
GS.TS. Huỳnh văn Minh, FACC, FAsCC
Phó Chủ tịch Hội Tim mạch Việt nam
Chủ tịch Phân hội THA Việt nam
ĐIỀU TRỊ TĂNG
HUYẾT ÁP
Ở NGƢỜI CÓ
TAI BIẾN
MẠCH NÃO
1
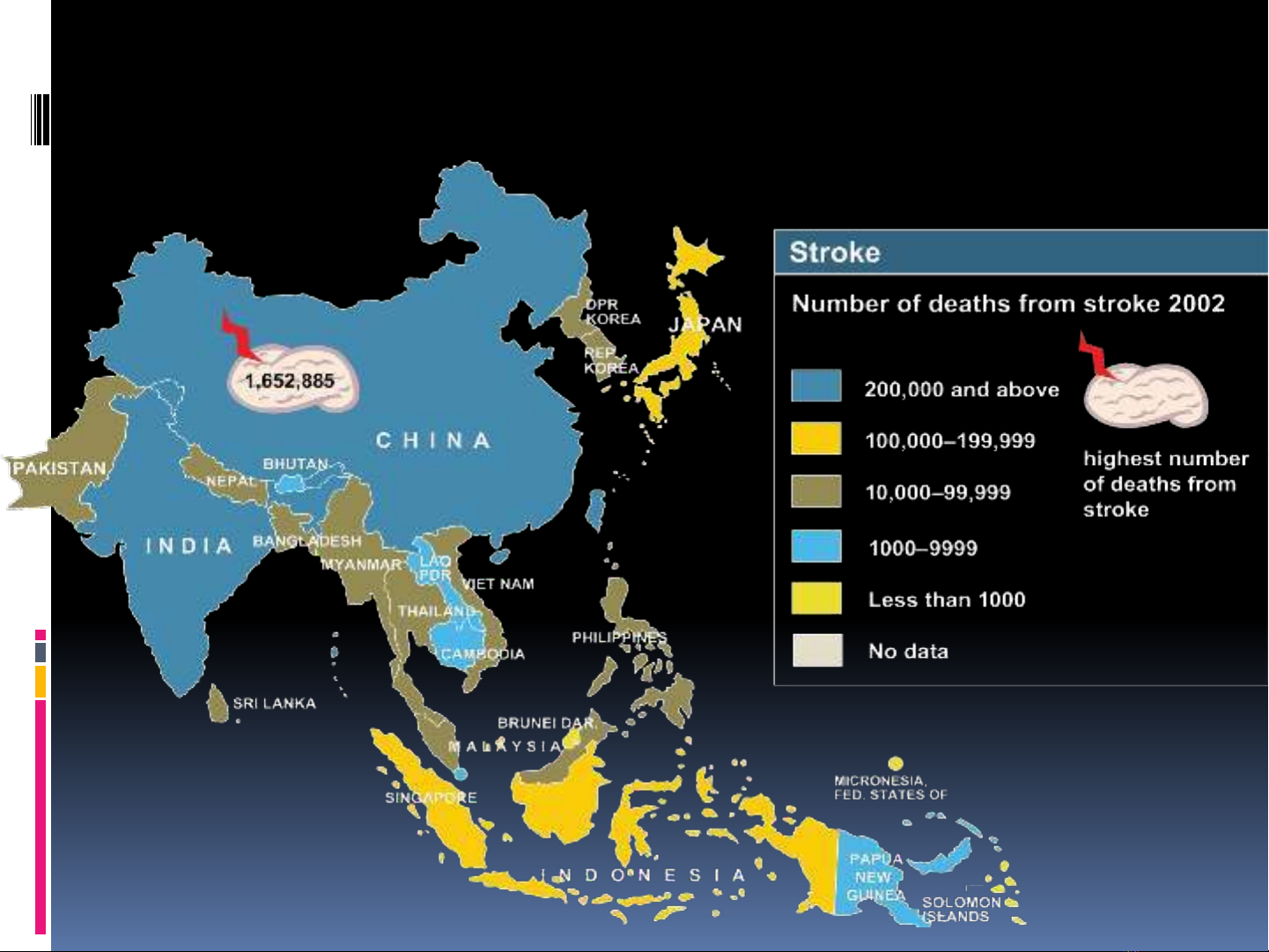
WHO CVD Atlas. 2002. WHO Stroke Atlas. 2002.
Tử vong do đột quị tại Châu Á
2
3
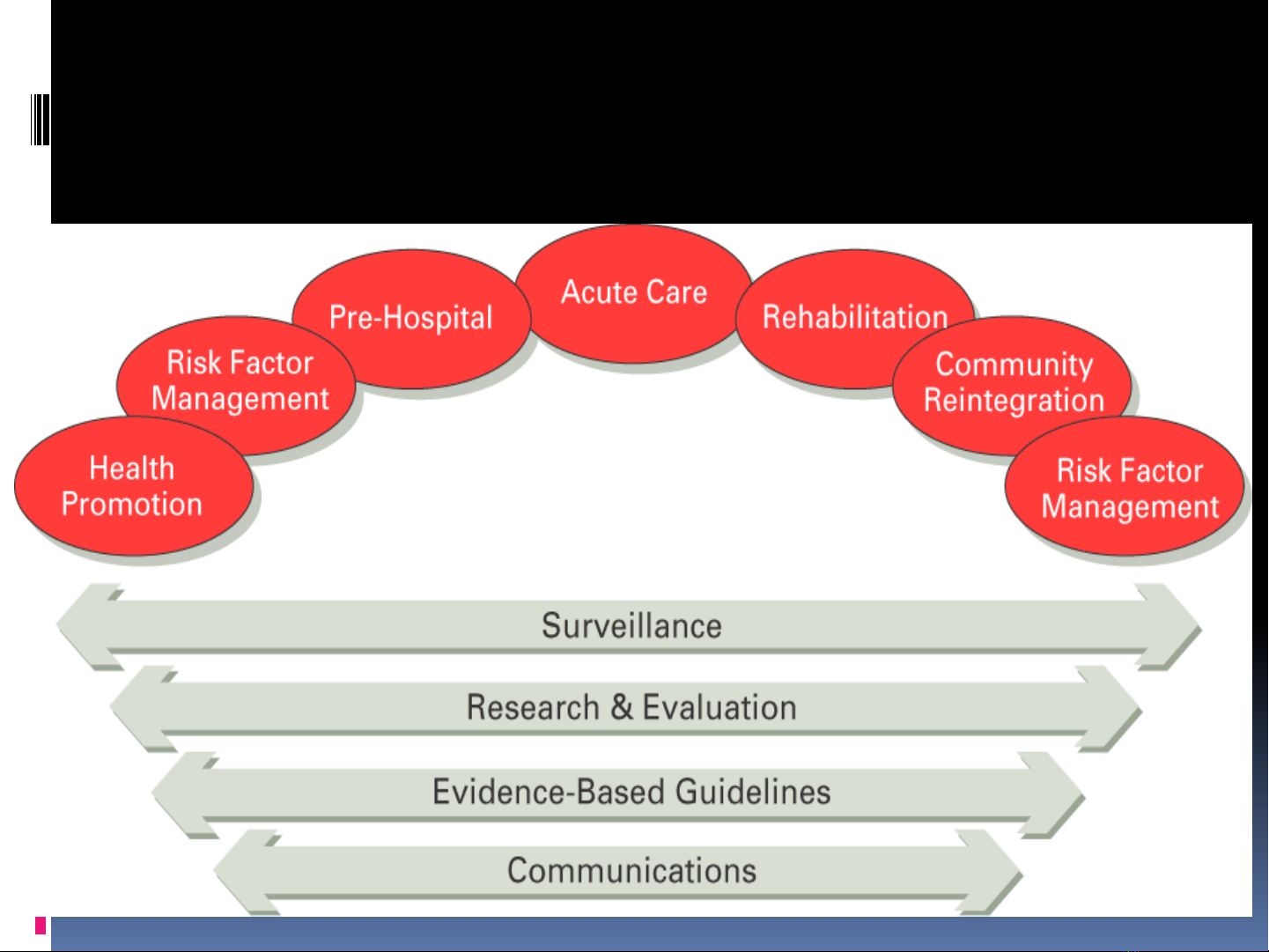
The Continuum of Stroke Care
ASA Guidelines. Stroke 2013

Guidelines Ischaemic Stroke 2008
Dự phòng thứ phát đột qui
Management of vascular risk factors
Antithrombotic therapy
Surgery and angioplasty

Dự phòng thứ phát đột qui
Warlow C, et al. Lancet 2003;362:1211–24
Patients who have suffered a stroke or TIA remain at an increased risk
of:
A further stroke (about 5% per year, maybe 10% in the first year)
MI (2–3% per year) Touze E et al. Stroke 2005;36:2748–55
Stroke, MI or vascular death (about 7% per year)
Risks higher in the immediate period following a stroke/TIA:
Risk of further stroke may be 12% in first 30 days post stroke
Risk of stroke 10% in first 90 days post TIA
Even higher risks reported in some studies
e.g. Coull AJ et al BMJ 2004;328:326–9
TIA = transient ischaemic attack MI = myocardial infarction


![Đề cương câu hỏi ôn tập Kỹ thuật xạ trị [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250709/kimphuong1001/135x160/21291752221145.jpg)
![Bài giảng thiếu máu thiếu sắt [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250603/minhquan0690/135x160/22871748938101.jpg)


![Bài giảng Viêm cầu thận [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250516/phongtrongkim0906/135x160/1331747392124.jpg)




![Bài ôn tập Giải phẫu răng [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251005/tuyetnhitk1305@gmail.com/135x160/78741759715471.jpg)





![Bài giảng Glass Ionomer Vương Lam Linh: Tổng hợp kiến thức [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250908/dangkhoa5304@gmail.com/135x160/90151757385750.jpg)






![Tài liệu triệu chứng học chấn thương [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250806/tuhaolg/135x160/99781754535086.jpg)
