
8/24/2015
1
GEOPET
BÀI GIẢNG CHỈ DÀNH CHO SINH VIÊN THEO HỌC LỚP
ĐỊA CHẤT KIẾN TRÚC & ĐO VẼ BẢN ĐỒ ĐỊA CHẤT
TS. Nguyễn Huỳnh Thông
1
NỘI DUNG
Đá là gì? Phân loại Đá?
Biến dạng là gì? (Definition)
Lực và ứng suất? (Stress & Strain)
Các giai đoạn biến dạng? (Stage)
Các yếu tố ảnh hưởng biến dạng? (Factor)
Đặc tính biến dạng dẻo-đàn hồi của Thạch quyển?
2
8/24/2015
2
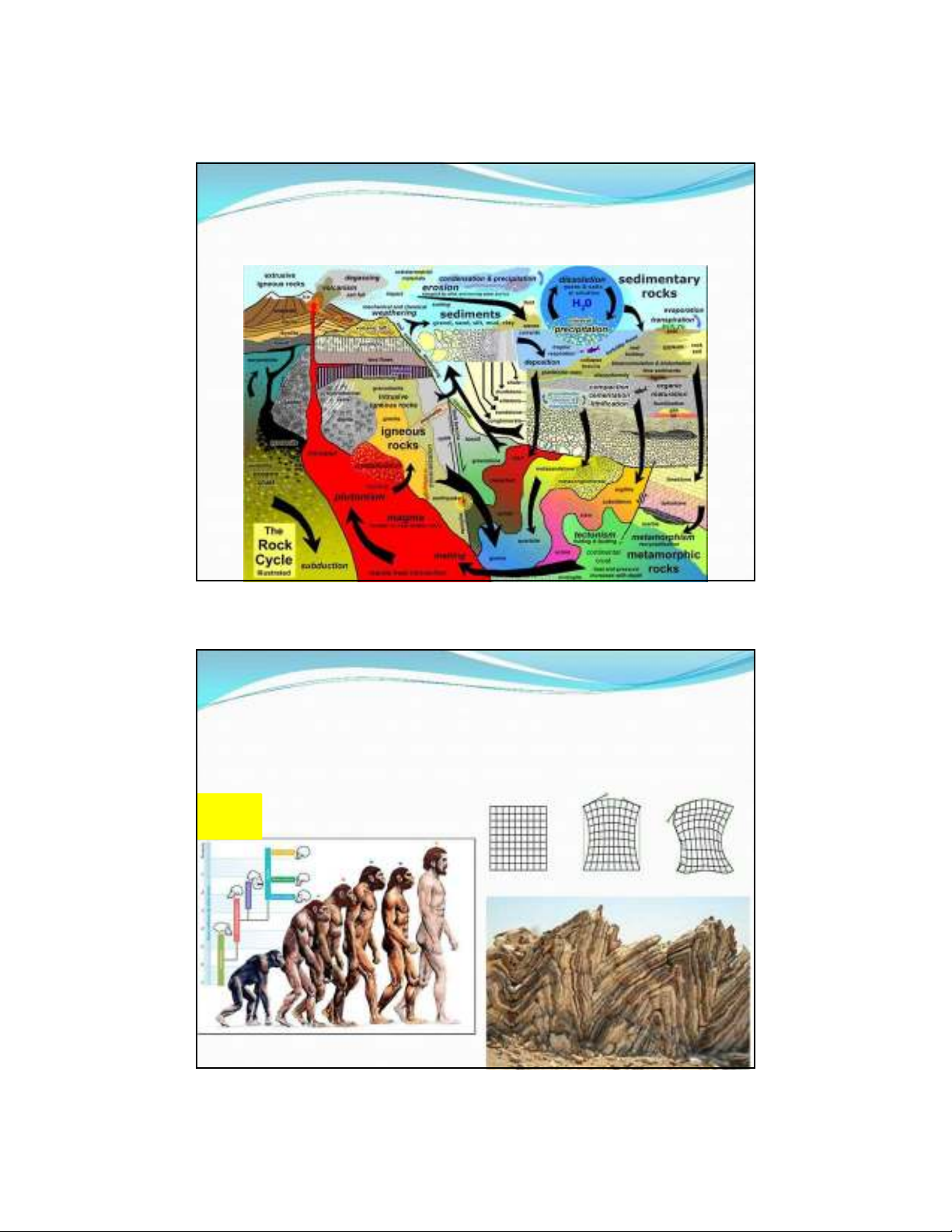
Đá là gì? Phân loại Đá?
Rock is a combination one or more minerals. The Earth's
outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock.
3
Biến dạng?
Deformation describes the transformations from some
initial to some final geometry
Deformation of a rock body occurs in response to a force
4
?
8/24/2015
3
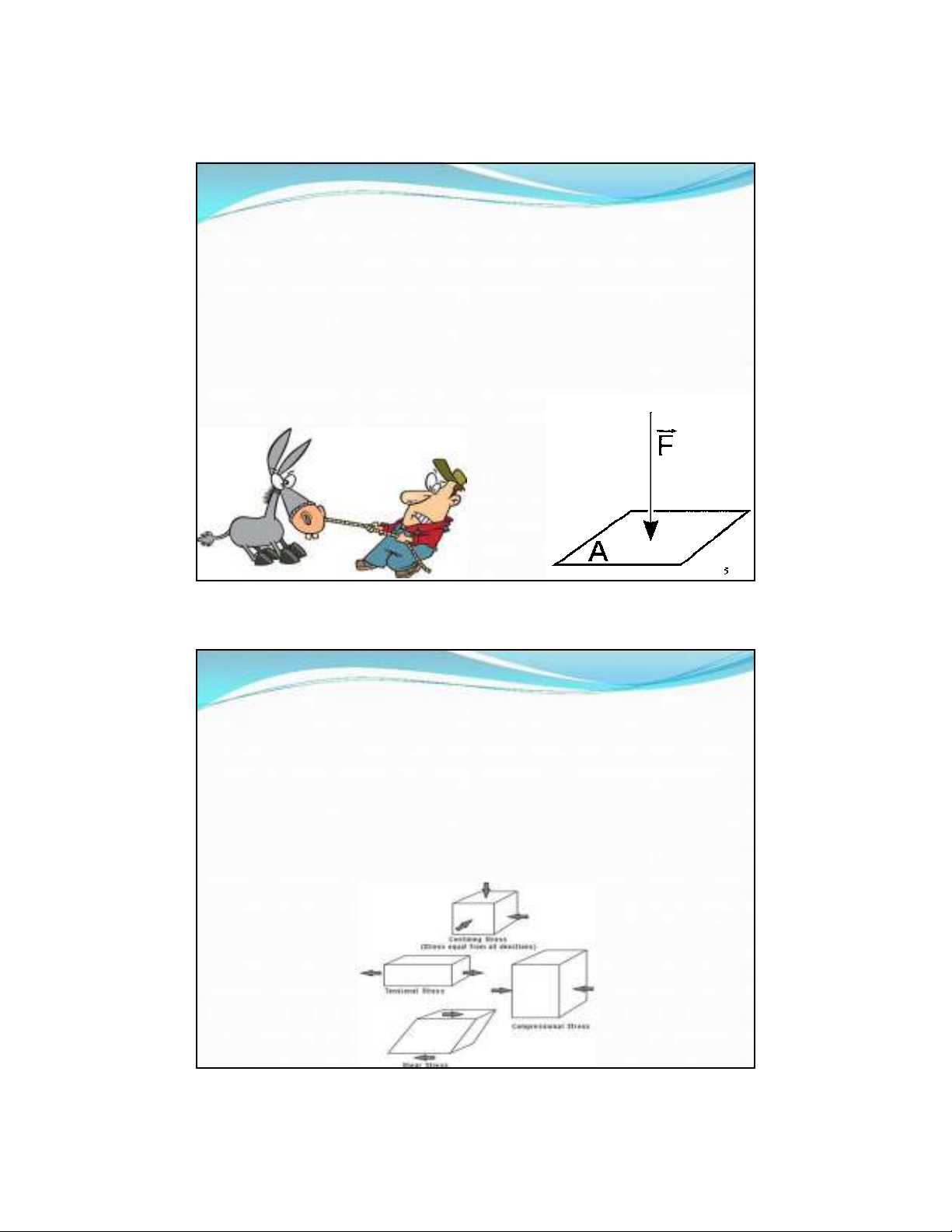
Lực và Ứng suất?
Force is Strength or energy as an attribute of physical
action (change the body) or movement (F = m*a)
Stress is a force applied over an area
Uniform stress =Pressure is a stress wherein the forces
act equally from all directions (X Y Z) (in fluid)
Confining stress = weight of overlying rocks is a uniform
stress (Z)
5
PHÂN LOẠI?
If stress is not equal from all directions then we say that
the stress is a differential stress. Three kinds of
differential stress occur:
·Tensional stress (or extensional stress), which
stretches rock;
·Compressional stress, which squeezes rock; and
·Shear stress, which result in slippage and translation.
6
8/24/2015
4
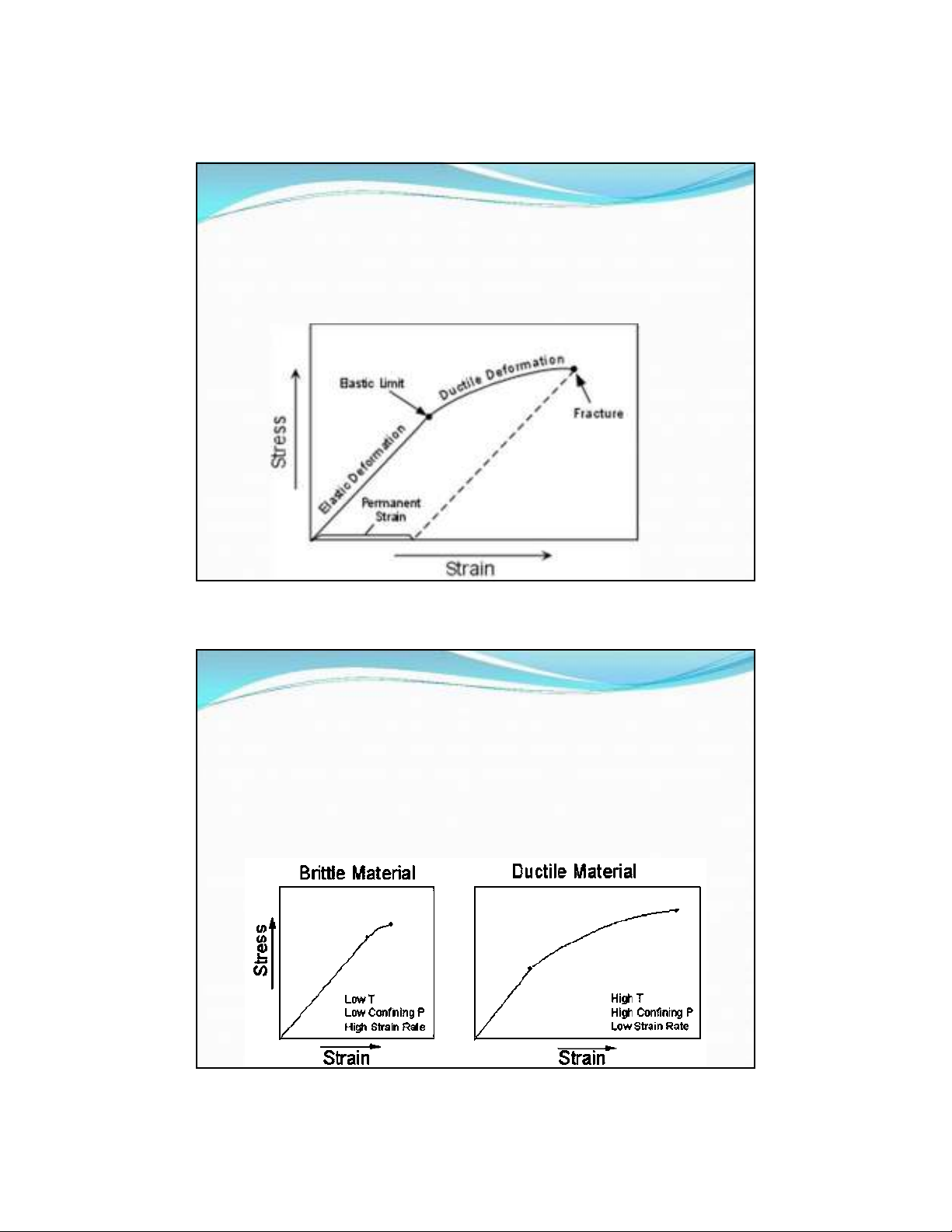
CÁC GIAI ĐOẠN BIẾN DẠNG
(Stages of Deformation)
Elastic Deformation -- wherein the strain is reversible.
Ductile Deformation -- wherein the strain is irreversible.
Fracture - irreversible strain wherein the material breaks.
7
We can divide materials into two classes that depend on
their relative behavior under stress
Brittle materials have a small or large region of
elastic behavior but only a small region of ductile
behavior before they fracture.
Ductile materials have a small region of elastic
behavior and a large region of ductile behavior before
they fracture.
8
8/24/2015
5
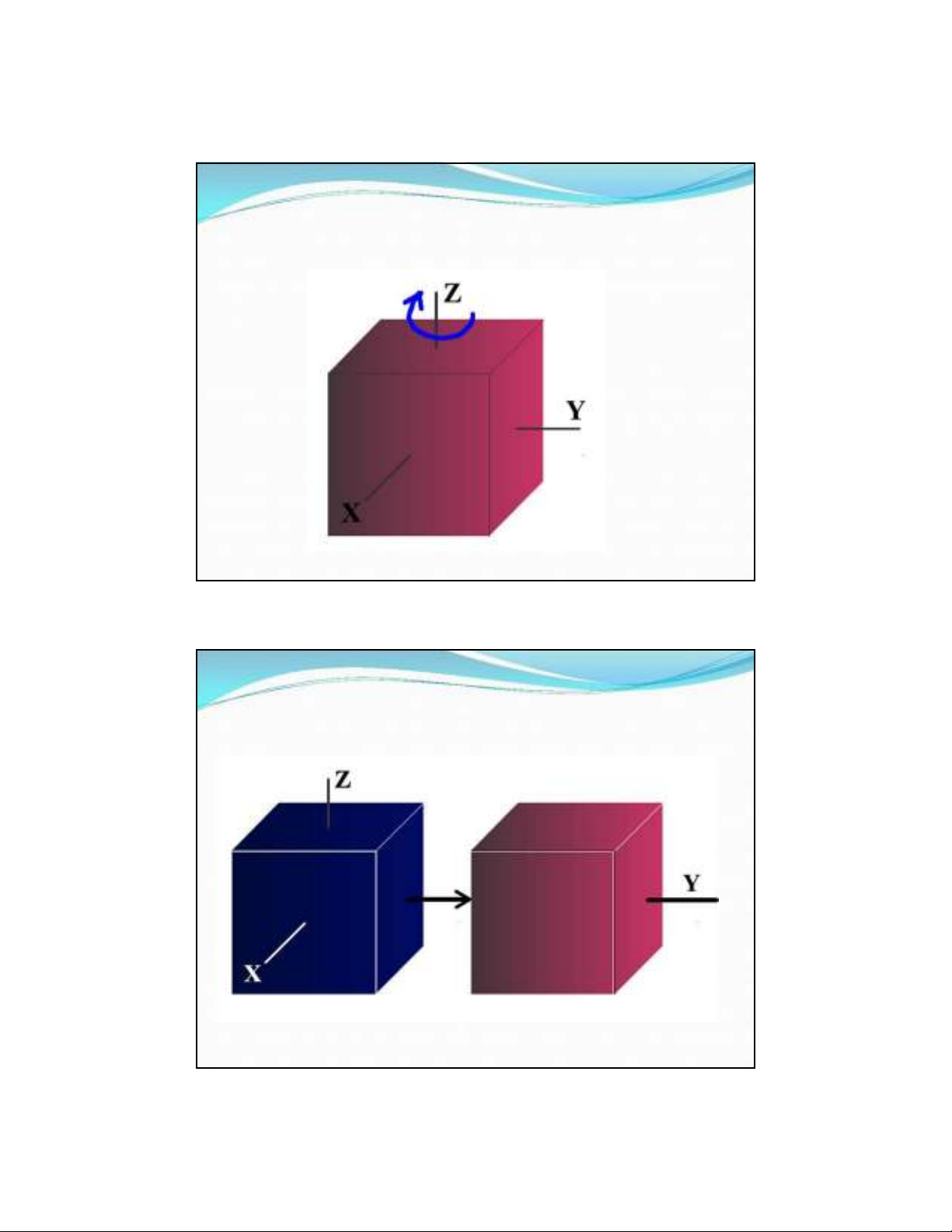
Clockw ise Rotation about the z-axis
.
Translation Parallel to the Y axis














![Quy hoạch tổng thể Cà Mau: Tài liệu [mới nhất/chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250827/tghong1621@gmail.com/135x160/49401756278390.jpg)


![Bài giảng Hàng hải địa văn [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250729/vijiraiya/135x160/43361753782101.jpg)
![Bài giảng Trắc địa cơ sở [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250729/vijiraiya/135x160/84_bai-giang-trac-dia-co-so.jpg)





![Atlas tài nguyên nước Việt Nam: Tài liệu [Mô tả/Hướng dẫn/Chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250715/vijiraiya/135x160/348_tai-lieu-atlas-tai-nguyen-nuoc-viet-nam.jpg)
![Hệ thống câu hỏi ôn tập Vùng kinh tế [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250709/kimphuong1001/135x160/76921752140578.jpg)
