
Lecture 3. NUMERICAL SUMMARYLecture 3. NUMERICAL SUMMARY
Data Measurements
Locations
Variability Measures
Shape
[1] Chapter 3, pp. 99 - 162
[3] Chapter 2
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS– Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 1
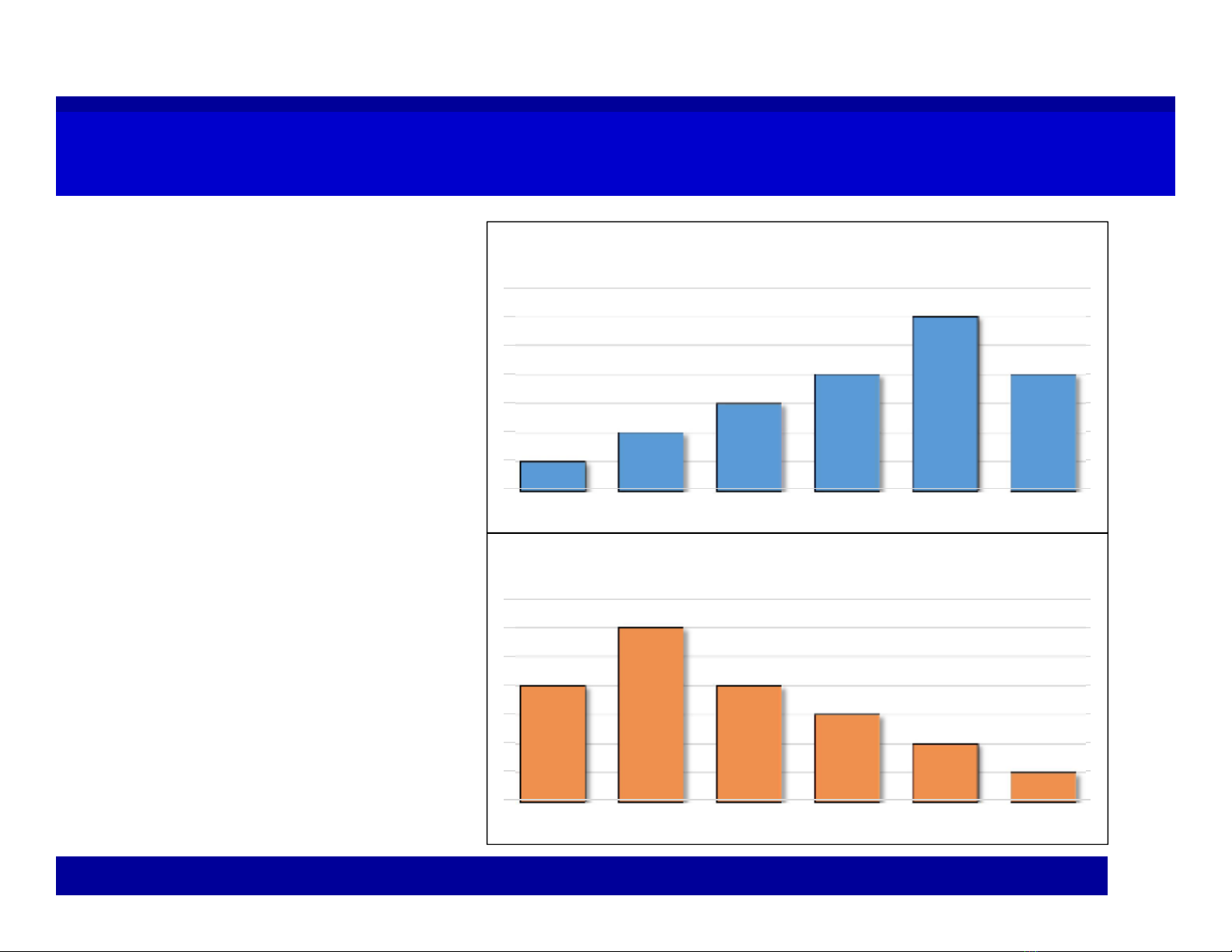
ComparisonComparison
Profit of two
project A & B
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS– Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 2
5%
10%
15%
20%
30%
20%
123456
Profit of Project A(million)
20%
30%
20%
15%
10%
5%
123456
Profit of Project B(million)
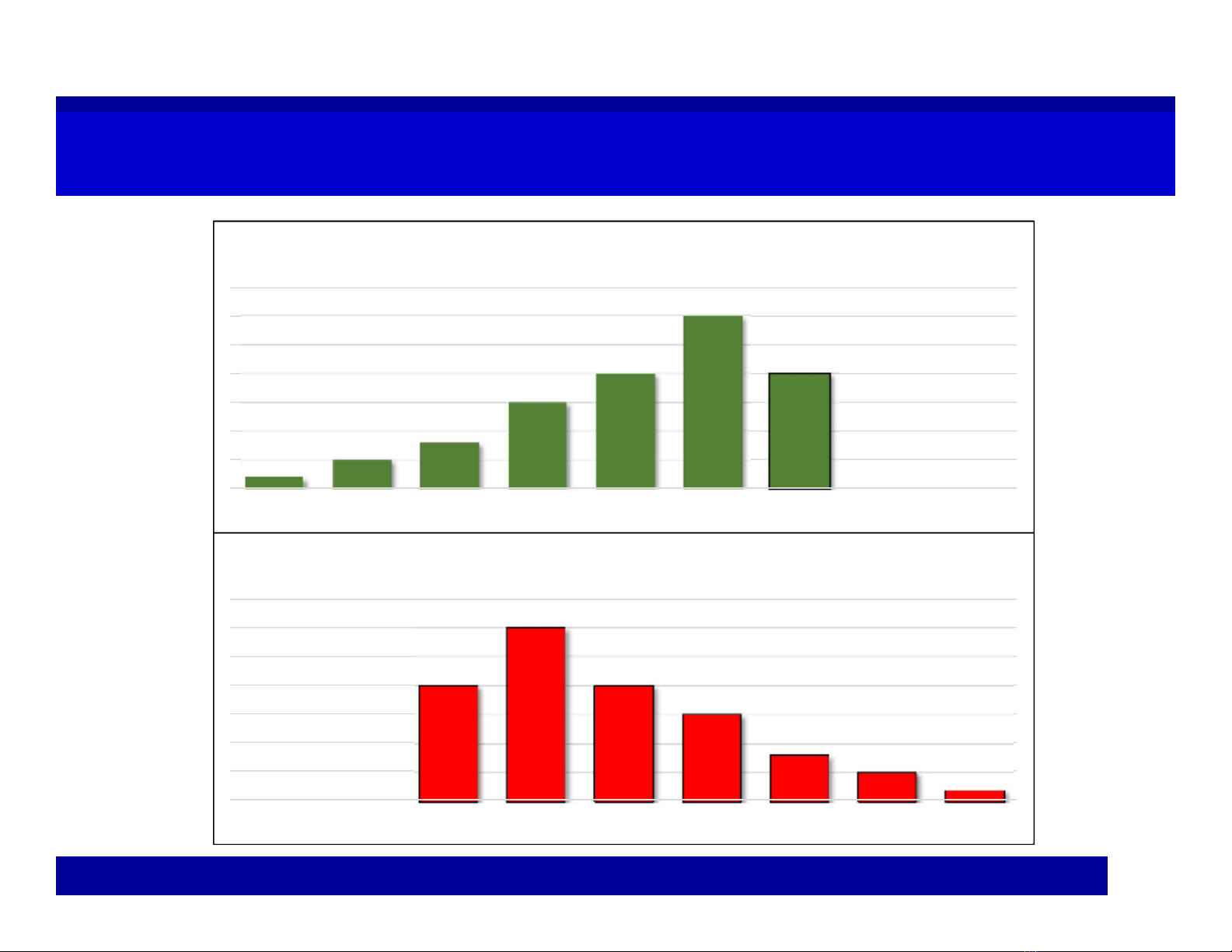
ComparisonComparison
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS – Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 3
2% 5% 8%
15%
20%
30%
20%
0% 0%
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Profit of Project C(million)
0% 0%
20%
30%
20%
15%
8% 5% 2%
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Profit of Project D(million)
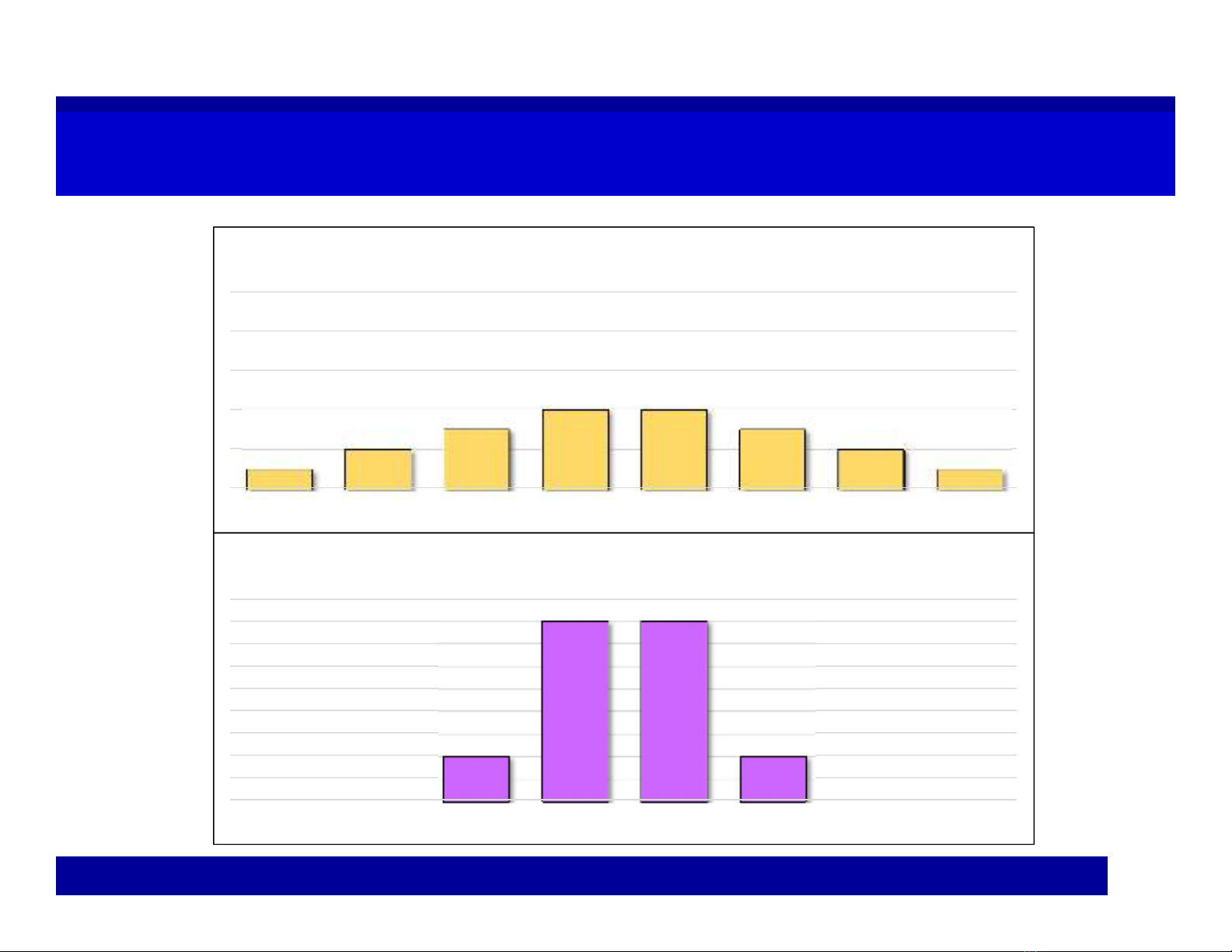
ComparisonComparison
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS – Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 4
0% 0%
10%
40% 40%
10%
0% 0%
-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Profit of Project F(million)
5% 10% 15% 20% 20% 15% 10% 5%
-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Profit of Project E(million)

Data MeasurementsData Measurements
Location:
Minimum, Maximum
Central Tendency: Mean, Median, Mode
Quantile: Quartile, Percentile
Variability:
Range
Variance (Var)
Standard Deviation (SD)
Coefficient of Variation (CV)
Interquartile Range (IQR)
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS – Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 5





![Bài giảng Tính toán tiến hóa: Bài 6 - TS. Huỳnh Thị Thanh Bình [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2023/20230211/kimphuong1001/135x160/8401676110802.jpg)




















