
1
INTRODUCTION
1.1. The reason for choosing the topic
Entrepreneurial motivation (EM) by the creation and maintenance of enterprises is
the driving force for economic development in every country. To become a developed
economy, it depends mainly on the growth in both quantity and quality of businesses.
Carree and Thurik (2003) point out that there is a close relationship between the creation
of new businesses and regional and local economic growth. The places which have a high
rate of establishment and maintenance of businesses often have high economic growth
rates.
The Northwest region, including four provinces: Son La, Dien Bien, Lai Chau, and
Hoa Binh, is the area where SME development has been shown by many previous studies as
one of the solutions to create development motivation. for the whole region. However, the
development of SMEs in this area is not commensurate with the inherent potential, mainly
due to the difficulties in topographical conditions, and low starting point. In addition, the
weakness of infrastructure, technology and management skills are also big barriers in
enhancing the competitive ability of these businesses, especially women-owned SMEs.
Meanwhile, there are no studies about the reasons or causes for women, female
entrepreneurs to start a business or their motivation in doing business, the barriers they face
in rural and urban areas conducted in mountainous areas and there is no research on factors
affecting EM of female SME owners in the northwest region, Vietnam, a region with
specific characteristics. Through the initial survey, most of the SMEs owned by women in
the subregion mainly develop from the business household model, the female business
owners are familiar with the household business management method with poor knowledge
and management skills. They have not fully exploited the natural potential of women and
the type of enterprise prioritized by the Government. This is also a remarkable point to
promote the establishment, maintenance and development of enterprises for women to
increase both the quantity and quality of the business sector, contributing to regional
economic growth and sustainable development
With the above reasons and arguments, the author chose the topic "Research on some
factors affecting entrepreneurial motivation of female SME owners in the Northwestern
subregion" as the research content for the thesis.
1.2. Objectives of the study
Based on the above reasons, the thesis focuses on the main objective: Researching
factors affecting EM of female SME owners in the context of the northwest subregion. The
thesis systematizes the theoretical basis of motivation and EM; builds and tests theoretical
models and hypotheses on the relationship between individual factors and the environment
2
in the EM of female SME owners in the northwest subregion and proposes some
recommendations to promote EM of women, female owners of small and medium-sized
SMEs
1.3. Research question
Firstly, what are the personal and environmental factors that significantly affect the
EM of female SME owners in the northwest subregion and their impact level?
Secondly, Which groups of factors has the greater impact on entrepreneurial
motivation of female SME owners in Northwestern subregion, the individual factors or the
environment ones?
Thirdly, what do policy makers and business women need to do to promote EM of
female SME owners in the northwest subregion?
1.4. Object and scope of the study
- The object of the thesis: Identifying factors affecting EM of female owners of
SMEs.
- Spatial scope: Data collected from qualitative research, interviewing experts and
surveys conducted in the northwest subregion including 04 provinces of Dien Bien, Lai
Chau, Son La, and Hoa Binh.
1.5. Research Methods
Qualitative research methods. Group discussion, in-depth interviewing techniques
used for SME owners and expert interviews.
Quantitative research method. The survey has 2 phases: a preliminary investigation
to adjust the scale, the appropriate questionnaire and the official investigation phase to
evaluate the scale, test models and research hypotheses.
1.6. Contribution of the thesis
In theory
Inheriting the published research, the thesis continues to analyze and explore the
factors affecting the EM of female owners of SMEs in the northwest subregion. Through
qualitative research and in-depth interviews with experts, there are 3 additional indicators,
the scale is adjusted to be more suitable with the research context.
Two separate factors in theory are "Social status of business women" and "Opinions
of people around" in fact in the northwest subregion, Vietnam becomes a unidirectional
factor "Social standards".
The research results show that there are 6 factors affecting the EM of female SME
owners in the northwest subregion including the factors in decreasing degree: (1) Access to

3
capital, (2) Social standards, (3) demand for success, (4) Barriers in awareness, (5) Model
female entrepreneur and (6) Optimism. In which, the negative factors are: Perception
barrier, and the remaining factors have positive effects. Interestingly, the Access to Capital
factor has the strongest impact and the Optimism factor is first considered in Vietnam from
the perspective of an independent variable. In addition, the thesis also shows that the group
of environmental factors has a greater impact than the group of individual factors on EM of
female SME owners in the northwest subregion, which is also compared for the first time in
Vietnam.
In practice
From the above research results combined with the characteristics of women, female
owners of small and medium-sized SMEs in the northwest region, the thesis proposes a
number of recommendations on factors affecting the EM of female owners of small SME in
this region, aiming to promote the formation, maintenance and development of women-
owned SMEs.
The thesis becomes a reference for policy makers and women themselves, and
women owners of small and medium enterprises to promote the formation, maintenance and
development of women-owned SMEs.
1.7. Bố cục luận án
In addition to the appendix, references the main contents of the thesis are presented
as follows: Introduction; Chapter 2: Overview of previous studies; Chapter 3: Theoretical
basis and research model; Chapter 4: Research method; Chapter 5: Research results;
Chapter 6: Discussion and recommendation; and Conclusion.
CHAPTER 2: OVERVIEW OF PREVIOUS STUDIES
2.1. Overview of entrepreneurial motivation and motivation
2.1.1. Motivation
2.1.1.1. Concept
Many concepts of motivation have been introduced, but whether in the field of
economics or psychology, all the definitions are based on three components of motivation as
stated by Arnold et al (1998): firstly , orientation which means what an individual is trying
to do; secondly, effort, that is, how an individual is trying; and thirdly, persistence, which
means how long a person keeps trying. Obviously, motivation is related to motive which
promotes an individual to behave in a certain way for the satisfaction or success they desire.
It is also goal-oriented behavior. An individual's motivation is promoted by internal
psychological factors (pull motivation) and external environment (motivation).
4
2.1.1.2. Types of motivation
Motivation can be classified in many different ways depending on the researchers'
point of view and the theory of motivation. Of these categories, the most commonly
accepted classification is that manifestation of motivation (implicit motivation and self-
expression); the cause of the motivation (inner motivation and outer motivation).
2.1.2. Overview of entrepreneurial motivation
2.1.2.1. Entrepreneurial motivation concept
Inheriting and unifying from the research on the EM, the thesis proposes the use of the
concept of EM in this research according to Malebana (2014) in association with Carsrud and
Brännback (2011) and Shane và cộng sự (2003) “EM is the reason, motive or goal for an
individual to start and run a business”. Through his motives or goals, an individual is said to
have a EM when he or she decides to seek, evaluate and exploit business opportunities during
the process of establishing, maintaining and developing a business.
2.1.2.2. Indicators of entrepreneurial motivation
Many motivational theories are given to discuss EM in the world, and among these
the pull factor ("pull") and push factor ("push") are most mentioned because these factors
are regarded as the entrepreneur's initial motivation to create a business (Munir and Sandhu,
2016).
Researches on EM in the world whether in developed, underdeveloped or developing
countries like in Vietnam with different research subjects like potential entrepreneurs, male or
female entrepreneurs, in this area or in others, almost all demonstrate that the registered
business is represented at the same time by two pull and push indicators, they are not mutually
exclusive. Derived from the concept of a EM, which is the reason, motive or goal for the
individual to start and run a business. The reason, motive or goal here is the pull and push
motivation (the initial motivation of the individual) to start and run a certain individual's
business. Trading volume is determined by both pull and push indicators.
2.2. Overview of the factors affecting entrepreneurial motivation
There have been studies on the factors affecting EM on many different angles, points of
view and scopes in the world. The factors affecting EM are very diverse such as the
environment, culture, institutions, individual characteristics and many other factors.
Traditionally, researches on EM are carried out in two different ways (Taormina and Lao,
2007). The first is the studies that examine the personal characteristics of the founders of
businesses to find out what makes them different from the others. Gartner (1989) calls this a
"trait-based approach" and this point of view can be derived from McClelland (1961).
According to the theory of characteristcs in psychology, this is the approach of researching on

5
human personality. Characteristics theory researchers are primarily interested in measuring
traits, which can be defined as patterns of habits of behaviors, thoughts, and emotions.
According to this point of view, personality traits are relatively stable over time, and influence
interpersonal behavior differently. Business characteristics represent one of the most
empirically studied topics in start-up (Vecchio, 2003). The second way focuses on external
(environmental) conditions as the key to change the number of times that a business is created
over time. The contextual theory states that entrepreneurial situations can help or prevent the
process of start-up (Gnyawali and Fogel, 1994). Many previous studies have shown that
environmental conditions, or more accurately, individuals' perception of the conditions of their
surroundings, have a great impact on starting a business (Elfving and Carsrud, 2009; Gnyawali
and Fogel, 1994). According to Aldrich (1990), this approach is called the “normative”
approach in which the Government keeps the rules and regulations to a minimum level, reduces
taxes and gives advisories in order to increase the likelihood of team organization or ILO
(2003) calls the “contextual approach” which also emphasizes issues such as laws, government
regulations, financial support, family and social communities. According to Gnyawali and
Fogel (1994), although it can not be denied the role of the founders’ personality, the external
environment is more helpful in understanding the starting of business. Therefore, researches on
business topics begins to emphasize macro environmental factors (such as socioeconomic
conditions) to explain the establishment of businesses. In support of this, Fereidouni et al (2010)
also emphasized factors in business environment, politics, and social status to explain the
motivation to start-up. Several studies have divided the individual's operating environment into
two groups. The group of environmental factors includes: actual business environment factors
such as deterrent factors, environmental support, the ability to access to finance source,
information and support, and preferential policies, the government laws, culture, economic status,
political society, institutions of nations. The group of emotional environmental factors includes
the model of business owners, opinions of people around and the social status of business owners
(Elfving and Carsrud, 2009; Nasurdin et al., 2009). Howeve, most studies such as Taormina and
Lao (2007), Yushuai et al (2014) and in this thesis, the above groups of factors are considered to
belong to a single environment, collectively referred to as environmental factors.
Based on the overview of domestic and foreign projects, the thesis emphasizes 2
groups: group of individual factors including Needs to Achieve, Accepting Risks,
Optimism, Personal capacity and group of environmental factors including Social Network
Access to capital, Business model, Social status of business owners, Opinions of people
around, Awareness barriers.
2.3. Identify gaps and research directions
The review process revealed some of the research gaps as follows:
6
Firstly, in the world, researches on factors affecting EM of individuals, potential
entrepreneurs, entrepreneurs, and female entrepreneurs are quite diverse. From foreign
research projects, we can see the stable impact of most personal and environmental factors
on EM such as Demand for success, Taking risks, personal capacity, Optimism,
Entrepreneurship model, Social status of business owners, Social networks, Perception
barriers. The approach to capital access factor alone has conflicting results. Meanwhile, in
Vietnam, there are also some similar influencing factors that are found in the world, but all
of them are on potential entrepreneurs including Demand for Success, Personal
Competency, Tendency to take risks, Access to capital. In particular, the factor of opinion
surrounding with its positive influence is mentioned by potential entrepreneurs in many
researches, especially young people, students. That is unlike in Western society where
people have a high level of independence in thinking development and career decisions. In
Vietnam, they still depend a lot on their families to study and accumulate experience and
many of them have to follow the arrangement of their parents.
On the basis of the overview of domestic and foreign works, the author realizes that
it is necessary to re-examine the above factors to confirm the stability of their impact on the
EM of female SME owners. There have not been any studies in Vietnam that mention the
Optimism factor as an independent variable in the group of individual factors, which should
be included in the model to verify the impact. There has also been no study comparing the
relative impact between individual and environmental factors on EM of female SME
owners, this is a gap that needs to be filled.
The northwest subregion, which has strategic significance in terms of security and
national defense, but underdeveloped economy, heavily localized social culture still faces
many difficulties in SME development, especially SMEs made by women. There are not
any researches on EM and the influencing factors. Through the preliminary research, the
author found that there are still many differences between the ethnic minority female
entrepreneurs compared to the Kinh female entrepreneurs in demographic factors such as
education level, marital status, number of children, age at the start-up. This needs to be
analyzed.
Secondly, researches on EM and the influencing factors mainly are conducted in
Western countries and developed countries; in developing countries like Vietnam researches
are limited or carried in regions with high economic conditions like Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh
City, Can Tho City .... The northwest subregion, which has strategic significance in terms of
security and national defense, but underdeveloped economy, heavily localized social culture
still faces many difficulties in SME development, especially SMEs made by women. The
owner has not had any research on EM and the influencing factors. Also here, through the

7
preliminary research, the author found that on female SME owners, demographic factors
such as education level, marital status, number of children, age at the start of establishment
and management of the group There are still many differences between the ethnic minority
female entrepreneurs compared to the Kinh group and this needs to be analyzed.
CHAPTER 3: THEORETICAL BASIS AND RESEARCH MODEL
3.1. Theoretical basis related to entrepreneurial motivation
3.1.1. The theory of individual personality
The traits theory is used to explain the relationship between the characteristics of the
businessman and the EM. According to this approach, the different personalities of each
businessman affect their EM, so different characteristics may affect the EM differently
(Munir and Sandhu, 2016). Psychoanalytic representatives claim that the entrepreneurs, who
are successful at starting their own businesses, are those who were born as an entrepreneur,
not someone who has been trained or educated to become an entrepreneur (Shane, 2003
gives an example, genes affect an entrepreneur's ability and success). This means that
successful entrepreneurs are gifted inborn, and have their own destiny to become an
entrepreneur. An entrepreneur's ability to survive who only complete business training or
education is less, and limited because they don't have the talent, senses, and instincts to
become an entrepreneur.
Talent, senses and instincts cannot be obtained by being taught or trained. They are
innate gifts. It is possible that a trained or educated person don’t have the suitable senses
and instincts to run their business so that they can exist in the business world – place with
tough competition.
Researchers based on this theory such as Lowell (2003) said that a person who is
motivated to establish, maintain and develop a business is someone who not only recognizes
business opportunities but also own individual personality traits. According to this point of
view, those who possess some certain personal characteristics and personalities can have the
business license such as risk-free personality, need for creative achievement, risk-taking,
self-control behavior, outrageous optimism...This view is that people who do not have the
qualities of business owners never become entrepreneurs. Individuals with different
identities have EM, even different pull and push motivations (Munir and Sandhu, 2016).
Studies based on this point of view suggest that only people with entrepreneurial qualities
and personalities can become entrepreneurs and there are different types of personality traits
of entrepreneurs to distinguish entrepreneurs from other groups.
8
3.1.2. Institutional theory
Institutional theory is developed and used by researchers in many different ways,
in which the two common approaches are institutional economics and institutional
theory from a sociological perspective. Institutions are devided into two types: formal
institutions and informal institutions. The formal institutions include the legal system,
policy, and regulation ... The informal institutions include customs, traditions, and
cultural norms that are recognized and followed by everyone in the community. It
greatly affects human behavior (Nguyen Van Thang, 2015). Therefore, environmental
factors can be deduced and explained by the institutional theory because they are the
perceptions and judgments of individuals and entrepreneurs towards the environment.
The theory related to institution is proposed by North (1990). North (1990) says that the
human-created institutions make interaction between people. These institutions as the
form of social norms define the roles and functions of community members or in the
form of legislation that sets out legal rules. The institutional analysis that takes into
account a variety of factors and policy - socio-political levels, making it the optimal tool
for assessing the performance of female entrepreneurs. Institutions contribute to the
formation of social structures in which organizations are operated through policies, thus
they fix economic and legal policies. In societies where clear legal policies, material
resources, knowledge for the formation of businesses are fully provided, businesses will
have great motivation to be formed and developed (Nguyen and partner, 2009). The
theory of cultural tendencies (Hofstede, 1980), value theory (Schwartz et al., 2001) can
explain the influence of the difference of "national culture" on the relationships
mentioned in the model of Factors affecting startup intentions. The core of culture is the
values, and the value of each individual in the society is expressed through his or her
views, thoughts, beliefs and behaviors (Hofstede et al., 2010) and this influences their
thinking. think, EM of businessman.
3.2. Research model and hypothesis
3.2.1. Research model of the thesis
Through the study of Theoretical basis together with the overview results from
related researches, 10 factors are proposed into the research model. They are divided into 2
groups of factors: groups of individual factors including Demand into Achievement, Self-
capacity, Risk-taking and Optimism and environmental factors including Social Network,
Entrepreneur's social status, Access to capital, Opinions around people, awareness Barriers,
Business model (Table 3.1).
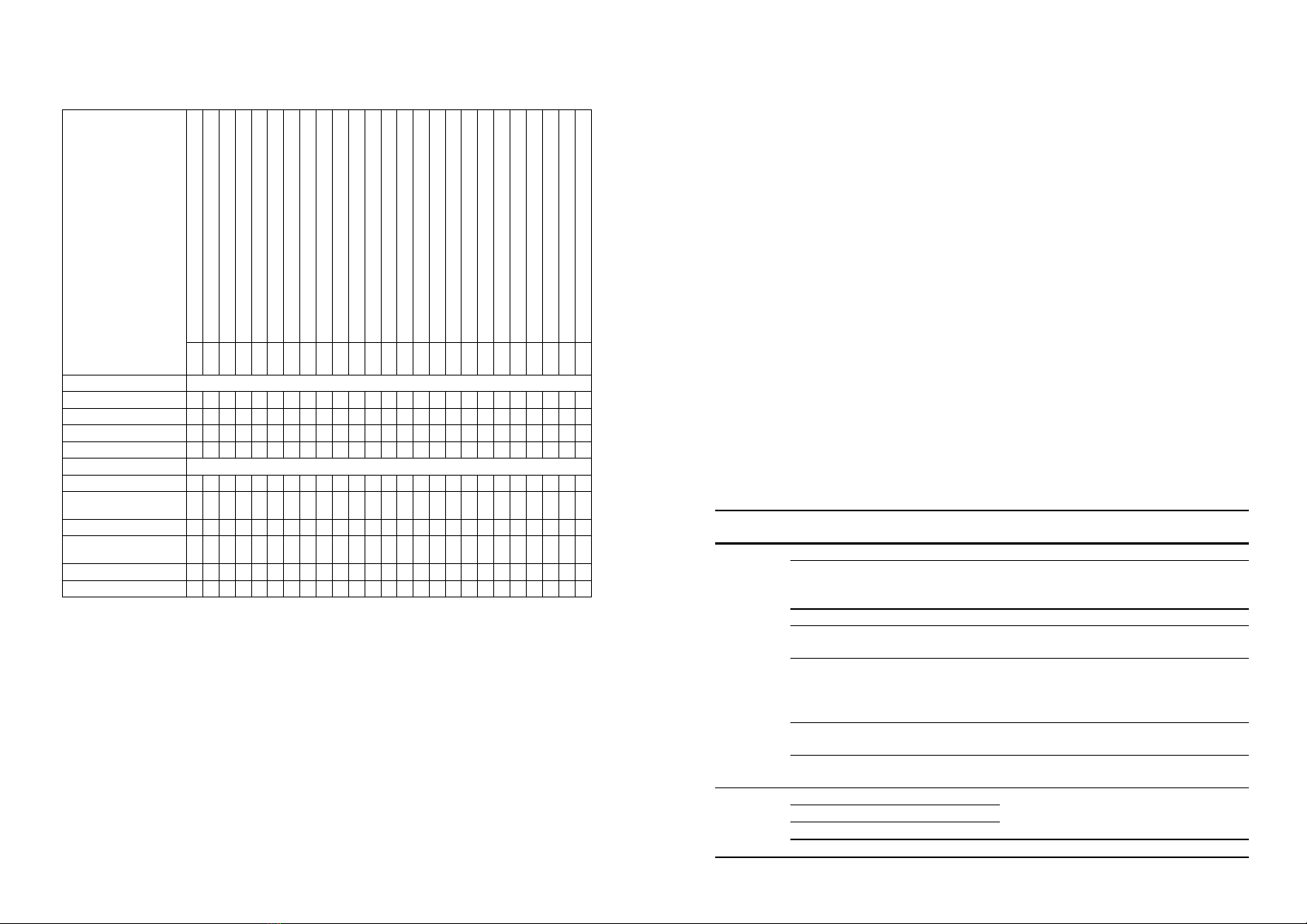
9
Table 3.1: Summary of impacts of individual and environmental factors on EM in previous
studies proposed in the research model
Factors affecting
entrepreneurial
motivation
Simon et al
Lüthje and Franke
Kristiansen and Indarti
Taormina and Lao
Nasurdin et al
Fereidouni et al
Keat et al
Bui Huynh Tuan Duy et al
Sesen
Dinis et al
Malebana
Yushuai et al
Cheng and Soo
Phan Anh Tu and Nguyen Thanh Son
Mekonnin
Phan Anh Tu and Giang Thi Cam Tien
Hassan and Midih
Hassan and Anas
Hassan and Ying
Nguyen Quoc Nghi vet al
Le Thi Trang Dai and Nguyen Thi Phuong Anh
Kabir et al
Nguyen Hai Quang and Cao Nguyen Trung Cuong
Nguyen Phuong Mai et al
Nguyen Thao Nguyen
1999
2003
2004
2007
2009
2010
2011
2011
2013
2013
2014
2014
2015
2015
2015
2015
2016
2016
2016
2016
2016
2017
2017
2018
2018
Personal factors
Demand for success
o
+
+
o
+
+
o
+
+
Individual ability
+
+
+
+
+
o
+
o
+
Optimism
o
+
+
Risks Taking
o
+
o
-
+
+
+
Environmental factors
Social network
+
+
o
Social status of
entrepreneurs
o
o
+
Access to capital
-
+
+
+
-
-
Comments of people
around
+
+
o
+
+
+
o
+
+
+
Perceived barrier
-
-
o
Businessman model
+
o
+
The symbol (+): positive effect; (-): negative impact; (o): no impact
(Source: The Author's compilation)
3.2.2. Development of research hypothesis
The author uses 10 pairs of hypothesis showing the expected impact of the above 10
factors on EM of female SME owners in the northwest subregion, in which, except for the
perceived Barrier factor with a negative impact, all other factors have a positive impact.
CHAPTER 4: RESEARCH METHODS
4.1. Qualitative research
4.1.1. Qualitative research objectives
The objective of the qualitative research is (1) to determine the most appropriate
factors influencing the EM of female SME owners in the context of the northwest
10
subregion, (2) to adjust the scales used in the pre-quantification studies for preliminary
investigations, to assess the validity of indicators, (3) discoveries also contribute to the
interpretation of quantitative results and used as a basis for supporting recommendations.
4.1.2. Content of qualitative research
Group discussions were conducted with 03 lecturers in economics and business
administration to form the initial model. Then, the author used the techniques of in-depth
interviewing experts including university lecturers, business managers, bank officials,
officials of the Department of Planning and Investment, tax officers, the heads of
associations and clubs. The theoretial sampling technique was used, 10 female SME owners
in Son La and Dien Bien provinces were selected for in-depth interviews to assess the
appropriateness of influencing factors and scales, questionnaire.
4.2. Quantitative research
4.2.1. Quantitative research objectives
Quantitative research method aims to: test the scale (2nd and official); sample
description statistics about yourself, your family, and describe the EM of the female SME
owner; determine the order of the influence of factors and compare the group of individual
factors and environmental factors to the EM of female SME owners.
4.2.2. Quantitative research content
Through experts’ opinions (in discussions and in-depth interviews), the suummary of
development variables in form of coded questions, sources and scales is shown in the
following tables:
Table 4.3. Entrepreneurial motivation Scale
Kind of
motivation
Question Source
Pull
motivation
For an interesting
job
Malebana (2014); Choo and Wong (2006);
Imitate a woman I admire Malebana (2014); Choo and Wong
(2006); Inherit and make some
adjustment
To challenge yourself Malebana (2014); Choo and Wong (2006)
To make more money Malebana (2014); Choo and Wong (2006);
Hassan and Midih (2016)
To be the owner
Malebana (2014); Choo and Wong (2006);
Taormina and Lao (2007), Fereidouni et
al (2010); Buttner and Moore (1997)
Inherit and make some adjustment
To take advantage of my creative
talents
Malebana (2014); Choo and Wong (2006)
To take advantage of opportunities
from the market
Inherit Malebana (2014); Choo and Wong
(2006); Hassan and Midih (2016)
Push
motivation
To maintain family traditions Malebana (2014); Choo and Wong (2006)
To increase my status / reputation
Job demand
Balance between work and home life Buttner and Moore (1997)


























