
Overview of Key Establishment
Overview of Key Establishment
Techniques:
Techniques:
Key Distribution, Key Agreement and PKI
Key Distribution, Key Agreement and PKI
Wade Trappe
Lecture Overview
Lecture Overview
We now begin our look at building protocols using the basic tools
that we have discussed.
The discussion in this lecture will focus on issues of key
establishment and the associated notion of authentication
These protocols are not real, but instead are meant to serve just as
a high-level survey
Later lectures will go into specific protocols and will uncover
practical challenges faced when implementing these protocols
Key Establishment: The problem
Key Establishment: The problem
Securing communication requires that the data is encrypted
before being transmitted.
Associated with encryption and decryption are keys that must be
shared by the participants.
The problem of securing the data then becomes the problem of
securing the establishment of keys.
Task: If the participants do not physically meet, then how do the
participants establish a shared key?
Two types of key establishment:
–Key Agreement
–Key Distribution
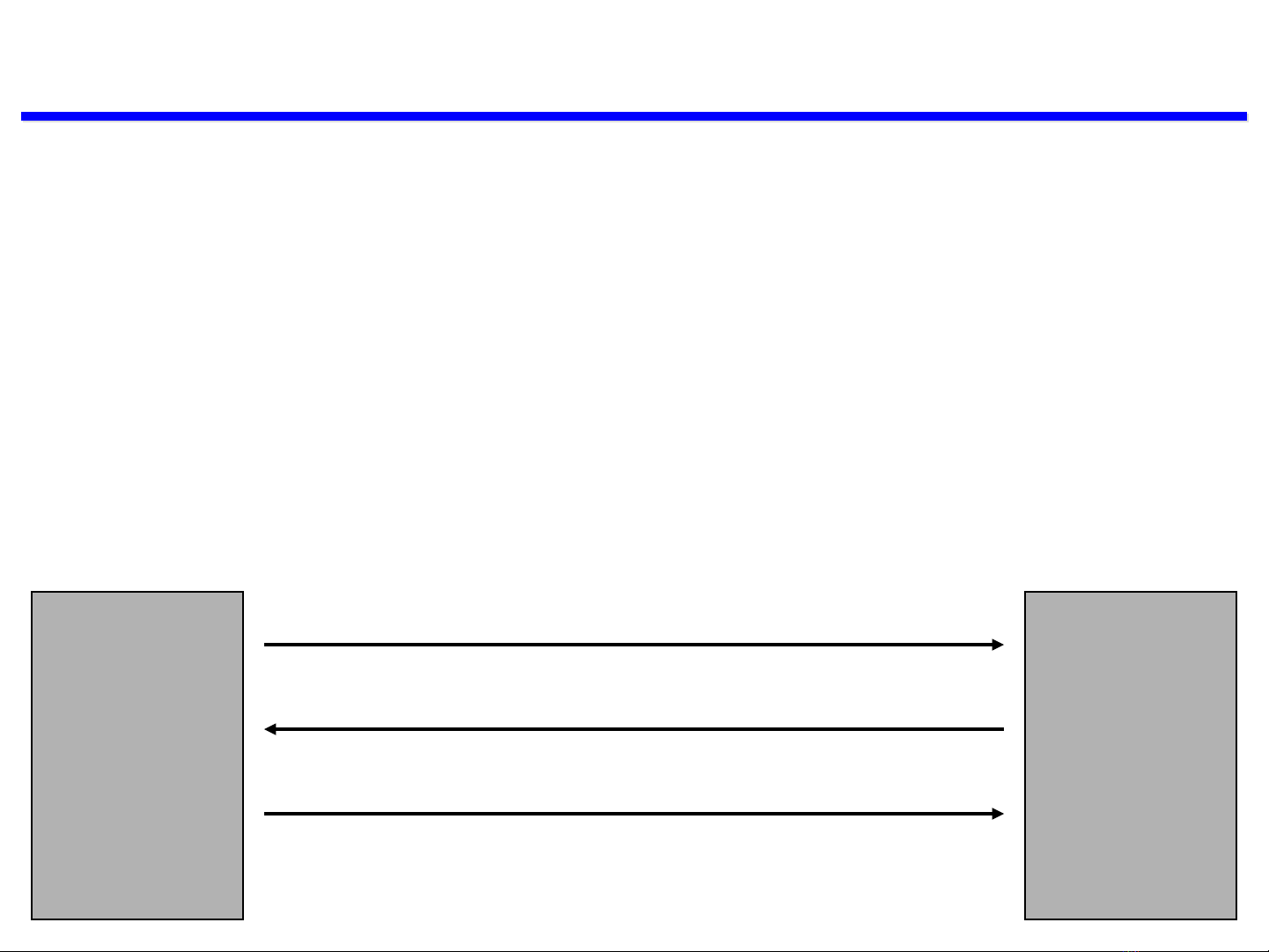
Key Distribution
Key Distribution
Key Agreement protocols: the key isn’t determined until after the
protocol is performed.
Key Distribution protocols: one party generates the key and
distributes it to Bob and/or Alice (Shamir’s 3pass, Kerberos).
Shamir’s Three-Pass Protocol:
–Alice generates and Bob generates .
–A key K is distributed by:
Alice Bob
pmodKK a
1=
pmodKK b
1
2=
( )
pmodKK 1
a
23
−
=
( )
pmodKK 1
b
3
−
=
Bob Calculates:
*
p
Za
∈
*
p
Zb
∈
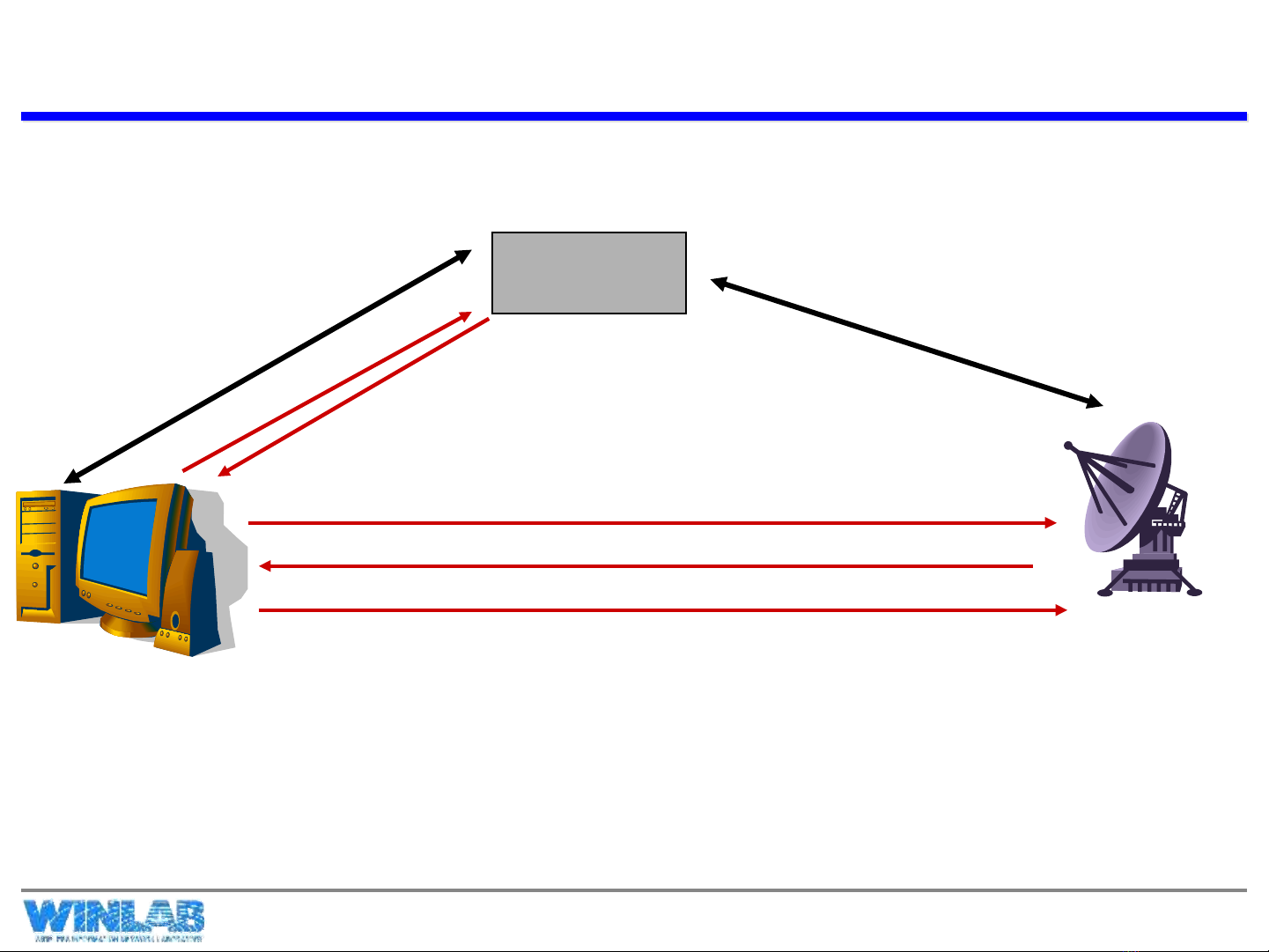
Basic TTP Key Distribution
Basic TTP Key Distribution
KDC
Ka
Kb
Step 1
Step 2
1. A Sends: {Request || IDA || IDB || N1}
2. KDC Sends: EKa[ KAB|| {Request || IDA || IDB || N1}||EKb(KAB, IDA)]
Step 3
Step 4
3. A Sends: EKb(KAB, IDA)
Step 5
4. B Sends: EKAB(N2) 5. A Sends: EKAB(f(N2))



![Chữ ký điện tử: Các loại và ứng dụng [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2013/20130601/dungtd_tq/135x160/5471370225804.jpg)
![Chữ ký số: Chương 6 [Hướng dẫn chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2013/20130523/sakuraphuong/135x160/791369296741.jpg)




















![Sổ tay Kỹ năng nhận diện & phòng chống lừa đảo trực tuyến [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251017/kimphuong1001/135x160/8271760665726.jpg)
