
Political Ecology
Dr. Annuska Derks

What is Political Ecology?
Difference between explaining
Serengeti‘s declining biodiversity
and destroyed landscape from a:
- apolitical ecology perspective
- political ecology perspective
http://www.planet-wissen.de/natur_technik/naturschutz/serengeti/img/intro_serengeti_grafik1_g.jpg

What is Political Ecology?
Political ecology perspective is about:
-Identifying broader system
-Viewing ecological systems as power-laden
-Taking an explicitly normative approach

What is Political Ecology?
3 assumptions (Bryant and Bailey 1997):
1. The costs and benefits associated with environmental
change are distributed unequally
2. This unequal distribution inevitably reinforces or
reduces existing social and economic inequalities
3. The unequal distribution of costs and benefits and the
reinforcing or reducing of pre-existing inequalities
holds political implications in terms of altered power
relationships between actors
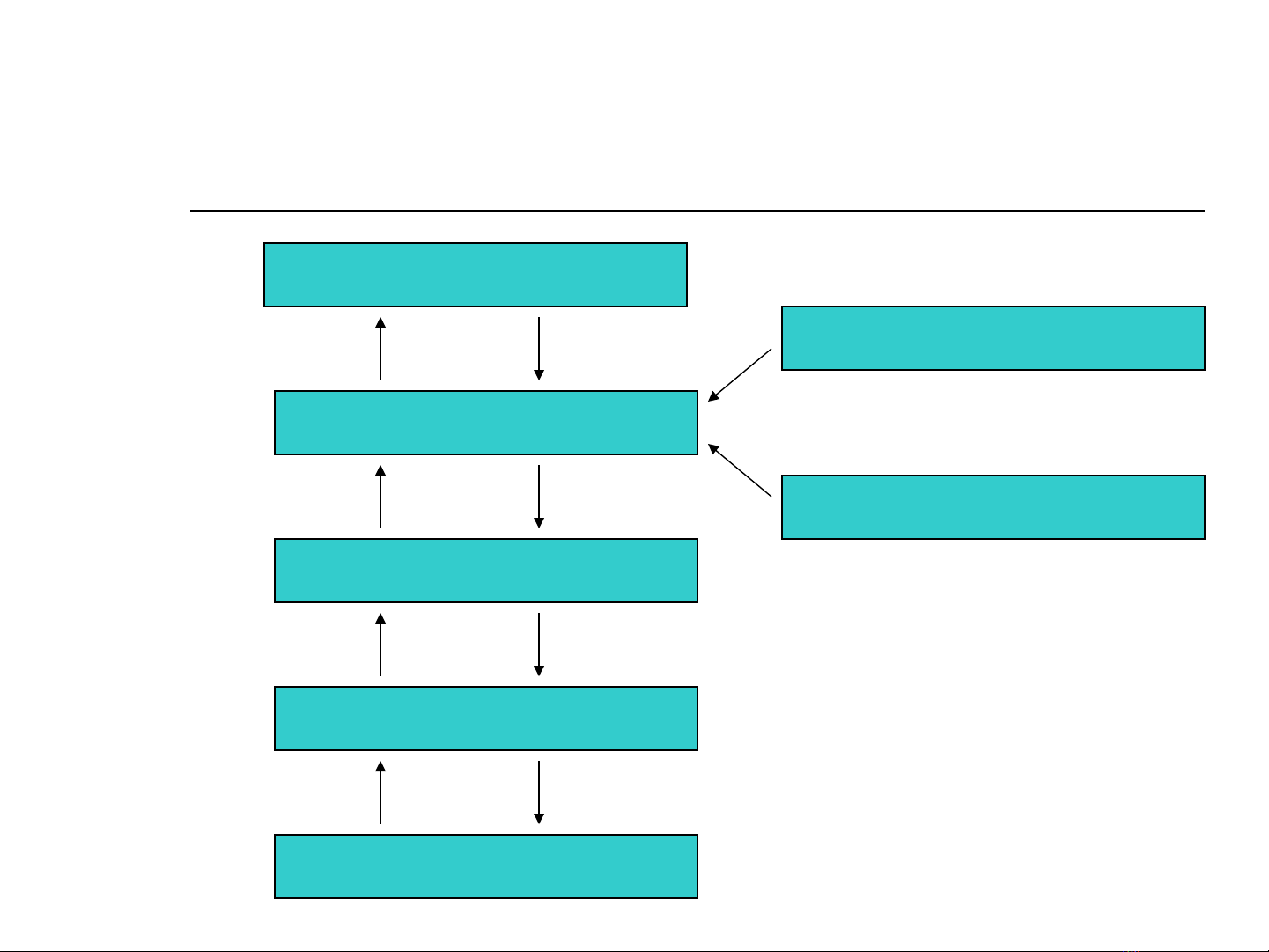
The chain of explanation
Transnational finance
The state
Local/regional institutions
Producers/Communities
Landscape/Ecological system
International institutions
Transnational firms
(Adapted from Robbins 2004: 74)


























