
Atomic Physics
Pham Tan Thi, Ph.D.!
Department of Biomedical Engineering!
Faculty of Applied Sciences!
Ho Chi Minh University of Technology
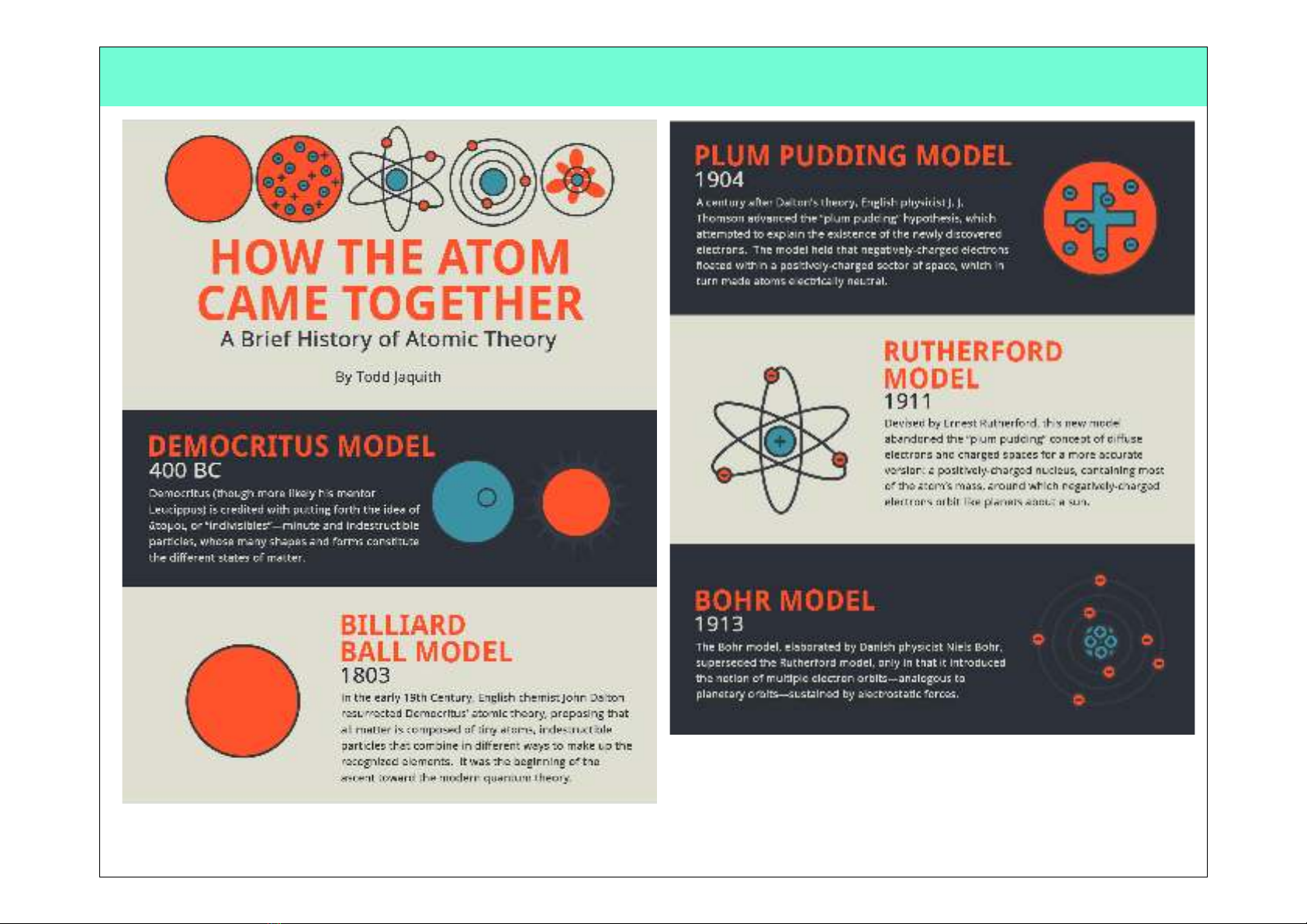
History of Atomic Model
History of Atomic Model
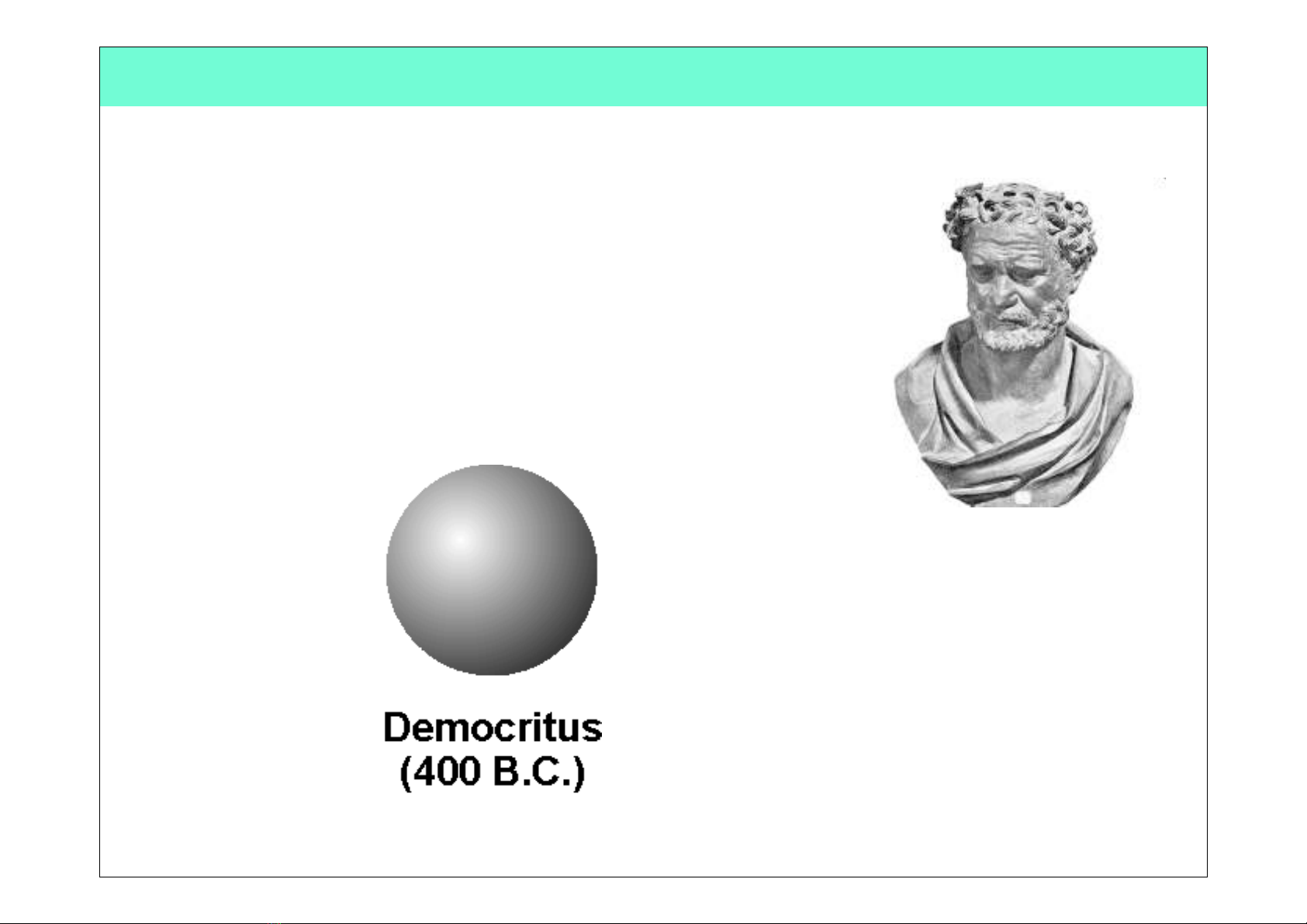
Democritus
(460 BC - 370 BC)
•Proposed an Atomic Theory which states that
all atoms are small, hard, indivisible and
indestructible particles made of a single
material formed into different shapes and
sizes.!
•Aristotle did not support his atomic theory.
History of Atomic Model
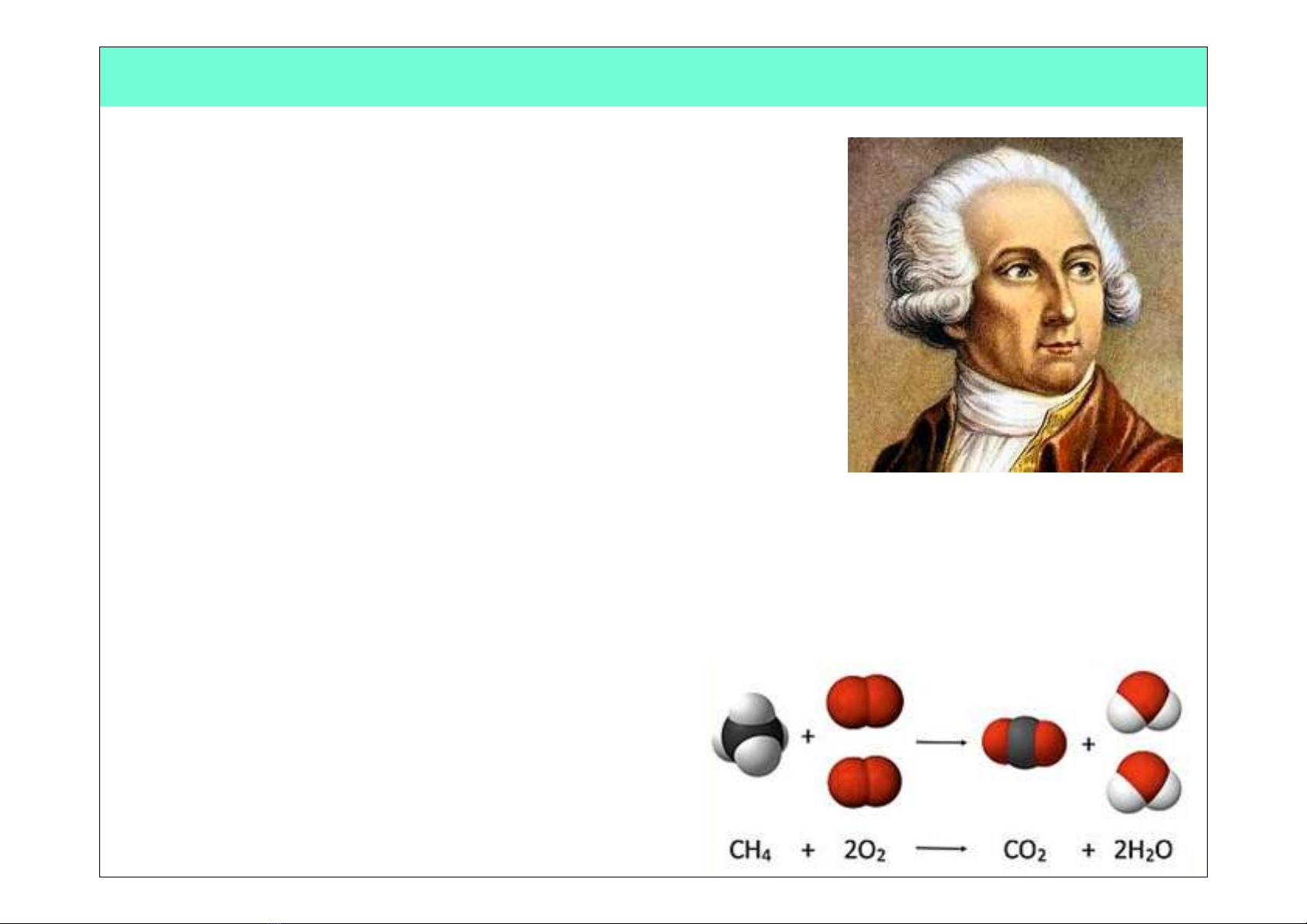
Antoine Lavoisier
(1743 - 1794)
•Known as the “Father of Modern Chemistry”!
•Was the first person to generate a list of 23
elements in his textbook!
•Devised the metric systems!
•Was married to a 13-year-old Marie-Anne
Pierette Paulze, who assisted him much of his
work!
•Discovered/proposed that combustion occurs
when oxygen combines with other elements!
•Discovered/proposed the Law of
Conservation of Mass (or Matter) which states
that, in a chemical reaction, matter is neither
created or destroyed
History of Atomic Model
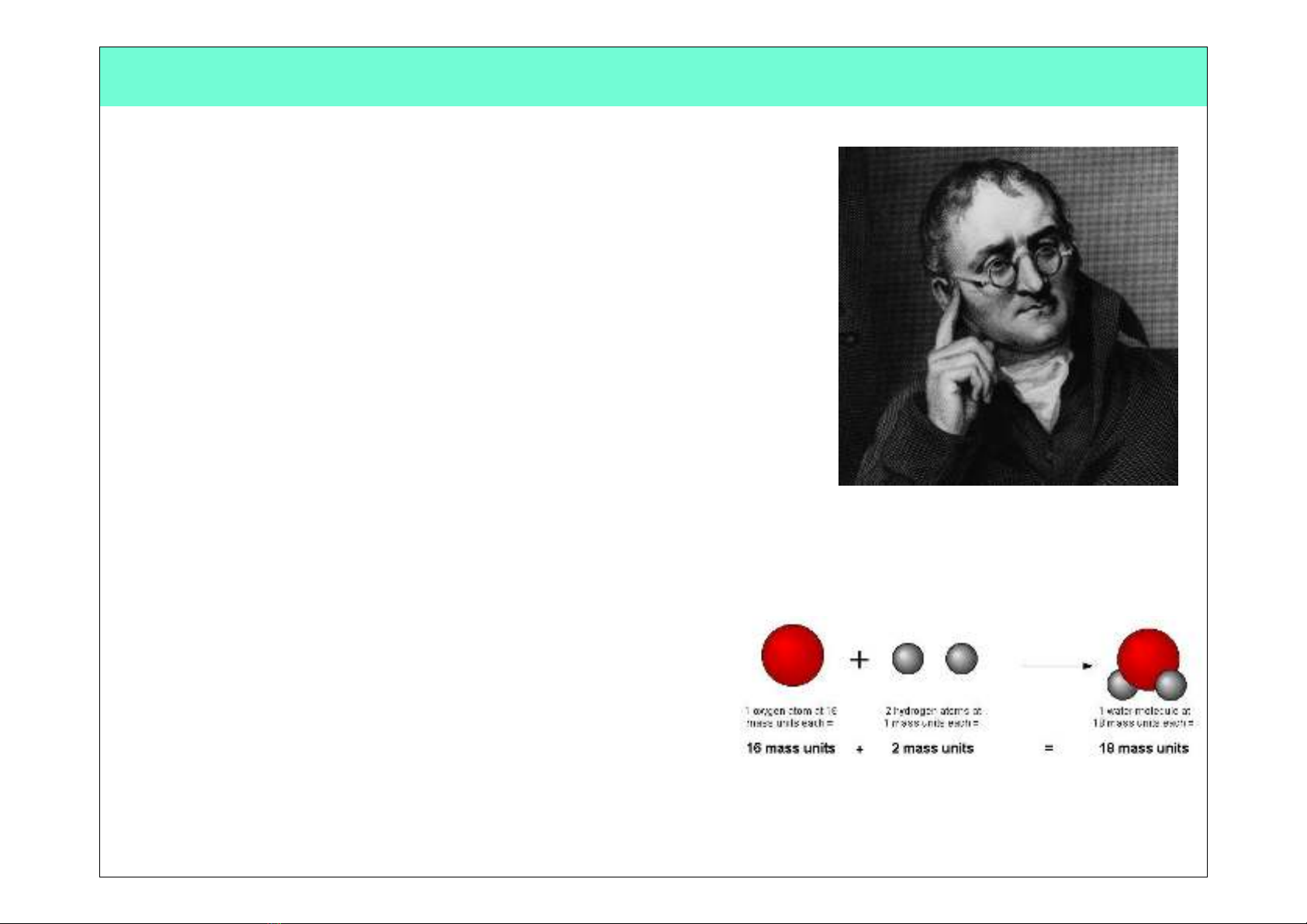
John Dalton
(1766 - 1844)
•In 1803, he proposed an Atomic Theory which
states that:!
•All substances are made of atoms; atoms
are small particles that cannot be created,
divided or destroyed.!
•Atoms of the same element are exactly
alike, and atoms of different elements are
different!
•Atoms join with other atoms to make new
substances!
•He calculated the atomic weights of many
various elements!
•He was a teacher at a very young age!
•He was color blind

![Bài giảng Vật lý đại cương và sinh lý [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250804/vijiraiya/135x160/88621754292979.jpg)


















![Bộ câu hỏi lý thuyết Vật lý đại cương 2 [chuẩn nhất/mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251003/kimphuong1001/135x160/74511759476041.jpg)
![Bài giảng Vật lý đại cương Chương 4 Học viện Kỹ thuật mật mã [Chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250925/kimphuong1001/135x160/46461758790667.jpg)




