
Newton (unit)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The newton (symbol: N) is the SI derived unit of force, named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his
work on classical mechanics.
Contents
1 Definition■2 Examples■3 Common use of kilonewtons in construction■4 Conversion factors■5 See also■6 References■
Definition
The newton is the unit of force derived in the SI system; it is equal to the amount of force required to
accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one metre per second per second. Algebraically:
[1]
Examples
1 N is the force of Earth's gravity on an object with a mass of about 102 g (1⁄9.8 kg) (such as a
small apple).
■
On Earth's surface, a mass of 1 kg exerts a force of approximately 9.80665 N [down] (or 1 kgf).
The approximation of 1 kg corresponding to 10 N is sometimes used as a rule of thumb in
everyday life and in engineering.
■
The force of Earth's gravity on a human being with a mass of 70 kg is approximately 687 N.■The dot product of force and distance is mechanical work. Thus, in SI units, a force of 1 N exerted
over a distance of 1 m is 1 N·m of work. The Work-Energy Theorem states that the work done on
a body is equal to the change in energy of the body. 1 N·m = 1 J (joule), the SI unit of energy.
■
It is common to see forces expressed in kilonewtons or kN, where 1 kN = 1 000 N.■
Common use of kilonewtons in construction
Kilonewtons are often used for stating safety holding values of fasteners, anchors and more in the
building industry.[2] They are also often used in the specifications for rock climbing equipment. The safe
working loads in both tension and shear measurements can be stated in kN (kilonewtons).
Page
1
of
3
Newton (unit)
-
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
10/3/2009
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton_(unit)
1 kN equals 101.97162 kilograms of load, but multiplying the kN value by 100 is a good rule of thumb.
[3]
Conversion factors
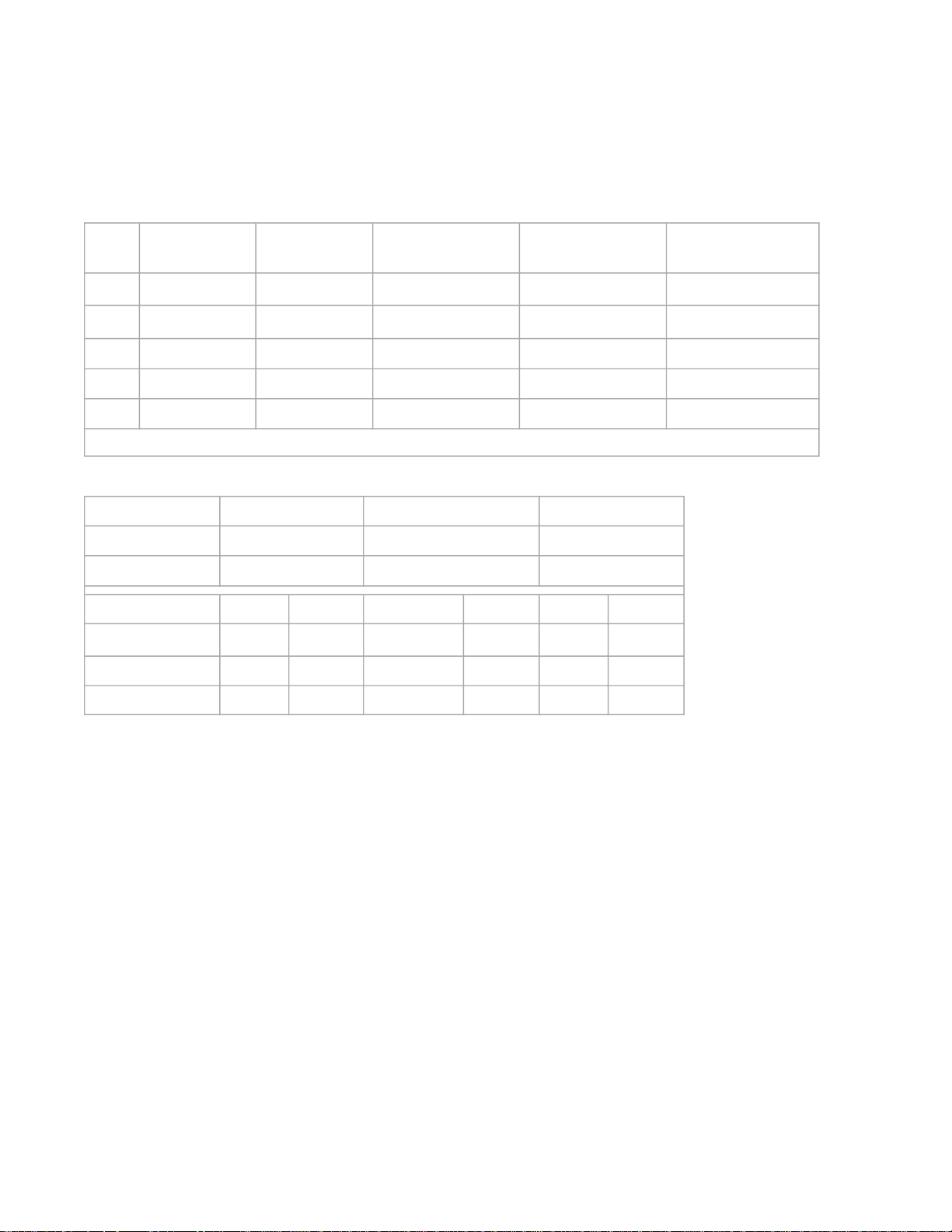
newton
(SI unit) dyne kilogram-force,
kilopond pound-force poundal
1 N ≡ 1 kg·m/s² = 105 dyn ≈ 0.10197 kp ≈ 0.22481 lbf≈ 7.2330 pdl
1 dyn = 10−5 N ≡ 1 g·cm/s² ≈ 1.0197×10−6 kp ≈ 2.2481×10−6 lbf≈ 7.2330×10−5 pdl
1 kp = 9.80665 N = 980665 dyn ≡ gn·(1 kg) ≈ 2.2046 lbf≈ 70.932 pdl
1 lbf≈ 4.448222 N ≈ 444822 dyn ≈ 0.45359 kp ≡ gn·(1 lb) ≈ 32.174 pdl
1 pdl ≈ 0.138255 N ≈ 13825 dyn ≈ 0.014098 kp ≈ 0.031081 lbf≡ 1 lb·ft/s²
The value of
g
n
as used in the
official definition of the kilogram
-
force is used here for all
gravitational units.
Units of
force
System Gravitational Engineering Absolute
Force (F)F = m·a F = m·a/gc = w·a/g F = m·a
Weight (w)w = m·g w = m·g/gc ≈ m w = m·g
Units English Metric English Metric English Metric
Acceleration
(
a
)
ft/s
2
m/s
2
ft/s
2
m/s
2
ft/s
2
m/s
2
Mass
(
m
)
slug
hyl
pound
-
mass
kilogram
pound
kilogram
Force
(
F
)
pound
kilopond
pound
-
force
kilopond
poundal
newton
Three approaches to mass and force
units
See also
Force gauge
■
International System of Units
(SI)
■
Joule
, SI unit of
energy
, 1 newton exerted over a distance
of 1 metre
■
Kilogram
-
force
, force exerted by Earth's
gravity at sea level on one kilogram of mass
■
Pascal
, SI unit of
pressure
, 1 newton acting on an area of 1
square
metre
■
References
^
"
Table 3. Coherent derived units in the SI with special names and
symbols
(http://www.bipm.org/en/si/si_brochure/chapter2/2-2/table3.html) ". The International System of Units (SI).
International Bureau of Weights and Measures. 2006. http://www.bipm.org/en/si/si_brochure/chapter2/2-
2/table3.html
.
1
.
^
http://www.shakshienterprises.com/steel
-
fasteners.html#application1
2
.
^
http://www.convertunits.com/from/kilonewtons/to/kilograms
-
force
3
.
Retrieved from "
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton_(unit)
"
Categories
:
Units of force
Page
2
of
3
Newton (unit)
-
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
10/3/2009
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton_(unit)

This page was last modified on 22 September 2009 at 19:50.■Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms
may apply. See Terms of Use for details.
Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit
organization.
■
Page
3
of
3
Newton (unit)
-
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
10/3/2009
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton_(unit)




















![Bộ câu hỏi lý thuyết Vật lý đại cương 2 [chuẩn nhất/mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251003/kimphuong1001/135x160/74511759476041.jpg)
![Bài giảng Vật lý đại cương Chương 4 Học viện Kỹ thuật mật mã [Chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250925/kimphuong1001/135x160/46461758790667.jpg)




