PEPTIC
ULCER
DISEASE
Peptic ulcer diseas-Tran Ngoc Anh MD
Objectives
PEPTIC
ULCER
DISEASE
1.Recognize the typical clinical
presentation and risk factor for
PUD
2.Understand pathophysiology of
PUD focusing on HP
3.Describe an appropriate
diagnostic plan
4.Prescribe an appropriate
therapeutic regime
Peptic ulcer diseas-Tran Ngoc Anh MD
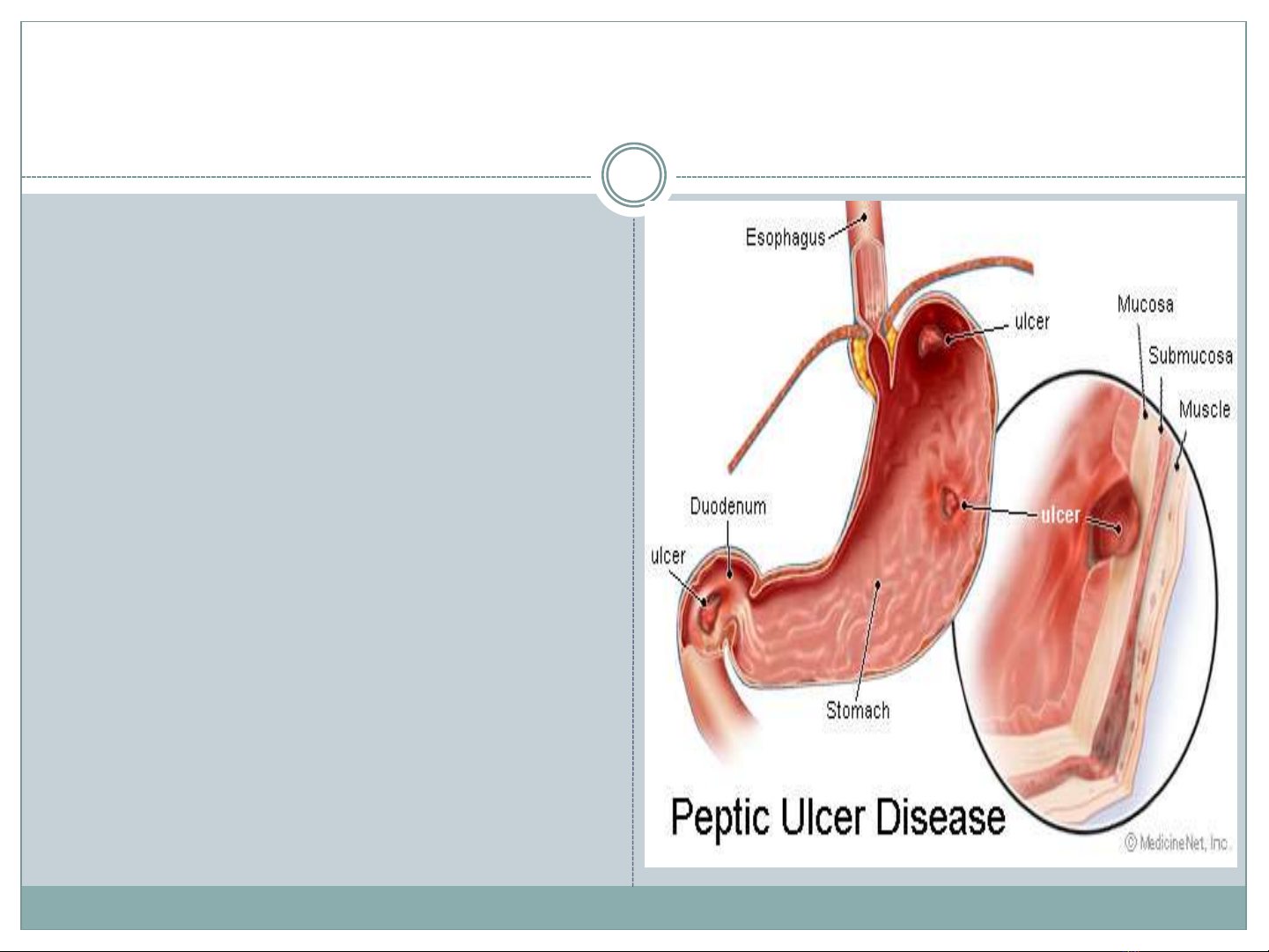
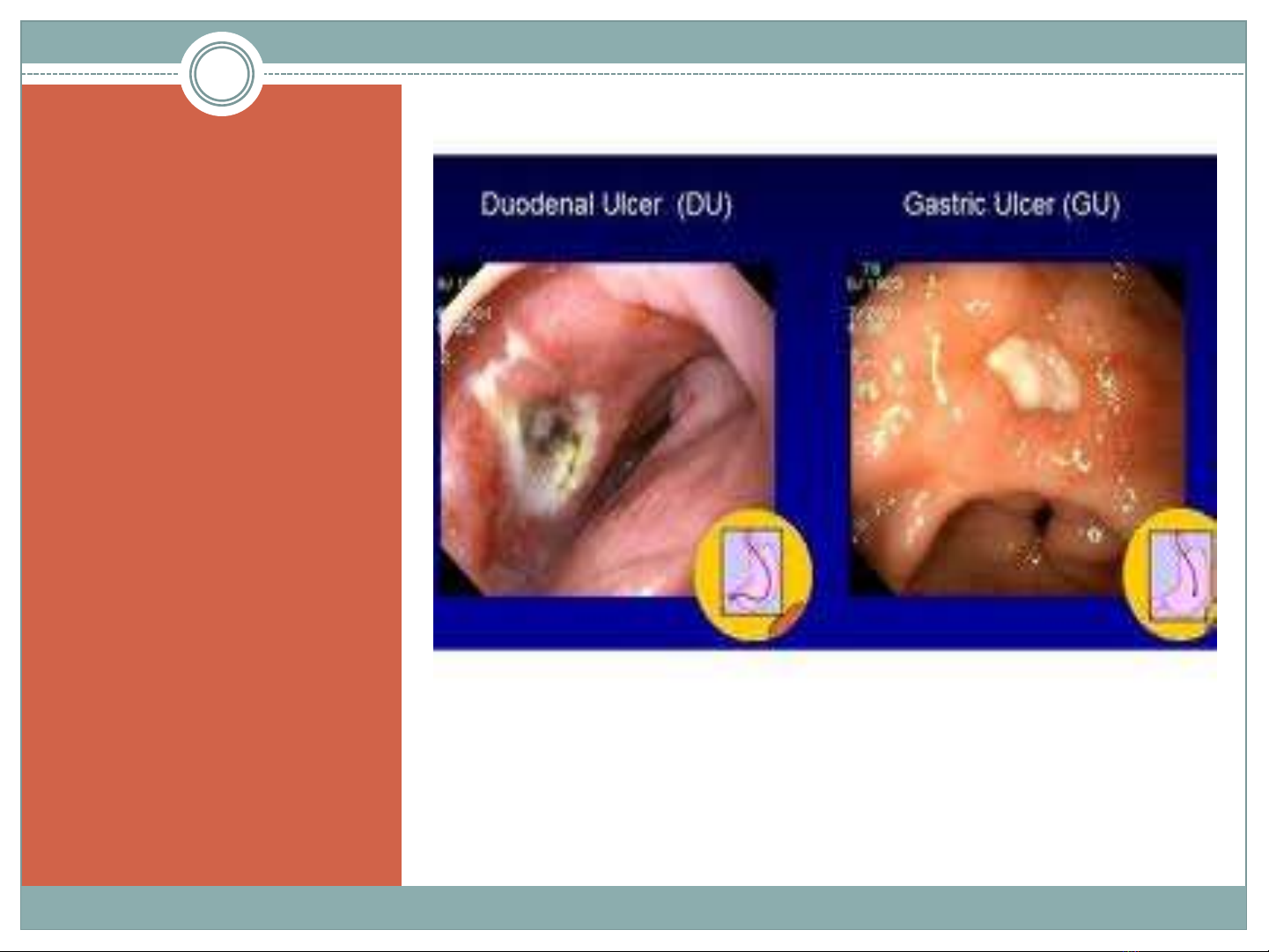
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
An ulcer: disruption of
the mucosal integrity
of the stomach and/or
duodenum (surface
>5mm in size, depth to
the submucosa)
Occur: Stomach
and/or duodenum
Chronic
Peptic ulcer diseas-Tran Ngoc Anh MD
ETIOLOGY and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Common
•Helicobacter
pylori
infection
•NAIS
•Stress-
related
mucosal
damage
Uncommon
•Zollinger
Ellison
•Tumors
(Cancer,
lymphoma)
•Viral infections
•Radiation/che
motherapy
•Vascular
insufficiency
Rare
•Crohn’s
disease
•Helicobacter
helimannil
•Idiopathic
Peptic ulcer diseas-Tran Ngoc Anh MD
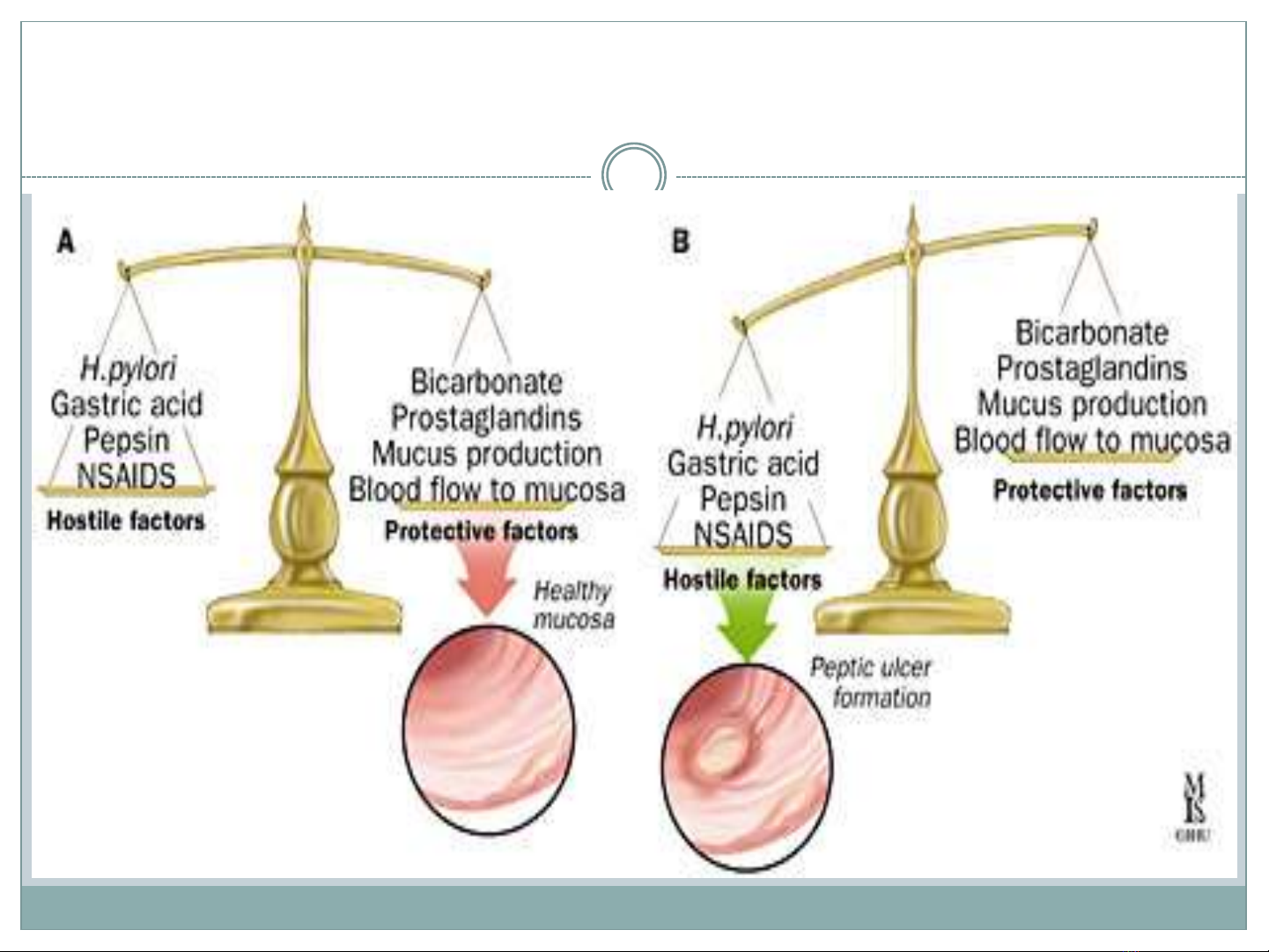
ETIOLOGY and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY













![Giáo trình Vi sinh - Ký sinh trùng [Tốt Nhất/Mới Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260124/lionelmessi01/135x160/53431769265754.jpg)












