http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 94 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 10, Issue 1, January-February 2019, pp. 94-103, Article ID: IJM_10_01_013
Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=10&IType=1
Journal Impact Factor (2019): 9.6780 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF PROJECT RISK,
MARKET RISK AND FIRM RISK
Dr. Giriraj Kiradoo
Associate Professor in MBA,
Government Engineering College Bikaner, Bikaner Area, India
ABSTRACT
This work aimed to study and analysis the various risk associated with different
environment. The selected method consists of market risks and operating risks. The
approach used in this paper is proved to be practical and useful in the decision-making
process of capital budgeting and investment because each value corresponds to a
specific risk measures, so that a specific risk component can be managed to an
acceptable risk level.
Keywords: Project Risk, Market Risk and Firm Risk
Cite this Article: Dr. Giriraj Kiradoo, Study and Analysis of Project Risk, Market
Risk and Firm Risk, International Journal of Management, 10 (1), 2019, pp. 94-103.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=10&IType=1
1. INTRODUCTION
It is a well-established undeniable fact that each project involves risk. Moreover, it's a observe
to incorporate a brief outline of project risks within the project appraisal report. There are sure
projects that economic advantages are often quantified whereas, for others, such quantification
isn't doable. The firm risk stems from a technological modification in production method,
managerial unskillfulness, the availability of raw material, labor issues and changes in
consumer preferences. The financial risk considers the distinction between EBIT (Earnings
before Interest and Taxes) and EBT (Earnings before Tax) whereas business risk causes the
variations between revenue and EBIT. These are ways that and suggests that to scale back the
project risks.

Study and Analysis of Project Risk, Market Risk and Firm Risk
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 95 editor@iaeme.com
Table 1 EBT and EBIT
2. ANALYSIS OF PROJECT RISKS
It is the traditional observe to incorporate a brief outline of project risks in every appraisal
report. The aim of this chapter is to produce an outline of project risks so as to assist guarantee
uniformity and consistency in appraisal reports.
• Relates to comes that economic advantages may be quantified and
• Deals with comes that such quantification isn't potential.
2.1. Projects with quantified benefits
The economic internal rate of return (EIRR) is that the measure most frequently accustomed
indicates the economic viability of financed projects. Calculation of the EIRR needs a collection
of assumptions concerning the conditions faced by the project that within the judgment of the
appraisal mission ar presumably to prevail throughout its life. However, since bank-financed
projects ordinarily have an awfully long life, the conditions faced by the project could
amendment for a spread of reasons. Sensitivity analysis is, therefore, allotted to work out the
results of attainable changes within the values of key variables (costs, yields, and value of inputs
and outputs) on the project's EIRR
The number of risks facing a project may be massive, and it's neither attainable nor
fascinating to spot all attainable risks related to a project. The risks mentioned within the
appraisal report should basically be those that entail major economic consequences. These
should be known from the sensitivity analysis and represented in descendant order of
importance with reference to their impact on the EIRR
Dr. Giriraj Kiradoo
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 96 editor@iaeme.com
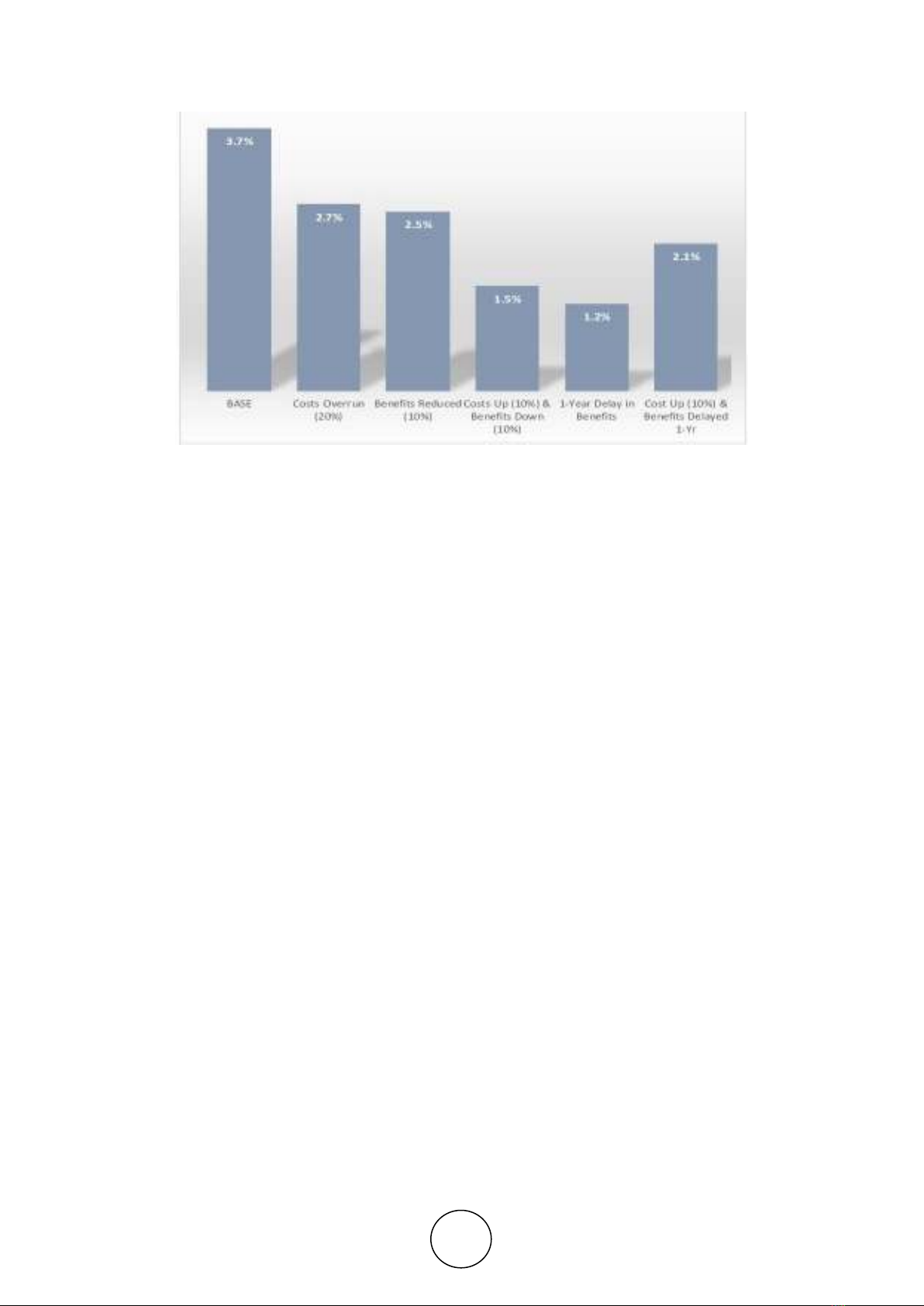
Figure 1 Economic internal rate of return (EIRR)
Particular attention should be paid to risks that might considerably cut back the project's
EIRR or render the project uneconomic by reducing its EIRR below the chance price of capital.
During this context, each of the base-case EIRR and also the sensitivity indicators are relevant.
If the base-case EIRR is high, the discussion of project risks should usually embrace risks to
that the project is extremely sensitive. For instance, the EIRR of most projects is extremely
sensitive to changes in project output, which can successively rely upon a variety of factors. A
discussion of the safeguards employed to reduce the risk of the outputs falling considerably
below the extent expected should thus be enclosed. For instance, in an irrigation project,
excluding the supply of water, the output could rely upon the availability of different inputs,
provision of extension services, and the effectiveness of water management by farmer's teams,
and accessibility of adequate infrastructure and storage facilities. Measures taken to confirm
adequate and timely accessibility of every should be in brief explained
Risks are clearly larger in projects that the base-case EIRR is simply marginally above the
chance cost of capital. These larger risks are even larger if the EIRR is extremely sensitive to
changes in key variables since even a little reduction within the EIRR would render the project
unviable. Even once the EIRR is comparatively insensitive to changes in key variables, combos
of adverse changes would possibly simply have an effect on the project's viability. Thus, in
such cases, the remedial action planned or adopted should be totally explained
If the project output is listed internationally, one risk could also be future changes within
the value of the output, notably if the share of a project or the country's output is little relative
to the global market. In such cases, a review of the world demands and provide forecasts for
the nice in question should be enclosed.
By their terribly nature, bound kinds of projects like gas and oil exploration involve terribly
high risks. For such projects, it's necessary to supplement the sensitivity analysis with a chance
analysis. The latter provides a spread of attainable outcomes in terms of a chance distribution
and supported that project connected call may be created a lot of showing intelligence.
However, the analysis is a lot of advanced and needs a lot of data concerning events touching
the project. thanks to the appreciable work due to, chance analysis of risks is typically
undertaken just for project carrying a high degree of risk or for giant comes wherever
miscalculations could lead on to a significant loss to the economy. For such comes, the nature
of the risks concerned and also the measures are taken or counselled to reduce the risks, at the
side of the results of the analyses, should be mentioned within the appraisal report.

Study and Analysis of Project Risk, Market Risk and Firm Risk
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 97 editor@iaeme.com
2.2. Projects for which benefits are not quantifiable
For projects in certain sectors or sub-sectors like education, health, sanitation, and family
planning, project benefits can't be quantified and also the risks can't be measured by sensitivity
analysis. In such cases, the connection of project risks to the project's objectives should be
explained. The eventualities that may impede the conclusion of the objectives should be
mentioned in relation to the project price and output, and also in relation to the socio-economic
objectives sought-after by the project
In such projects, the risks are larger on the profit facet than on the value facet. as an example,
in education projects, college buildings and instrumentation are provided to assist accomplish
a prescribed annual output of graduates with a certain talent level. However, the supply of the
facilities alone might not make sure the achievement of the project objectives. Their
achievement might rely additional upon the availability of trained lecturers, provision of spare
funds for the recurring expenditures of the institutions, syllabus and admission standards, and
motivation of the scholars.
While it's unattainable to eliminate all such risks, it's essential to attenuate them. Major risks
of this kind should be known and explained together with the remedial measures planned within
the section within which project risks are mentioned.
The real benefits of this kind of project associated with broad socio-economic goals. For
education projects, these might embrace raised financial gain levels for the trainees and the next
level of commercial and agriculturally production. For birth prevention comes, the broad goals
could also be a raised variety of acceptors and a consequent reduction within the rate of
increment. The success of those projects depends not just on the facilities provided, however
conjointly on the continuing favorable conditions assumed by the appraisal mission. For such
comes, the assumptions created concerning the connection between the facilities provided and
also the project's long objectives should be clearly explained. The conditions or facilities
necessary however external to the project should even be known, together with relevant
assurances received from the govt. For projects like these, this is often one among the foremost
necessary aspects to be mentioned within the section managing project risks.
3. MARKET RISK
The market risk affects all the projects within the trade and not a selected project. During this
section, the construct of market risk has been explained with relevancy factors that are beyond
the management of individual corporates. The market risk is more sub-divided into:
• Security market risk
• Interest rate risk
• Purchasing Power Risk
3.1. Security market risk
Often we have a tendency to read within the newspaper that the exchange is within the bear hug
or within the bull grip. This means that the complete market is taking possession in a specific
direction either downward or upward. The economic conditions, political things and also the
sociological changes have an effect on the security market. The recession within the economy
affects the profit prospect of the business and also the exchange. The 1998 recession
experienced by developed and developing countries has affected the stock markets everywhere
the globe. The Southeast Asian crisis has affected the exchange worldwide. Their factors are
on the far side of the control of the company and also the capitalist. Theycannot be entirely
avoided by the capitalist. It drives home the point that the market risk is inevitable.

Dr. Giriraj Kiradoo
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 98 editor@iaeme.com
Jack Clark Francis has outlined market risk as that portion of the entire variability of a return
caused by the alternating forces of bull and bear markets. Once the protection index moves
upward haltingly for a major period of your time, it's referred to as a bull market. Within the
bull market, the index moves from a low level to the height. A market is simply reverse to the
bull market; the index declines not fluently from the height to a market low point known as a
trough for a significant amount of your time. Throughout the bull and market, over eighty p.c
of the securities’ costs rise or fall together with the exchange indices.
The forces that have an effect on the exchange are tangible and intangible events. The
tangible events are real events like earthquakes, war, political uncertainty and fall within the
price of a currency. Another example that may be cited is that thePokhran blast on might
thirteen, 1998, and therefore the fall of BSESensex by 162 points. At hand sanctions, dampened
sentiments and FIIs mercantilism of stocks set a bear section. Many examples like fall within
the price of rupee and post-budget blue may be cited for triggering the bear section.
Intangible events are associated with market scientific discipline. The market scientific
discipline is littered with real events. However, reactions to tangible events become
overreactions and that they push the market in a specific direction. Consider instance, the Bull
Run in 1994 FII’s investment and relaxation policies gave buoyancy to the market. The market
scientific discipline was positive. Little investors entered the market and the costs of stocks
while not adequate validator basic factors soared up. In 1996, the political turmoil and recession
within the economy resulted in the fall of share costs and therefore the little investors lost faith
within the market. There was a rush to sell the shares and therefore the stocks that were floated
within the primary market weren't received well.
Thus, any untoward political or economic event would lead to a fall within the worth of the
security which might be further accentuated by the overreactions and therefore the herd-like
behavior of the investors. If some financial establishments begin disposing of the stocks, the
concern grips in and spread to different investors. This leads to a rush to sell the stocks. The
actions of the financial establishments would have a snowballing result. This sort of
overreaction affects the market adversely and therefore the costs of the scraps fall below their
intrinsic values. This can be on the far side the control of the company
3.2. Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk is that the variation within the single period rates of coming back caused by
the fluctuations in the market interest rate. Most typically interest rate risk affects the value of
bonds, debentures, and stocks. The fluctuations in the interest rates square measure caused by
the changes within the government financial policy and also the changes that occur in the
interest rates of treasury bills and also the government bonds. The bonds issued by the govt.
and quasi-government are thought-about to be risk-free. If higher interest rates are offered, the
capitalist would really like to change his investments from private sector bonds to public sector
bonds. If the govt. to serve the deficit in the budget floats a replacement loan/bond of a better
rate of interest, there would be a precise shift in the funds from low yielding bonds to high
yielding bonds and from stocks to bonds.
The rise of the fall in the interest rate affects the value of borrowing. Once the decision
when rating changes. Most of the stock traders trade the stock exchange with the borrowed
funds. the rise in the value of margin affects the profitableness of the traders. This could dampen
the spirit of the speculative traders who use the borrowed funds. The autumn in the demand for
securities would lead to a fall in the price of the stock index.
Interest rates not only have an effect on the security traders however additionally the
company bodies who carry their business with borrowed funds. The value of borrowing would
increase and an important outflow of profit would occur in the type of interest the capital


























