hypothesis: A variable does not Granger cause the other
S. No Null Hypothesis F-
statistics
p -
value
p value &
Significant level Decision
1
LNEXRATE does not Granger
Cause LNFOREXCRESERVE 3.80371 0.0227
0.022 < 0.05
Reject Null
Hypothesis.
LNFOREXCRESERVE does not
Granger Cause LNEXRATE
0.63018 0.5328 0.532 > 0.05 Can’t Reject
Null Hypothesis
The above statistical table depicts a causal relationship between Exchange rate and foreign exchange
reserve. The p values (0.02 < 0.05) show that Foreign Exchange Reserve cause changes in change in
Exchange Rate.
Empirical Analysis of Long Run Equilibrium between Exchange Rate and Foreign Exchange Reserve – An
Indian Perspective
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 93 editor@iaeme.com
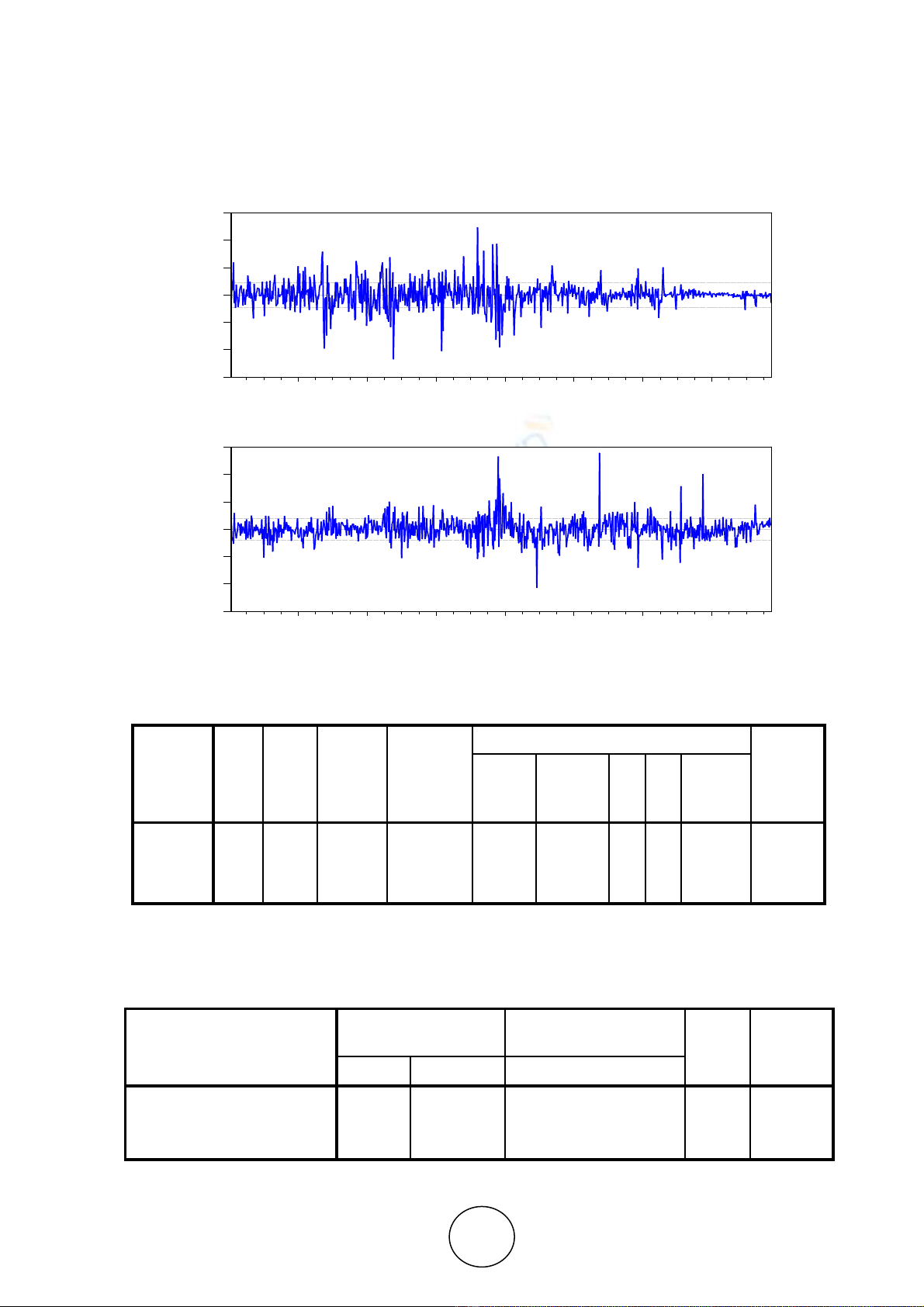
7. RESIDUAL GRAPH
The residual graphs show that no autocorrelation exists between residuals
8. REGRESSION ANALYSIS
Model Summary
b
Model
R
R
Square
Adjusted
R
Square
Std. Error
of the
Estimate
Change Statistics
Durbin-
Watson
R
Square
Change
F Change
df1
df2
Sig. F
Change
dimension0
1 .563
a
.453 .448
.12881 .448 111.253
1 784
.000 .005
a. Predictors: (Constant), LNFOREXCRESERVE
b. Dependent Variable: LNEXRATE
Coefficients
a
Model Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig. B Std. Error Beta
1 (Constant) 2.953 .089
33.010
.000
LNFOREXCRESERV
E
.078 .007 .353 10.548
.000
a. Dependent Variable: LNEXRATE
-.06
-.04
-.02
.00
.02
.04
.06
100 200 300 400 500 600 700
LNEXRATE Residuals
-.06
-.04
-.02
.00
.02
.04
.06
100 200 300 400 500 600 700
LNFOREXCRESERVE Residuals



















![Giáo trình Ngân hàng quốc tế 1: Phần 2 [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260305/hoatulip2026/135x160/74011773045693.jpg)
![Giáo trình Ngân hàng quốc tế 1: Phần 1 [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260305/hoatulip2026/135x160/86951773045694.jpg)





