1/26/2013
1
ĐI HC QUC GIA TP.H CHÍ MINH
TRƯNG ĐI HC BÁCH KHOA
KHOA ĐINĐIN T
B MÔN K THU!T ĐIN T
TP.H" Chí Minh 01/2013
X LÝ TÍN HiU S V1I FPGA
Chaper 1: Introduction
GV: Hoàng Trang
Email: hoangtrang@hcmut.edu.vn
mr.hoangtrang@gmail.com
Thank to: thEy H" Trung MG
11
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013
Content
2
+ Tng quan môn h%c
+ Phương pháp lu*n thi+t k+ và
gi/i pháp FPGA
+ Thi+t k+ gi/i thu*t DSP v0i FPGA
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com
1/26/2013
2
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013
Outline: how to evaluate?
3
How to evaluate?
1. Quiz: 10%
2. Homework (textbook) : 10% (team work)
3. Project: 20% (team work)
4. Midterm: 20%
5. Final exam: 40%
Textbook:
“VLSI Digital Signal Processing: Design and Implementation”
Keshab K. Parhi
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013 4
Outline
Hardware
• DSP Systems, A/D and D/A
converters
• FPGA for signal processing
(Altera, Xilinx),
• Application domain specific
instruction set processors
• SoC, DSP Multiprocessors
• Signal processing arithmetic
units
Algorithm design and
transformations
• Scheduling, Resource
Allocation, Synthesis
• Finiteword length effects
• Algorithmic transformations
• FIR filter design
• FFT design
• IIR filter design
• Adaptive filter design
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com
1/26/2013
3
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013 5
Course Conduct
•Course notes will be posted on the course web
page
•Assignments with solutions will be provided and
will not be graded
•The exam will be prepared based on lecture
slides, references and assignments
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013 6
Course Objectives … To
•Understand tradeoffs in implementing DSP
algorithms
•Know basic DSP architectures
•Know some reduced complexity strategies for
algorithms mainly on FPGA.
•Know about commercial DSP solution
•Know and understand system-level design tools
•Understand research topics related to algorithmic
modifications and algorithm-architecture
matching
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com
1/26/2013
4
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013 7
Why this course?
There is the demand to derive more information per
signal. “More” means
•Faster: Derive more information per unit time;
–Faster hardware
–Newer algorithms with fewer operations
•Cheaper: Derive information at a reduced cost in
processor size, weight, power consumption, or
dollars;
•Better: Derive higher quality information, (higher
precision, finer resolution, higher SNR)
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013 8
Hardware and software elements
Progress in signal processing capability is the product of
progress in IC devices, architectures, algorithms and
mathematics.
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com
1/26/2013
5
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013 9
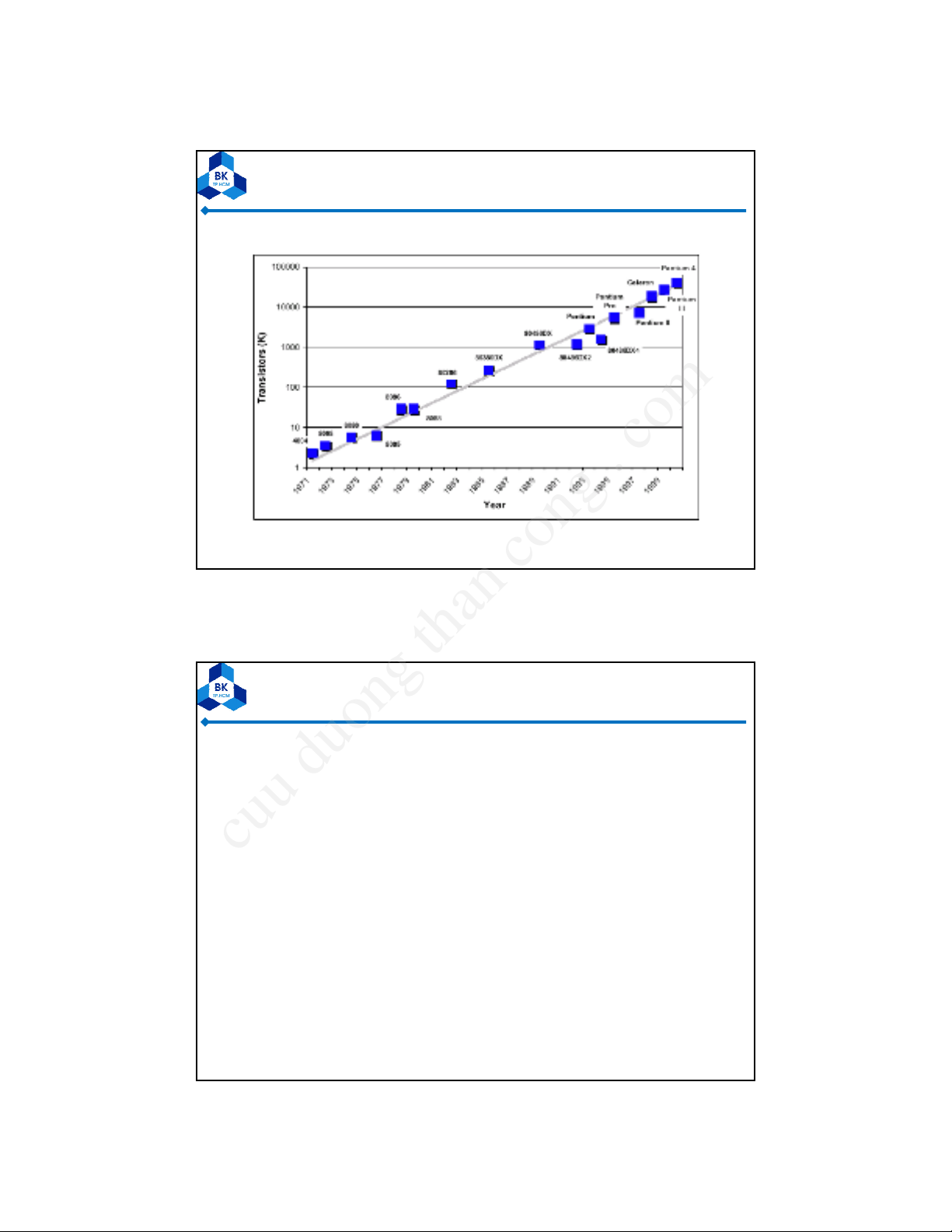
Moore’s Law
9
Hoàng Trang
BM Đin TDSPFPGAchapter1 01/2013 10
What is Signal Processing?
10
•Ways to manipulate signal
in its original medium or an
abstract representation.
•Signal can be abstracted as
functions of time or spatial
coordinates.
•Types of processing:
–Transformation
–Filtering
–Detection
–Estimation
–Recognition and classification
–Coding (compression)
–Synthesis and reproduction
–Recording, archiving
–Analyzing, modeling
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt
cuu duong than cong . com












![Trắc nghiệm Mạch điện: Tổng hợp câu hỏi và bài tập [năm hiện tại]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251118/trungkiendt9/135x160/61371763448593.jpg)













