See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317047369
Science and technology diplomacy: a framework at the national level
Article · July 2017
DOI: 10.1108/JSTPM-09-2016-0023
CITATIONS
5
READS
216
6 authors, including:
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Can Iran meet the Paris agreement's target? A scenario-based study to find the strategic gaps between the real and possible state of Iran in 2030 View project
Analysis of Energy System in Sweden based on Time Series Forecasting and Regression Analysis View project
Mohammad Mahdi Zolfagharzadeh
University of Tehran
19 PUBLICATIONS20 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Alireza Aslani
University of Tehran
108 PUBLICATIONS941 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Ali Asghar Sadabadi
University of Tehran
26 PUBLICATIONS43 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Mahdi Hajari
University of Tehran
8 PUBLICATIONS7 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
All content following this page was uploaded by Alireza Aslani on 22 July 2020.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.

Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management
Science and technology diplomacy: a framework at the national level
Mohammad Mahdi Zolfagharzadeh, Alireza Aslani, Ali Asghar Sadabadi, Mahdi Sanaei, Fahimeh Lesan Toosi, Mahdi Hajari,
Article information:
To cite this document:
Mohammad Mahdi Zolfagharzadeh, Alireza Aslani, Ali Asghar Sadabadi, Mahdi Sanaei, Fahimeh Lesan Toosi, Mahdi Hajari,
(2017) "Science and technology diplomacy: a framework at the national level", Journal of Science and Technology Policy
Management, Vol. 8 Issue: 2, doi: 10.1108/JSTPM-09-2016-0023
Permanent link to this document:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/JSTPM-09-2016-0023
Downloaded on: 24 May 2017, At: 01:11 (PT)
References: this document contains references to 0 other documents.
To copy this document: permissions@emeraldinsight.com
The fulltext of this document has been downloaded 5 times since 2017*
Access to this document was granted through an Emerald subscription provided by emerald-srm:401304 []
For Authors
If you would like to write for this, or any other Emerald publication, then please use our Emerald for Authors service
information about how to choose which publication to write for and submission guidelines are available for all. Please
visit www.emeraldinsight.com/authors for more information.
About Emerald www.emeraldinsight.com
Emerald is a global publisher linking research and practice to the benefit of society. The company manages a portfolio of
more than 290 journals and over 2,350 books and book series volumes, as well as providing an extensive range of online
products and additional customer resources and services.
Emerald is both COUNTER 4 and TRANSFER compliant. The organization is a partner of the Committee on Publication
Ethics (COPE) and also works with Portico and the LOCKSS initiative for digital archive preservation.
*Related content and download information correct at time of download.
Downloaded by Australian Catholic University At 01:11 24 May 2017 (PT)

1
Science and Technology Diplomacy: a Framework at
the National Level
Abstract
Purpose:
Science and Technology Diplomacy (STD) is an emerging area in the field of
public policy and technology management. The current work is to overview the
concept of STD based on two approaches “Science and Technology” and
“Diplomacy” to explain its necessity for Non-Aligned Movement (NAM)
member countries.
Methodology:
The present research is designed based on the thematic analysis to identify
major domains and sub-domains of STD. Using MAXQDA software, the initial
codes have been analyzed and validated for the case study. Then, 6 areas and 29
sub-domains are identified based on the fuzzy Delphi and the framework is
designed.
Findings:
Science and Technology diplomacy is defined based on the viewpoint of six
different fields including, political, economics, law and legal issues, social
sciences, philosophy, and science and technology. Each field has its particular
mechanism in STD which will be discussed in the article.
Key Words:
Science and Technology Diplomacy, Political Sciences, NAM countries.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, societies have been increasingly and significantly changing.
Most of these changes are based on a technological transformation; such as ICT
revolution, cognitive sciences and technologies, biological technologies,
astrological and nuclear developments. Until mid-twentieth, technology
influenced only certain parts of industries while in recent decades, it has
Downloaded by Australian Catholic University At 01:11 24 May 2017 (PT)

2
influenced almost all aspects of an individual’s life to the extent that it is
impossible to imagine life without technology. Thus, the governments have
tried to develop their science and technology infrastructures to improve the
quality of the life of their citizens (adikwu et al., 2016). Therefore, science and
technology are crucial factors for both governance and development.
At the same time, the development of technology in a number of fields has a
direct impact on global political issues, such as the invention of the atomic
bomb, nuclear energy, biological sciences, and human space conquest, as well
as economy, particularly the creation of knowledge-based economy.
In such a situation, each country, especially the pioneering ones with the power
of affecting global issues, attempt to be influential as much as possible
(Shabudin et. al., 2017). Yet, the domain of “Science and Technology
Diplomacy has remained untapped in their attempts” (STD). This novel field, in
its basic form, is made of the confrontation and contribution of two major
strategic fields of “diplomacy” and “science and technology” and is considered
an important tool for pioneering countries today, to pursue their goals at the
global level.
Defined as the technique of pursuing foreign policy, the term diplomacy has a
long record in the literature of foreign policy and international affairs. Thus in
general, diplomacy involves methods, procedures, and measures adopted by a
country adopt to achieve its goals in foreign policy. In this respect, diplomacy is
a tool to assist the countries in achieving their goals regarding their relations
with other countries. Having the quality of a tool, diplomacy has the power to
be used along with other tools in order to accomplish even more ambitious
goals. In other words, diplomacy provides the appropriate condition for other
tools to play their roles (Barati, 2012). Therefore, it can be said that the main
purpose of STD is “to take advantage of not only the capacity of science and
technology in order to accomplish the goals in the field of foreign policy but
also the capacity of diplomacy in order to pursue science and technology goals”.
Science and technology have a lot of interesting aspects such as providing
authority, providing wealth, being the core of development, entering every
aspect of human life, which leads diplomacy to make advantage of it; (Vice-
Presidency for Science and Technology, 2011). In addition, the potential of
diplomacy makes it even more applicable in science and technology
development such as creation of new markets for knowledge-based,
technological products through interaction with other countries.
(Miremadi,2014) .
Downloaded by Australian Catholic University At 01:11 24 May 2017 (PT)
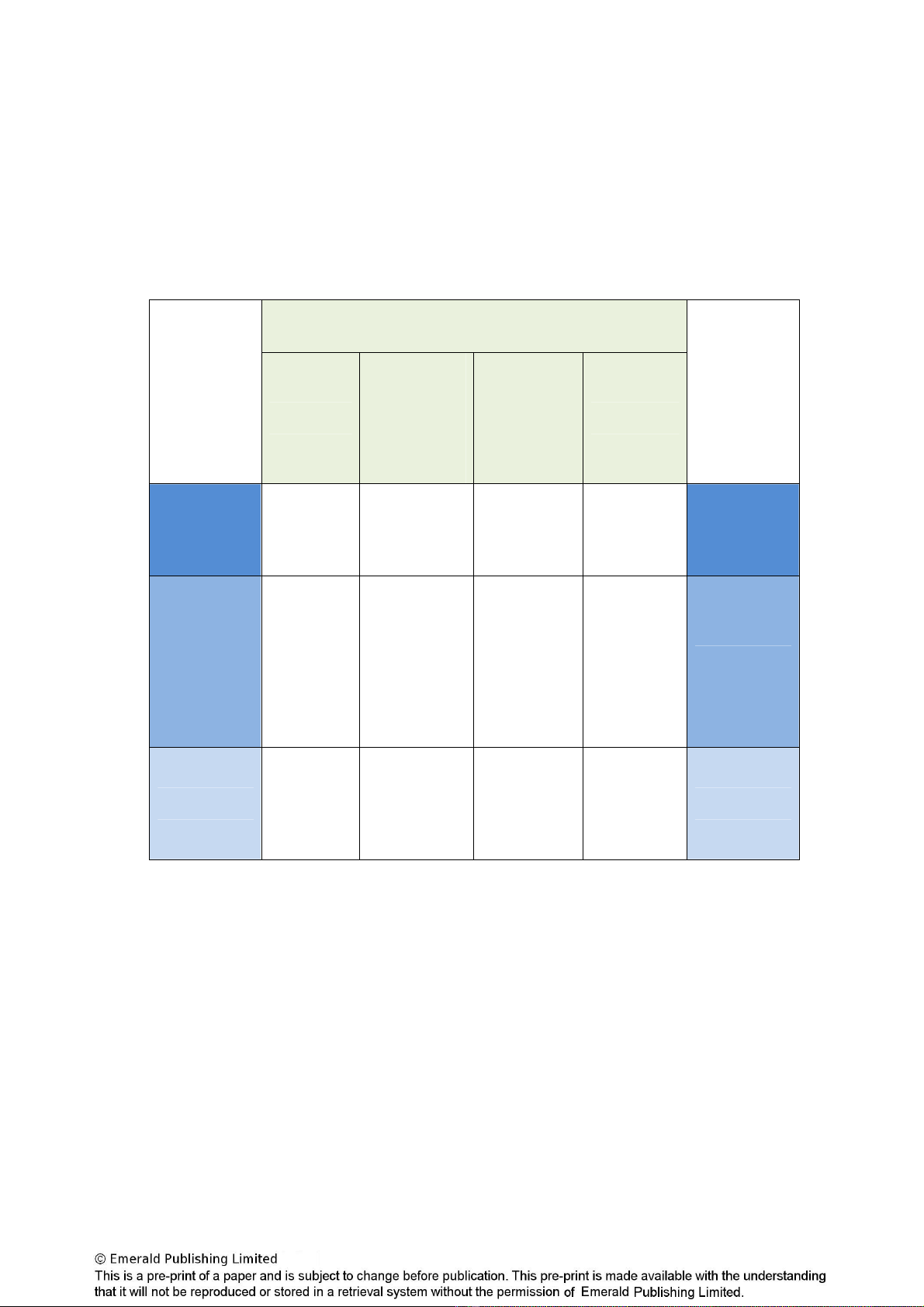
3
Miremadi, based on Katz and Smith’s model, reveals the reciprocal services
possible between scientific communities and diplomatic ones. The following
table illustrates such reciprocal services.
Reciprocal services between scientific communities and diplomatic circles
Levels of
Contributions
The Reciprocal Services of Scientific and Diplomatic
Communities
Levels of
Contributions
Tools
Scientific
Community’s
Contribution
to Foreign
Policy’s
Mission
Government’
s
Contribution
to Scientific
Community
Goals
Tools
Highest Level
Corporate
Collaboration
Catching up
the
Technological
Gap
Financial and
Scientific
Capabilities
Bilateral
Agreements
Highest Level
Medium Level
International
Team
Collaboration
Building
Bridges
among
Nations
through The
Universal
Language of
Science
Financial and
Scientific
Capabilities
Regional
Instruments
Medium
Level
Lowest Level
International
Personal
Collaboration
between
Scholars
Nation
Branding as
Technology
Leader or
Follower
International
Recognition of
The Right to
Technology
Internationa
l
Instruments
Lowest Level
Comparing the concept of STD with the similar concept of science and
technology cooperation helps in better understanding of STD and at the same
time the fact that which phenomena can be defined based on this concept.
International science and technology diplomacy and STD might overlap in some
cases but they are analytically different. International cooperation generally
concerns scientific development while STD mainly aims to use science for the
advancement of foreign policy goals of one country or mutual benefit of several
countries. That is, international scientific cooperation is administrated by
scientific groups while STD is consisted of government members active in both
foreign policy and scientific cooperation. Thus, scientific cooperation might be
defined kind of STD or might not. (Turekian, et al., 2014)
Downloaded by Australian Catholic University At 01:11 24 May 2017 (PT)







![Chính sách đối ngoại, hội nhập quốc tế [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250716/truonglam.lxagvn@gmail.com/135x160/81071752736922.jpg)


















