Journal of Water Resources & Environmental Engineering - No. 87 (12/2023)
9
Mechanical-microstructural characteristics
of concrete containing high volumes of coal bottom ash
Nguyen Van Dung
1*
, Mai Thi Hong
1
, Nguyen Thi Thanh
1
, Nguyen Vu Linh
1
Abstract: This paper aims
to study the effect of coal bottom ash (CBA) as a fine aggregate substitution
at high levels on the mechanical properties and microstructure characteristics of concrete. CBA that
sourced from a local coal-fired power plant in Vietnam was used to replace t
he natural sand (NS) in the
concrete mixtures at different levels of 0, 30, 50, 70, and 100%. The concrete samples were prepared in
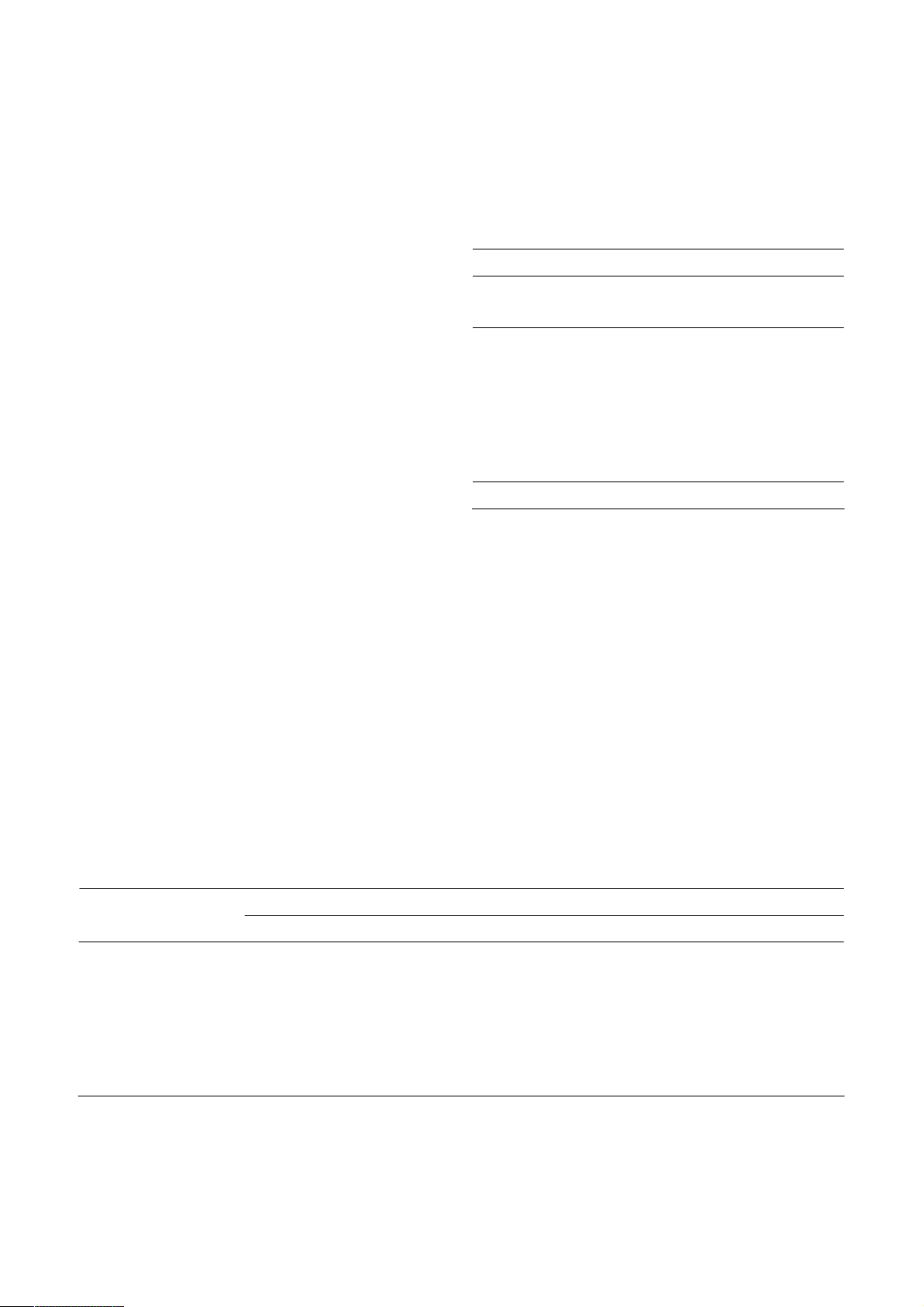
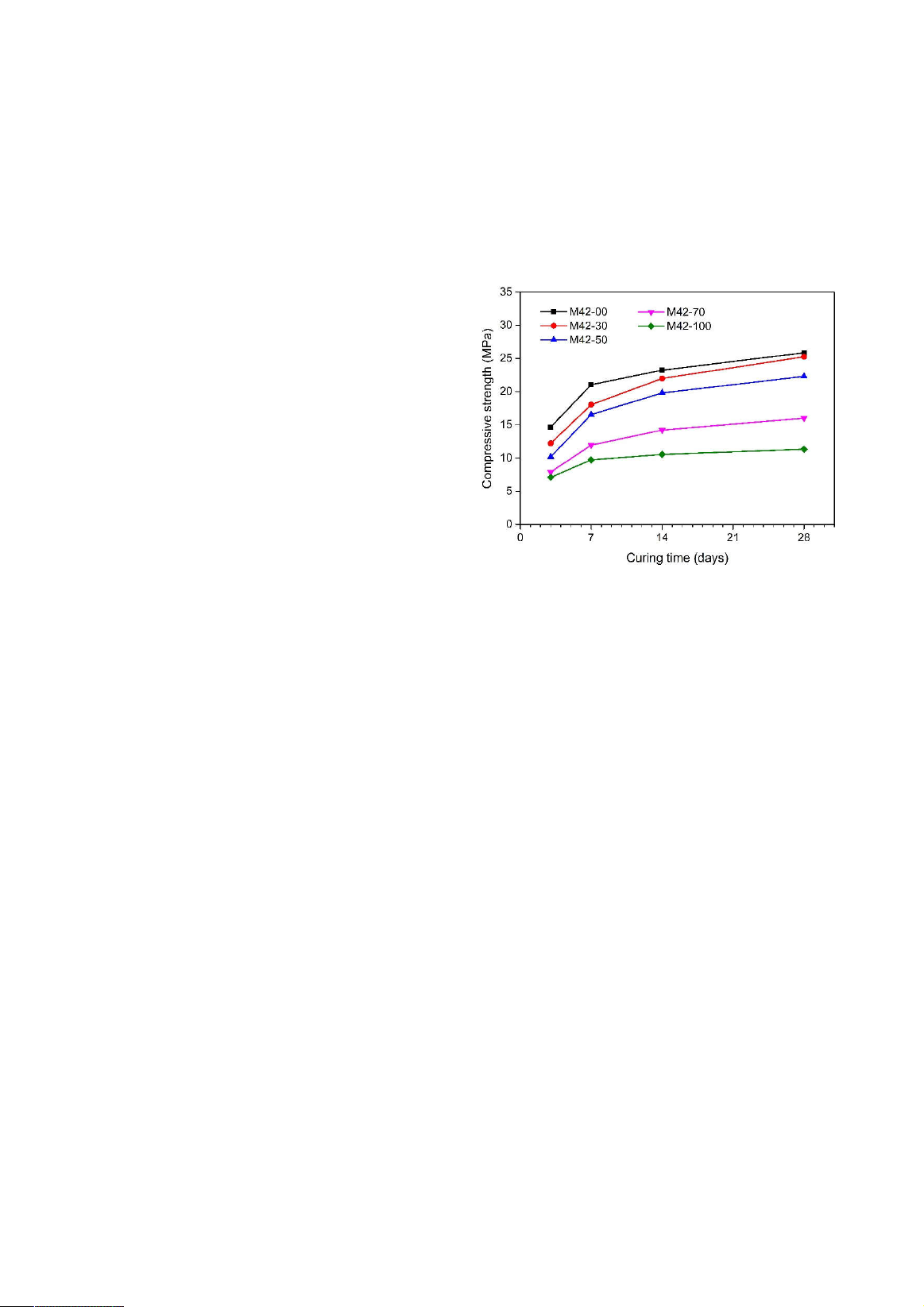
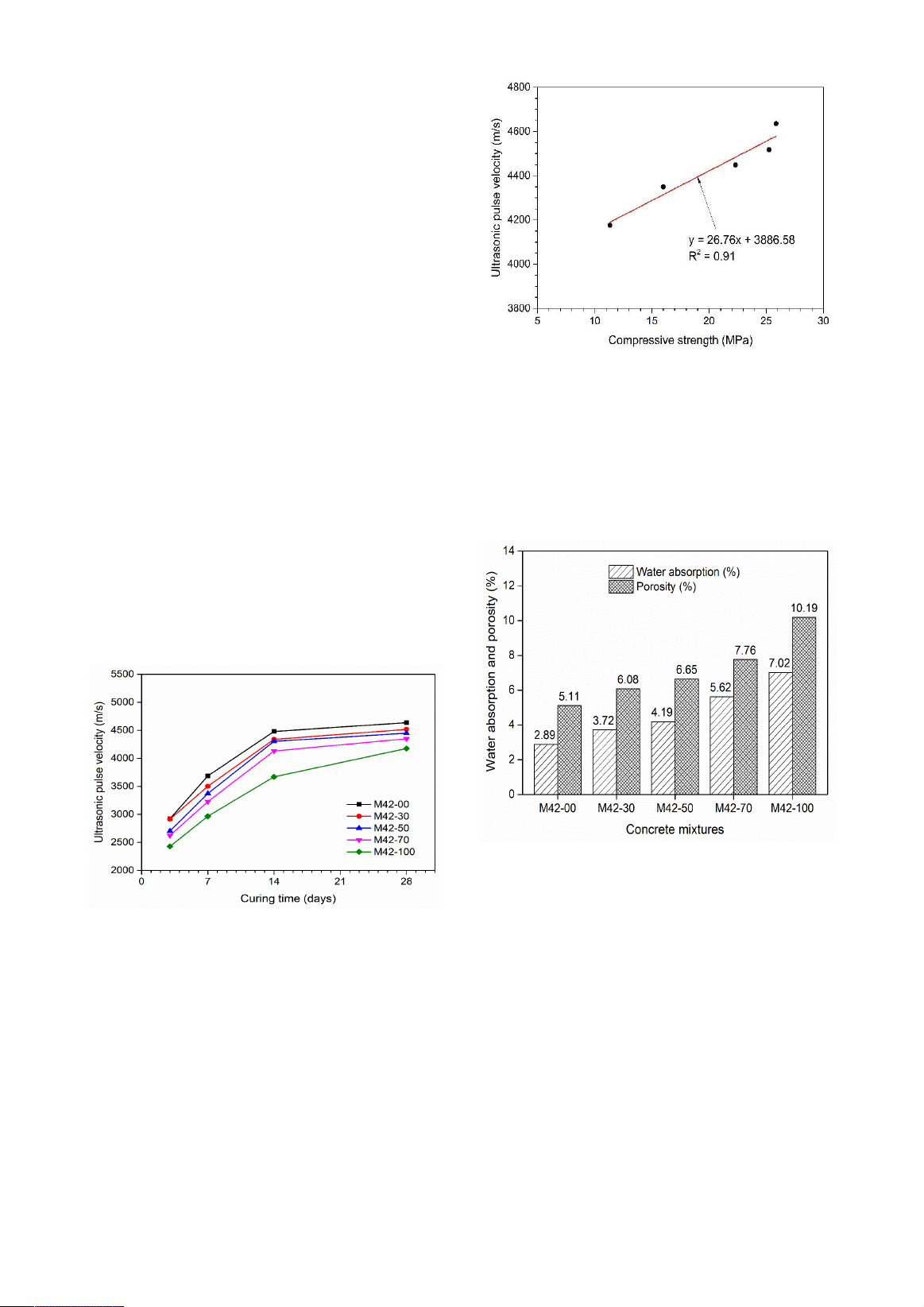
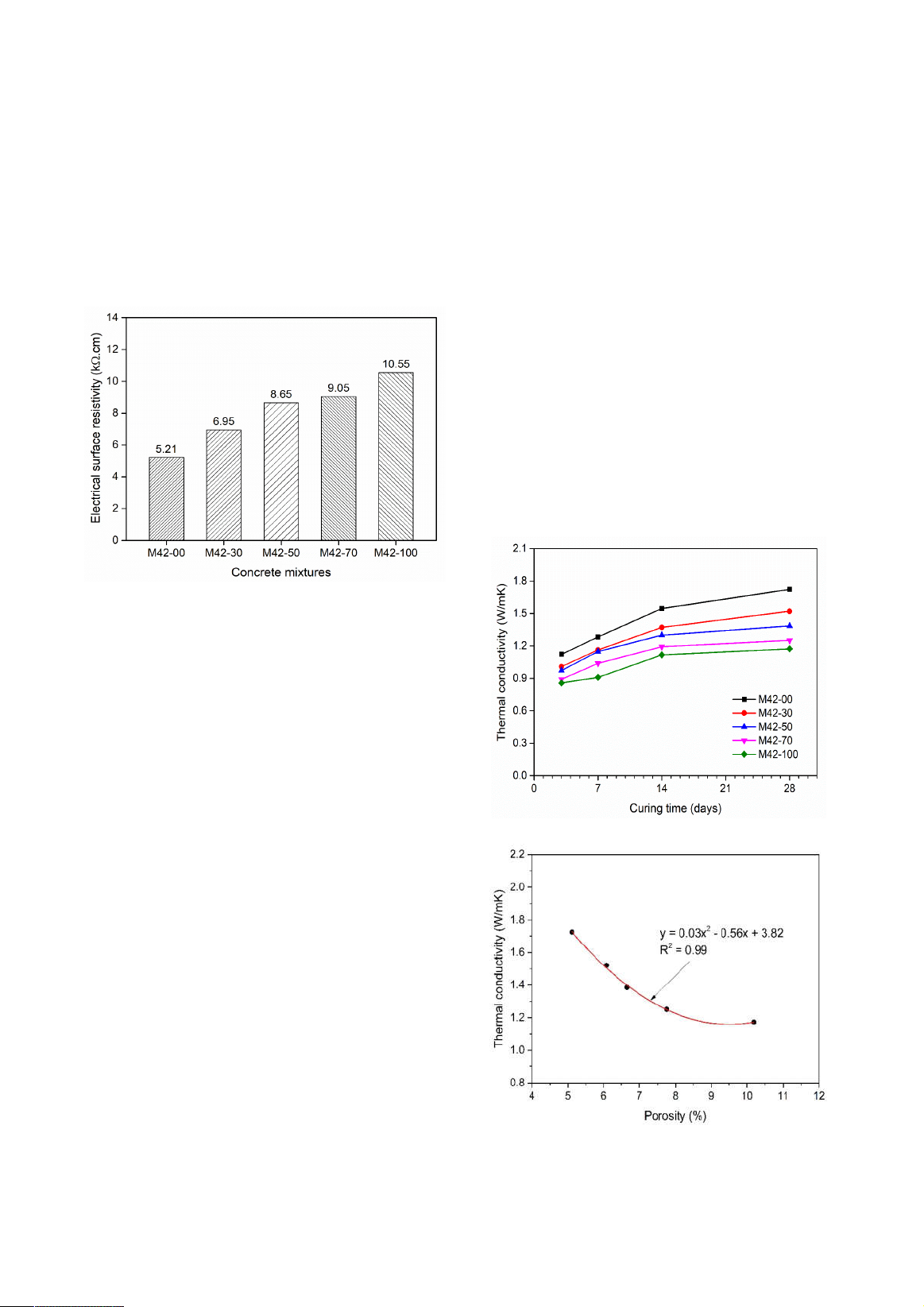
the laboratory and checked for properties through the tests of compressive strength (CS), ultrasonic
pulse velocity (UPV), w
ater absorption (WA), porosity, electrical surface resistivity (ESR), and thermal
conductivity (TC). Notably, the scanning electron microscope was also used to characterize the
microstructure of the hardened concrete. Test results show that the replacement
of NS by CBA affected
the concrete’s properties significantly. However, all of the concrete samples were classified as good
quality with the UPV, CS, WA, porosity, ESR, and TC values fell within the ranges of 4176 –
4636 m/s,
11.3 – 25.9 MPa, 2.89 – 7.02%, 5.11 – 10.19%, 5.21 – 10.55 kΩ.cm, and 1.17 –
1.72 W/mK,
respectively. Therefore, the proper quantity of CBA will be suggested depending on the requirement for
the quality of the concrete for a specific application.
Keywords: Concrete, coal bottom ash, mechanical property, durability, microstructure.
1. Introduction
*
Recently, the rapid development of the
construction industry requires a large quantity of
concrete, which is a well-known and major
construction material so far. In which, natural
aggregate such as river sand or crushed sand is one
of the main components that occupy a large
proportion of the concrete mixture. Hence, the
consumption of a large quantity of concrete requires
a considerable amount of NS every year, leading to
the depletion of this type of natural aggregate as
announcing by the local Government in Vietnam. In
addition, the over-exploitation of NS has also been
caused by many environmental issues, e.g., water
pollution, erosion, and landside, etc.
Besides, the rapid development of other
industrial activities generates a large number of
1
Hong Duc University
* Corresponding author; Email: nguyenvandung@hdu.edu.vn
Received 20
th
Jun. 2023
Accepted 28
th
Aug. 2023
Available online 31
st
Dec. 2023
different types of solid waste. In which, CBA is
one of the solid wastes that generated with a
considerable quantity by the coal-fired power
plants. In Vietnam, the Government statistic
points out that about 15 million tons of CBA are
generated in 2020. The CBA quantity will be
jumped to about 17 and 21 million tons in 2025
and 2030, respectively. It is important to remark
that the generation of such a large quantity of
CBA will cause serious pollution to the
environment if there are no sufficient treatment
methods. Thus, one of the possible ways to treat
the CBA is by turning it into construction
materials. By the way, more CBA is consumed
sufficiently.
Therefore, this paper is conducted with the
purpose of using CBA sourced from a local coal-
fired power plant in Vietnam as fine aggregate to
partially and fully replace NS in the production of
concrete. The potential of utilization and
application of CBA in concrete is evaluated
through the study of the effect of CBA on both the