
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC BÁCH KHOA – ĐHQG TP. HCM
⁕-⁕ -⁕
TS. HUỲNH PHƯỚC HIỂN
BỘ MÔN CÔNG NGHỆ NHIỆT LẠNH – KHOA CƠKHÍ
1
NHIỆT ĐỘNG LỰC HỌC KỸ THUẬT
THERMODYNAMICS
CHƯƠNG 7: KHÔNG KHÍ ẨM
THERMODYNAMICS –CHAPTER 7 H.P.Hien (Dr.Eng.)
CHƯƠNG 7: KHÔNG KHÍ ẨM
2
7.1 GIỚI THIỆU
7.2 CÁC THÔNG SỐ CỦA KHÔNG KHÍ ẨM
7.3 NHIỆT ĐỘ NHIỆT KẾ ƯỚT
7.4 ĐỒ THỊ KHÔNG KHÍ ẨM
7.5 CÁC QUÁ TRÌNH NHIỆT ĐỘNG CƠ BẢN
THERMODYNAMICS –CHAPTER 7 H.P.Hien (Dr.Eng.)
7.1 GIỚI THIỆU
3
7.1.1 Không khí ẩm (atmospheric air or moist air)
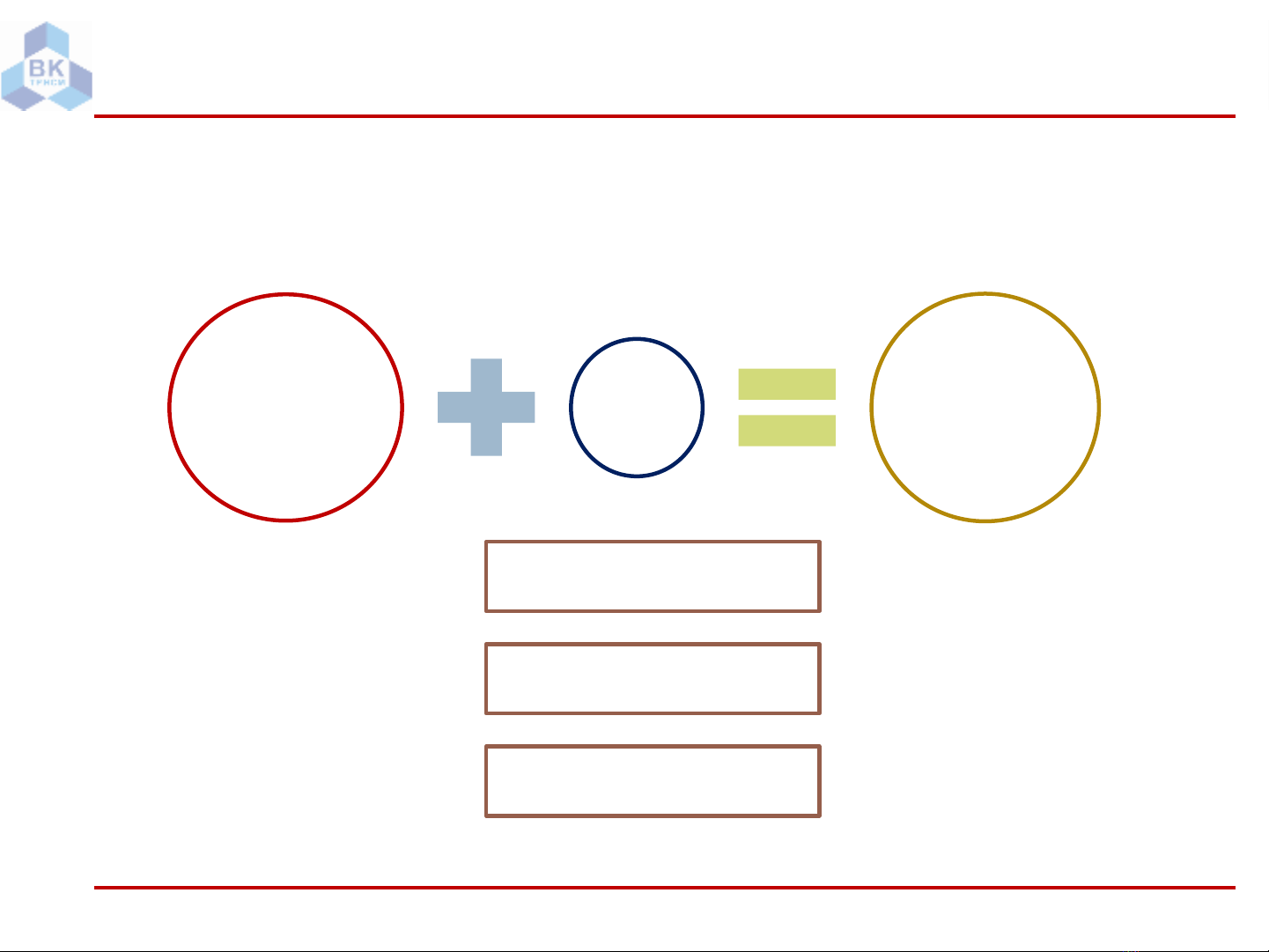
Không khí ẩm (KKA) là hỗn hợp của không khí khô (KKK –dry air) và hơi
nước (water vapor)
KHÔNG
KHÍ KHÔ
(N2+ O2)
HƠI
NƯỚC KHÔNG
KHÍ ẨM
𝐩 = 𝐩𝐡+ 𝐩𝐚
𝐭 = 𝐭𝐡= 𝐭𝐚
𝐆 = 𝐆𝐡+ 𝐆𝐚
THERMODYNAMICS –CHAPTER 7 H.P.Hien (Dr.Eng.)
7.1 GIỚI THIỆU
4
7.1.2 Phân loại không khí ẩm
Được phân loại dựa trên trạng thái của hơi nước trong KKA
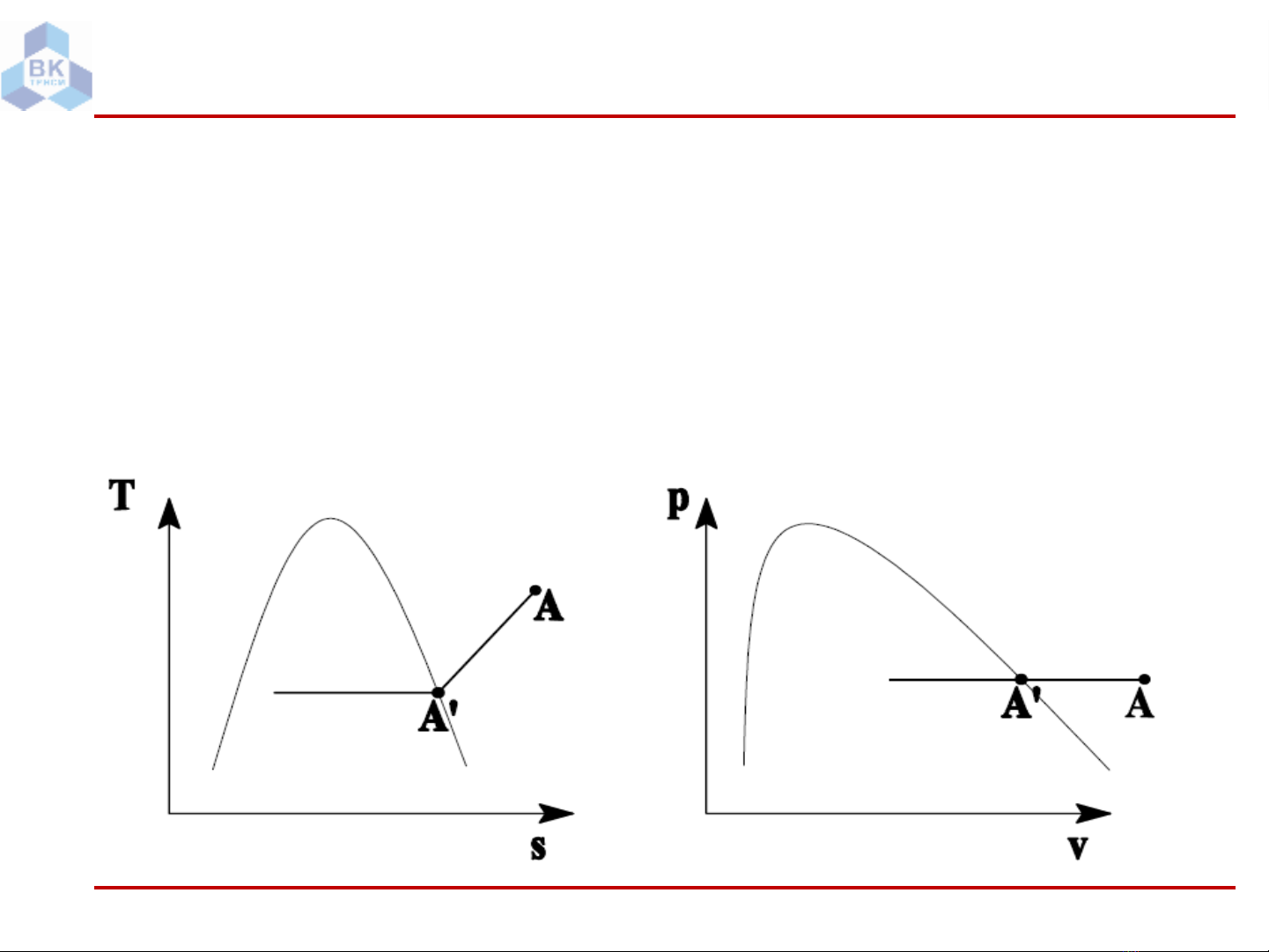
KKA chưa bão hòa (unsaturated air): trạng thái của hơi nước trong KKA là
hơiquá nhiệt (điểm A)
KKA bão hòa (saturated air): trạng thái của hơi nước trong KKA là hơi bão
hòa khô (điểm A’)
THERMODYNAMICS –CHAPTER 7 H.P.Hien (Dr.Eng.)
7.1 GIỚI THIỆU
5
7.1.2 Phân loại không khí ẩm
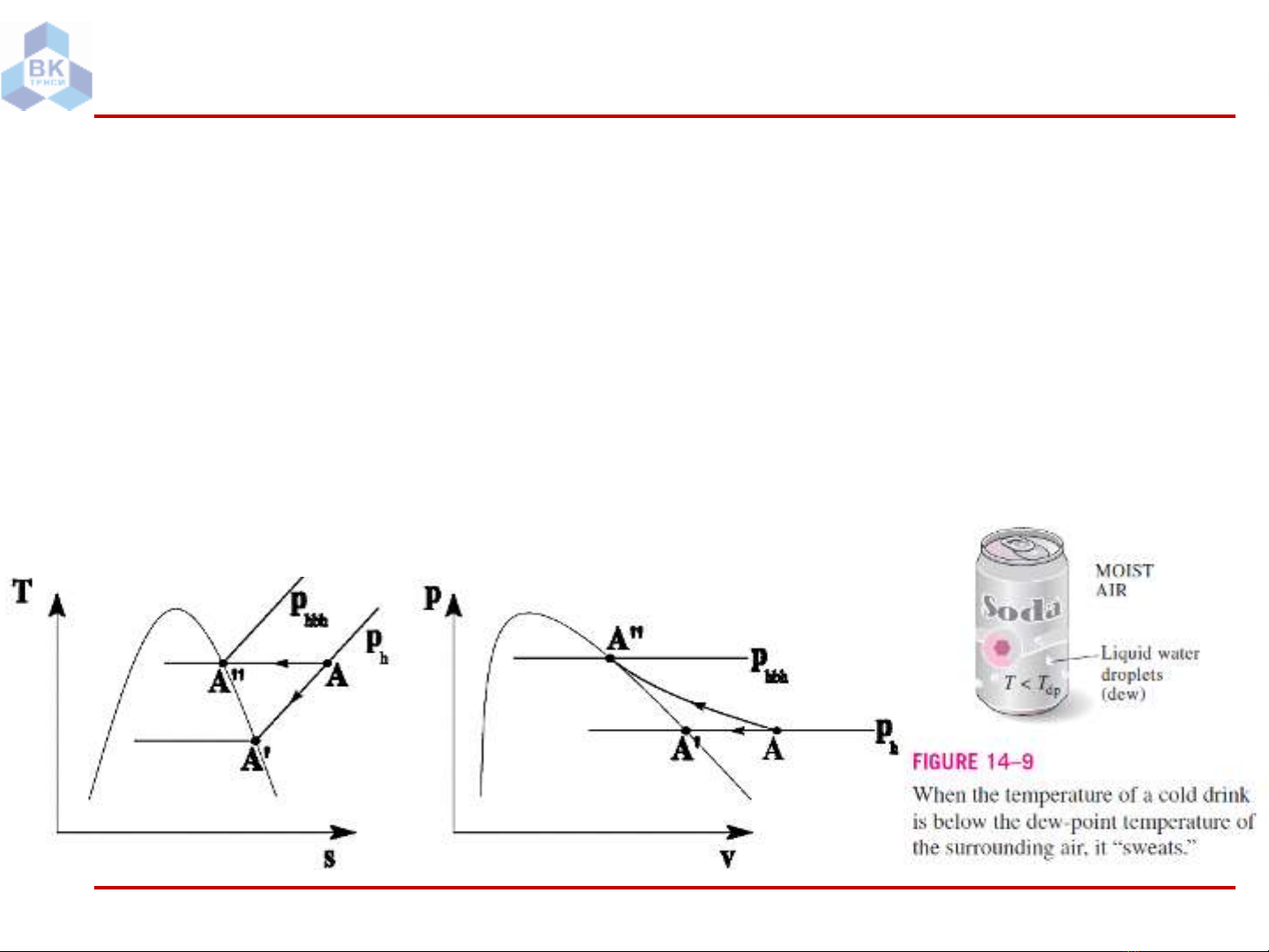
Để đưa KKA chưa bão hòa thành KKA bão hòa, có thể thực hiện quá trình sau
t = const,tăng áp phđến áp suất bão hòa của hơi nước tại nhiệt độ của KKA
ph= const, làm lạnh KKA đến nhiệt độ tA’ là nhiệt độ bão hòa của hơi nước
ứng với áp suất ph.
tA’ còn được gọi là nhiệt độ đọng sương tđs (dew-point temperature)
tđs = tbh (ph)



















![Ngân hàng trắc nghiệm Kỹ thuật lạnh ứng dụng: Đề cương [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251007/kimphuong1001/135x160/25391759827353.jpg)






