http://buihongquan.com
Chương 3. Đng hc phn ng to sinh khi
3.1. Cac khai niê m cơ ban
3.2. Qua t rinh tao sinh kho i vi sinh va t
3.3. Ky thua t nuo i ca y thêo mê
3.4. Ky thu a t nuo i ca y thêo mê co bo sungcơ cha t
3.5. Phương trinh Monod va Đo ng hoc tao sinh kho i vi
sinh va t
12/23/2018 152 Bioreaction engineering.
http://buihongquan.com
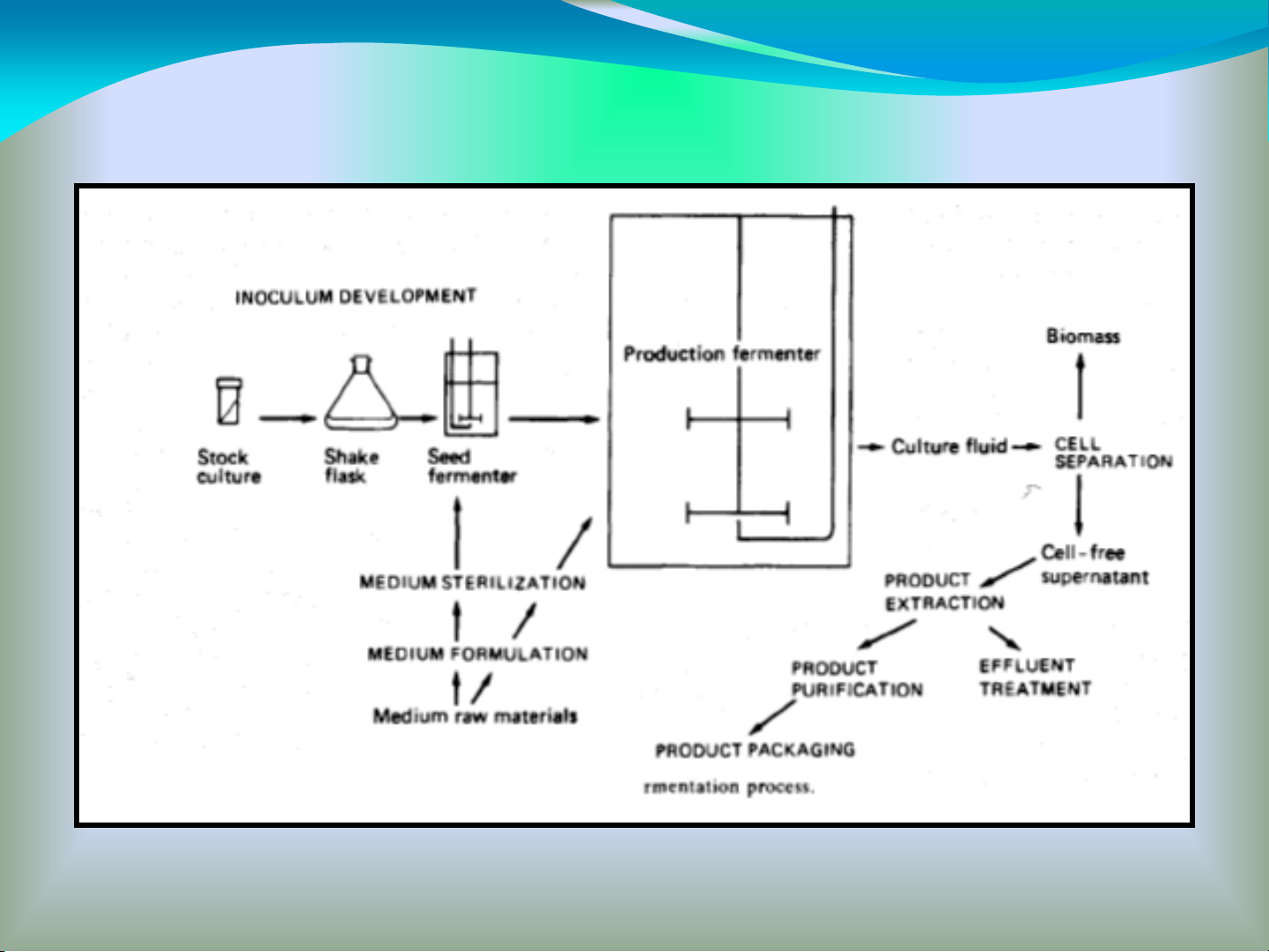
Fermentation Process
12/23/2018 154 Bioreaction engineering.
http://buihongquan.com
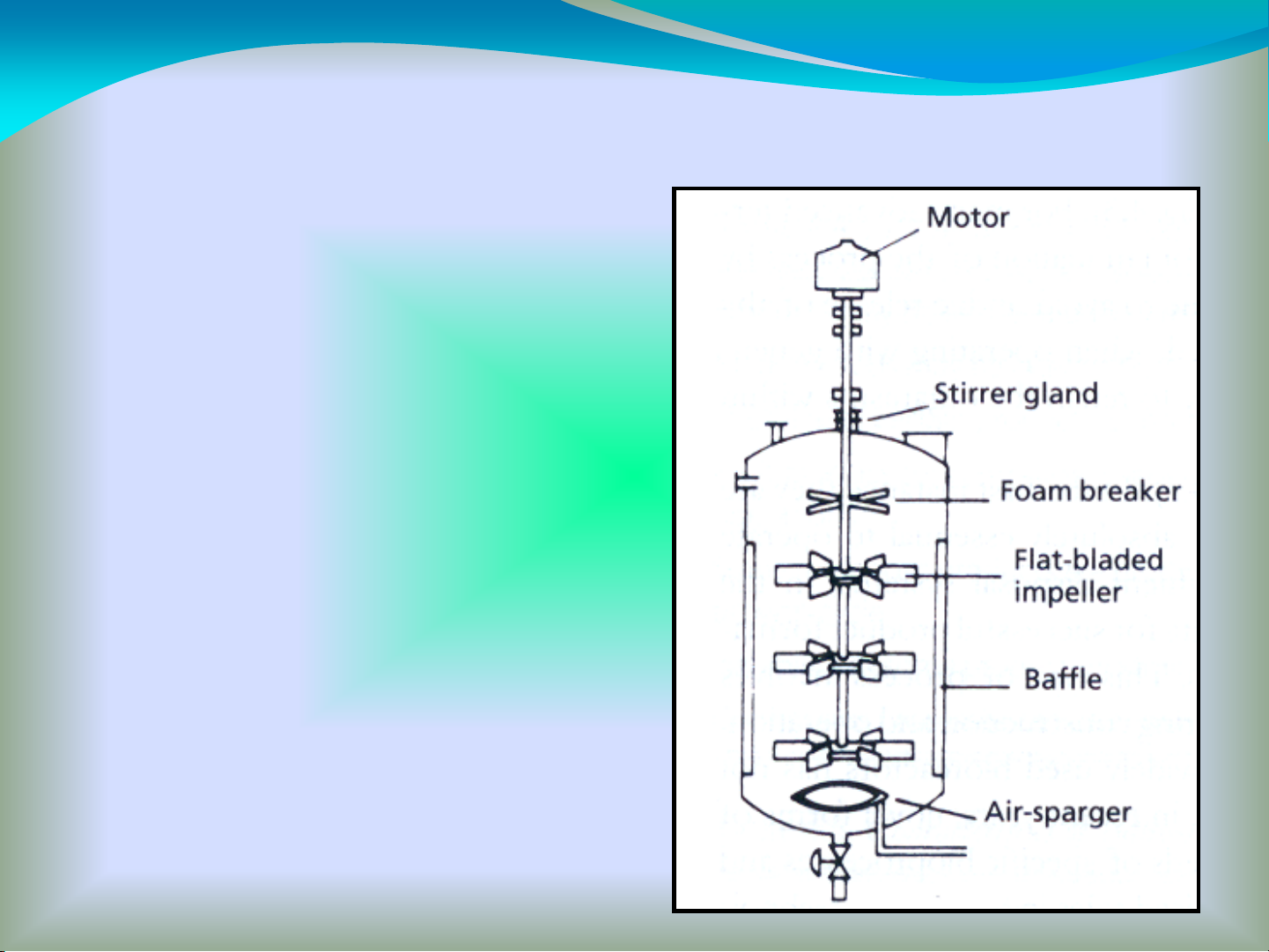
Major Functions of a Bioreactor
1) Provide operation free from
contamination;
2) Maintain a specific temperature;
3) Provide adequate mixing and aeration;
4) Control the pH of the culture;
5) Allow monitoring and/or control of
dissolved oxygen;
6) Allow feeding of nutrient solutions and
reagents;
7) Provide access points for inoculation
and sampling;
8) Minimize liquid loss from the vessel;
9) Facilitate the growth of a wide range of
organisms.
Ref;(Allman A.R., 1999: Fermentation
Microbiology and Biotechnology)
12/23/2018 155 Bioreaction engineering.
http://buihongquan.com
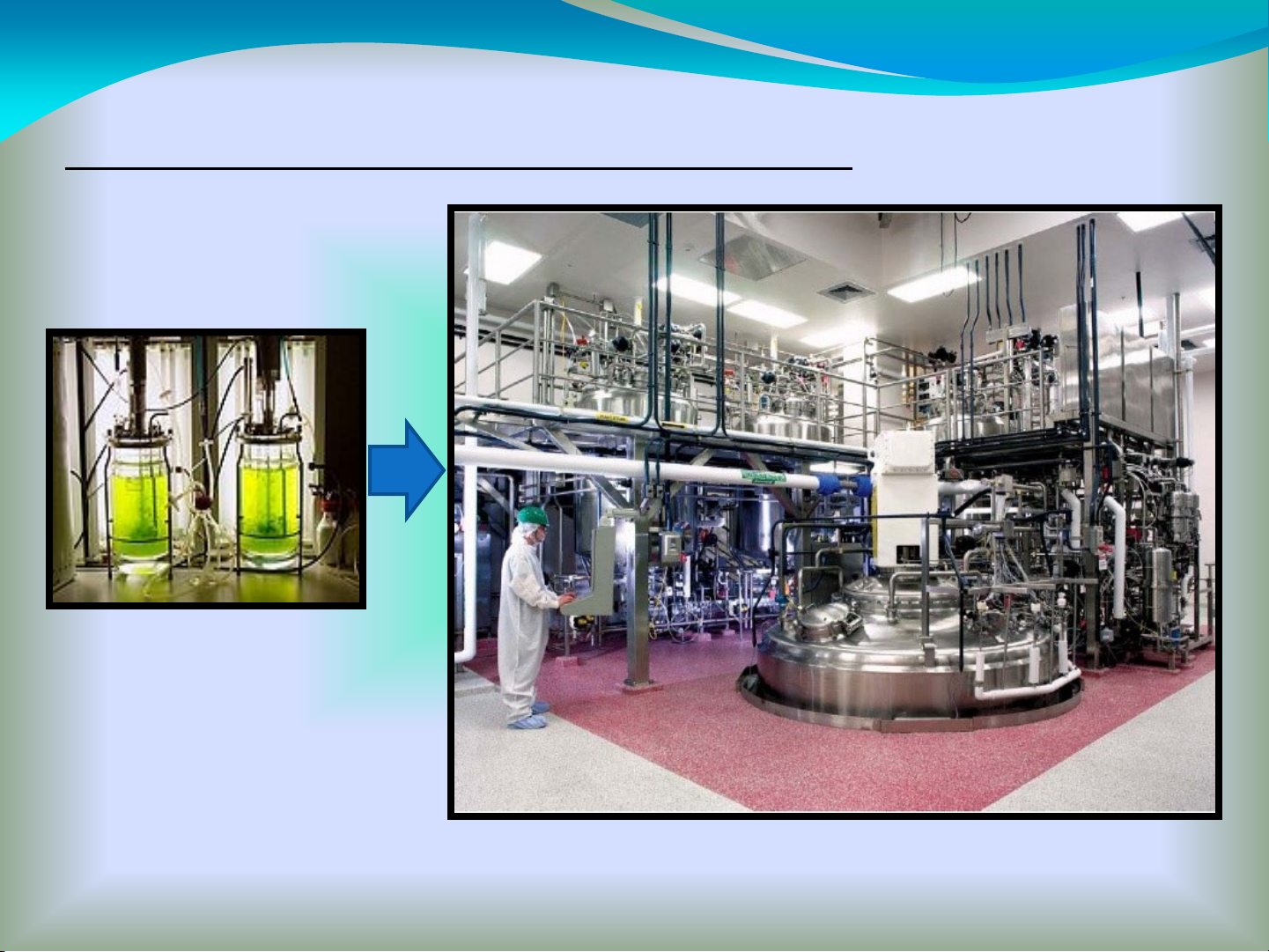
Biotechnological Processes Of Growing
Microorganisms In A Bioreactor
1) Batch culture: microorganisms are inoculated into a fixed
volume of medium and as growth takes place nutrients are
consumed and products of growth (biomass, metabolites)
accumulate.
2) Semi-continuous:
fed batch
-gradual addition of concentrated
nutrients so that the culture volume and product amount are
increased (e.g. industrial production of baker’s yeast);
Perfusion
-addition of medium to the culture and withdrawal of an
equal volume of used cell-free medium (e.g. animal cell
cultivations).
3) Continuous: fresh medium is added to the bioreactor at the
exponential phase of growth with a corresponding withdrawal of
medium and cells. Cells will grow at a constant rate under a
constant condition.
12/23/2018 156 Bioreaction engineering.













![Giáo trình Vi sinh vật học môi trường Phần 1: [Thêm thông tin chi tiết nếu có để tối ưu SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251015/khanhchi0906/135x160/45461768548101.jpg)





![Bài giảng Sinh học đại cương: Sinh thái học [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250812/oursky02/135x160/99371768295754.jpg)



![Đề cương ôn tập cuối kì môn Sinh học tế bào [Năm học mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260106/hoang52006/135x160/1251767755234.jpg)

![Cẩm Nang An Toàn Sinh Học Phòng Xét Nghiệm (Ấn Bản 4) [Mới Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251225/tangtuy08/135x160/61761766722917.jpg)