
Vietnam Journal of Biotechnology 22(2): 212-226, 2024. DOI: 10.15625/vjbt-19499
212
IDENTIFICATION OF GENETIC VARIANTS IN TWO VIETNAMESE
PATIENTS WITH HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY BY WHOLE
EXOME SEQUENCING
Nguyen Thi Kim Lien1,, Nguyen Van Tung 1, Le Trong Tu 2,3, Dang Thi Hai Van 2,
Vu Quynh Nga3, Nguyen Ngoc Lan1, Nguyen Thanh Hien1, Le Tat Thanh1,
Nguyen Minh Duc 1,4, Nguyen Huy Hoang1
1Institute of Genome Research, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam
2Hanoi Medical University, Ministry of Health, Hanoi, Vietnam
3Hanoi Heart Hospital, Ministry of Health, Hanoi, Vietnam
4National Research Center for Medicinal Plant Germplasm and Breeding, National Institute
of Medicinal Materials, Hanoi, Vietnam
To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: ntkimlienibt@gmail.com
Received: 27.11.2023
Accepted: 18.06.2024
ABSTRACT
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a common genetic cardiovascular disease and a
major cause of sudden death. It is also involved in increasing morbidity and mortality of
various cardiovascular diseases. Genetic factors have been found to be important in
determining the phenotypic manifestation of cardiac hypertrophy. However, only 50–60%
of HCM patients have been identified as having pathogenic variants in known genes,
suggesting that more studies are needed to find more disease genes. In this study, whole
exome sequencing was performed on two patients from two unrelated families who were
diagnosed with HCM to screen the associated mutations. Two heterozygous variants
c.836A>C (p.Tyr279Ser) in the PTPN11 gene and c.83A>C, (p.His28Pro) in the PRKAG2
gene have been identified in patients 1 and 2, respectively. Assessment of the level of impact
using prediction software shows that these are potentially harmful variants and may be the
cause of disease in patients. Our results provided an understanding of the cause of the
patient’s disease, helping clinicians diagnose and provide better genetic counseling to the
patients’ family.
Keywords: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), PRKAG2, PTPN11, variant, Vietnamese
patient, whole exome sequencing (WES).
INTRODUCTION
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is
considered the leading cause of sudden
cardiac death (SCD) in adolescents (Marian,
Braunwald, 2017). HCM is characterized by
hypertrophy of the ventricular myocardium,
which results from increased sensitivity to

Vietnam Journal of Biotechnology 22(2): 212-228, 2024. DOI: 10.15625/vjbt-19499
213
calcium. Cardiac hypertrophy is defined as
an increase in the mass of the heart muscle.
HCM is the most common genetic
cardiovascular disease, and the prevalence
of HCM is approximately 1: 500 in young
individuals (Marian, 2008). The prevalence
may be higher in older people because the
penetrance of causative variants is age-
dependent. The prevalence ranges from 0.02
to 0.2% in Western countries (Maron et al.,
2016) and Asian countries (Moon et al.,
2020; Bai et al., 2022). Heritability of the
diseases in the general population was
estimated to be from 20 to 70% (Sharma et
al., 2006). The clinical manifestations of
HCM include heart failure (HF) (Maron et
al., 2018), stroke (Fauchier et al., 2022),
atrial fibrillation (AF) (Garg et al., 2019),
arrhythmia, and SCD. SCD is the first and
most serious manifestation of the disease
and usually occurs in otherwise healthy and
asymptomatic young people (Elliott et al.,
2006). Of all SCD cases in people aged 5 to
34 years, 14% were determined to be due to
HCM (Jayaraman et al., 2018).
Diagnosis is made based on
echocardiography or cardiac magnetic
resonance imaging for identifying the wall
thickness of the left ventricular (Maron,
2012; Fabris et al., 2013; Sternick et al.,
2014; Mavrogeni et al., 2015; Poyhonen et
al., 2015; Yogasundaram et al., 2016; Maron,
Maron, 2016). HCM is a genetically
heterogeneous myocardial disorder
determined by unexplained left ventricular
hypertrophy (LVH), with histopathological
findings including myocyte hypertrophy,
myocyte disorders, and myocardial fibrosis
(Elliott et al., 2014; Esposito et al., 2019).
HCM develops in childhood or adulthood
(Bick et al., 2012; Maron et al., 2012), but
has asymptomatic or mild symptoms
(Semsarian et al., 2015; Baxi et al., 2016;
Maron, 2018). The weak genotype-
phenotype correlation and wide phenotypic
variability of the disease are the causes that
limit the ability to use genetics for definitive
diagnosis (Mogensen et al., 2004; Tower-
Rader et al., 2017).
Genetic advances (next-generation
sequencing) have improved knowledge
about HCM at the molecular level and
provided clinical genetic testing. Early
diagnosis of HCM is important for providing
appropriate treatment and prevention
strategies for patients as well as clinical
surveillance and genetic counseling for
family members (Elliott et al., 2014). Wang
et al. (2017) provided a list of 44 genes
related to HCM. HCM is primarily inherited
as an autosomal dominant trait by variations
in the gene encoding the sarcomere protein
(Elliott et al., 2014).
Variants in the PTPN11 gene that encodes
for the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP),
SHP2, nonreceptor type 11 (Shoji et al.,
2019; Caiazza et al., 2020), have been
identified to be leading causes of HCM. So
far, 162 variants in the PTPN11 gene
associated with cardiovascular diseases have
been published in the HGMD database.
PTPN11 variants cause hypertyrosyl
phosphorylation of the transmembrane
glycoprotein, protein zero-related (PZR),
and increasing SHP2 binding. The catalytic
activity of SHP2 is tightly regulated by
intramolecular conformational constraints.
The “closed” conformation, which is
mediated by the interaction between the SH2
and phosphatase domains, is destabilized
due to the binding of the N-terminal SH2
domain and phosphotyrosine peptides,
resulting in an “open” conformation which
makes the catalytic domain substrate
accessible (Mohi et al., 2005). Studies in
mouse models show that enhanced PZR

Nguyen Thi Kim Lien et al.
214
tyrosyl phosphorylation in the hearts of mice
induces myocardial fibrosis by engaging the
Src/NF-κB pathway, leading to enhanced
IL-6 activation. These results demonstrate
that PTPN11 variants are responsible for
PZR hypertyrosyl phosphorylation, which
activates pathophysiological signaling that
leads to HCM and cardiac fibrosis.
In addition, PRKAG2 syndrome (PS) is a
rare early-onset autosomal dominant genetic
disorder that also presents with symptoms
such as cardiac hypertrophy, ventricular
preexcitation (VPE), and progressive
abnormalities (Murphy et al., 2005).
Murphy et al., (2005) estimated to be 1% in
patients with both hypertrophy
cardiomyopathy (HCM) and premature
sinoatrial or atrioventricular conduction
disease. To date, 63 variants in the PRKAG2
gene associated with cardiovascular diseases
have been identified (HGMD database). The
PRKAG2 gene encodes the γ2 regulatory
subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase
(AMPK-γ2) (Scott et al., 2004). AMPK is
known as a ubiquitously expressed fuel
meter in eukaryotic cells that regulates
cellular energy homeostasis by turning on
ATP-generating pathways and turning off
anabolic pathways in response to cellular
stress (Hardie, 2015). The AMPK-γ2 subunit
is mainly expressed in the heart and has the
role of regulating AMPK activity by
competitively binding with ATP or AMP
(Cheung et al., 2000; Scott et al., 2004).
Identifying PRKAG2 variants provides a
new insight into the molecular basis of left
ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) which is not
explained by variants in genes encoding the
sarcomeric proteins.
In our study, whole exome sequencing was
performed to identify HCM-associated
variants in two patients from two unrelated
families.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
Patient 1 is a 7-year-old boy who was
diagnosed with hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy at the Hanoi Heart Hospital
when he was two years old. The patient was
admitted to the hospital with chest pain and
difficulty in breathing due to exercise. Other
clinical symptoms include left chest pain,
3/6 systolic murmur at the apex of the heart,
regular heart rate of 110 beats/minute, SpO2
100%, and hepatomegaly 1 cm below the
right costal margin. Echocardiogram: left
ventricular concentric thickening, mild left
ventricular outflow tract narrowing, mild
mitral regurgitation, left ventricular systolic
function, ejection fraction (EF) 75.8%
(Figure 1). Electrocardiogram (ECG): sinus
rhythm, rate 110 beats/minute, no
arrhythmia, increased biventricular load.
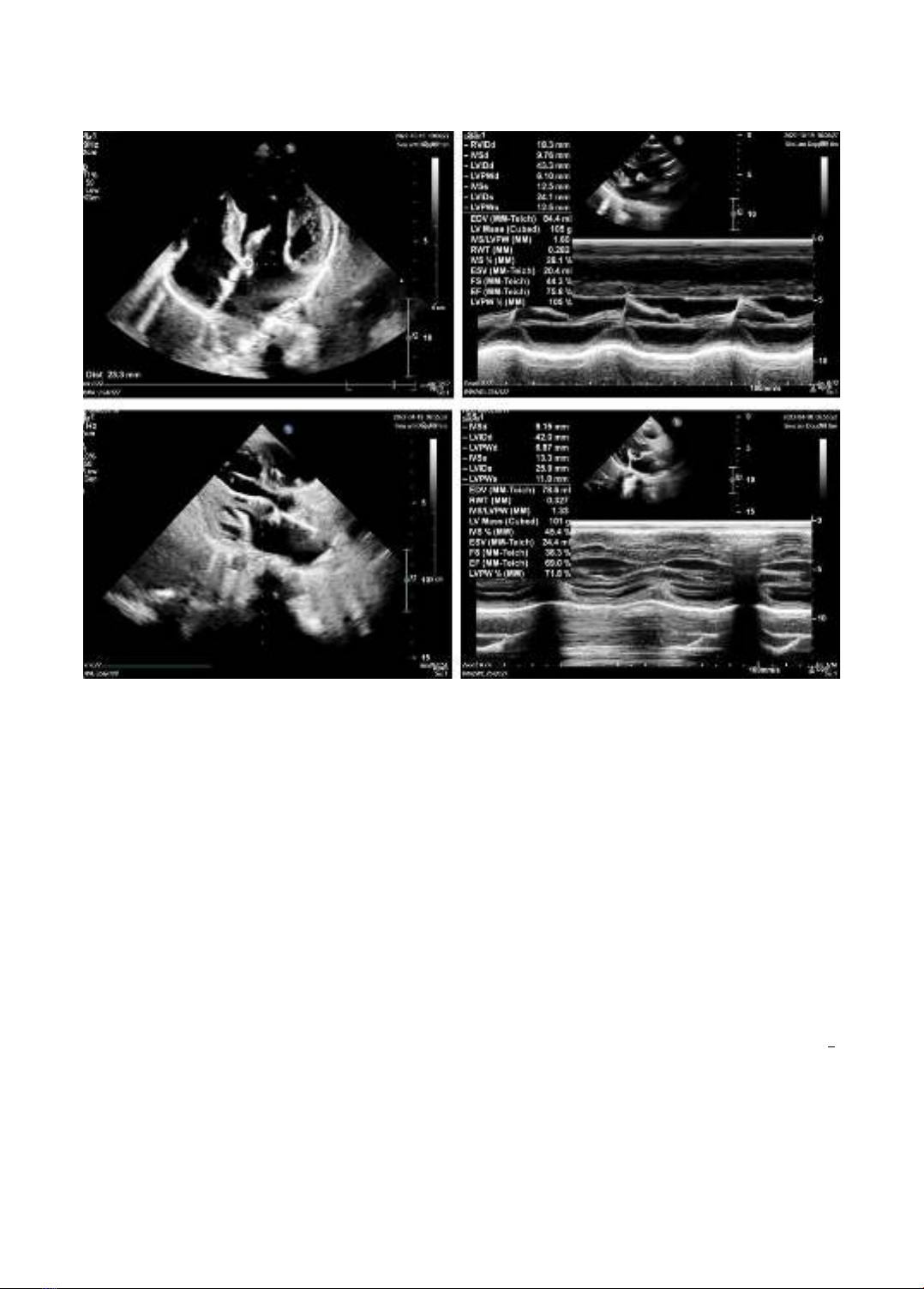
Vietnam Journal of Biotechnology 22(2): 212-228, 2024. DOI: 10.15625/vjbt-19499
215
Figure 1. Echocardiogram with images of left ventricular concentric hypertrophy of patient 1.
Patient 2 is a 1-year-old girl who was
diagnosed with hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy through postnatal screening
echocardiography. The child was examined
and treated at the Hanoi Heart Hospital for
symptoms: difficulty in breathing, SpO2
95%, pale skin, infrequent urination, moist
rale lungs, liver 2 cm below the costal
margin, rapid breathing, frequency (45
times/minute). The child has been prescribed
an echocardiogram with images of left
ventricular concentric hypertrophy (Figure
2), an ejection fraction (EF) of 42%, a mildly
dilated left heart chamber, decreased regular
heart wall movement, a right ventricular
(Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion -
TAPSE) of 11.8 mm, a mild mitral
regurgitation, a moderate tricuspid valve,
and a PGmax (pressure gradient max) across
the tricuspid valve of 44 mmHg.
Electrocardiogram showed increased left
and right ventricular loading; Blood test:
NT-ProBNP 2,890 pg/ml, white blood cell
(WBC) 15,000/mm3, C-reactive protein
(CRP) 15 mg/l.
Parents of patients provided written
informed consent under a research protocol
approved by the Institute of Genome
Research Institutional Review Board (No:
02-2021/NCHG-HĐĐĐ).

Nguyen Thi Kim Lien et al.
216
Figure 2. Echocardiogram with images of left ventricular concentric hypertrophy of patient 2.
Whole exome sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted from
peripheral blood white cells using the
QIAamp DNA blood mini kit manufactured
by QIAGEN (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany).
The concentration and purity of the extracted
DNA were determined by NanoDrop One of
Thermo Fisher. Whole exome sequencing
(WES) was performed on DNA samples
from the affected patients on the Illumina
system (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA). The
Agilent SureSelect Human All Exon v7
capture kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA) was
used for exome capture. Data were aligned
to the hg19 reference genome and followed
by creating indexes, marking, and removing
repeated reads using the Picard tool
(http://broadinstitute.gith-ub.io/picard/). To
determine variants and minor allele
frequencies the Genome Analysis Toolkit
(GATK) (https://gatk.broadinstitute.org
/hc/en-us) was used.
In silico analysis
To predict the effect of the detected variants,
the different in silico tools: FATHMM
(http://fathmm.biocompute.org.uk/inherited
.html), MCAP (http://bejerano.stanford.edu/
mcap/), Mutation Assessor (http://
mutationassessor.org/r3/), Mutation Taster
(https://www.genecascade.org/MutationTas
ter2021/), PolyPhen-2 (http://genetics.bwh
.harvard.edu/pph2/), PROVEAN (http://
provean.jcvi.org/seq_submit.php), SIFT
(https://sift.bii.a-star.edu.sg/), and CADD
(https://cadd.gs.washington.edu/snv) were
used. To evaluate the effect of variants on
protein structure, the three-dimensional
structure of the wild type and mutant type
was constructed using Swiss-PDB Viewer
v4.1 with PDB: Q9UGJ0 as a template.
PCR and Sanger sequencing
Sanger sequencing was performed on DNA
samples from the family trio to confirm














![Bài tập Đa dạng thế giới sống [kèm đáp án/ hướng dẫn giải]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251123/thaohoang9203@gmail.com/135x160/5861763951302.jpg)











