
Lecture 4. BASIC PROBABILITYLecture 4. BASIC PROBABILITY
Probability
Outcome – Event
Complement Event, Intersection Event, Union Event
Mutually Exclusive, Independent, Collectively
Exhausive, Partitions
Bernoulli Formula
Total Probability, Bayes’ Theorem
[1] Chapter 4, pp. 169 - 212
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS – Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 1

“Problem of Points”“Problem of Points”
2 players A and B, contributed 50 Franc each.
The game is winner – loser only (no draw), A and B are
equally-likely to win in each match.
Game rule: play 9 matches, the one wins more is final
winner and takes all of 100F
But the game had stopped after 7 matches, and scores
at that time of A and B are 4 and 3, respectively.
How could they distribute the money?
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS – Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 2

4.1. Probability4.1. Probability
Probability is quantitative measure of uncertainty, the
chance that an uncertain event will occur.
Probability: Subjective and Objective
Probability of event A is denoted by P(A)
0 ≤ P(event) ≤ 1
P(always) = 1
P(impossible) = 0
() > (): A is more possible to occur than B
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS – Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 3
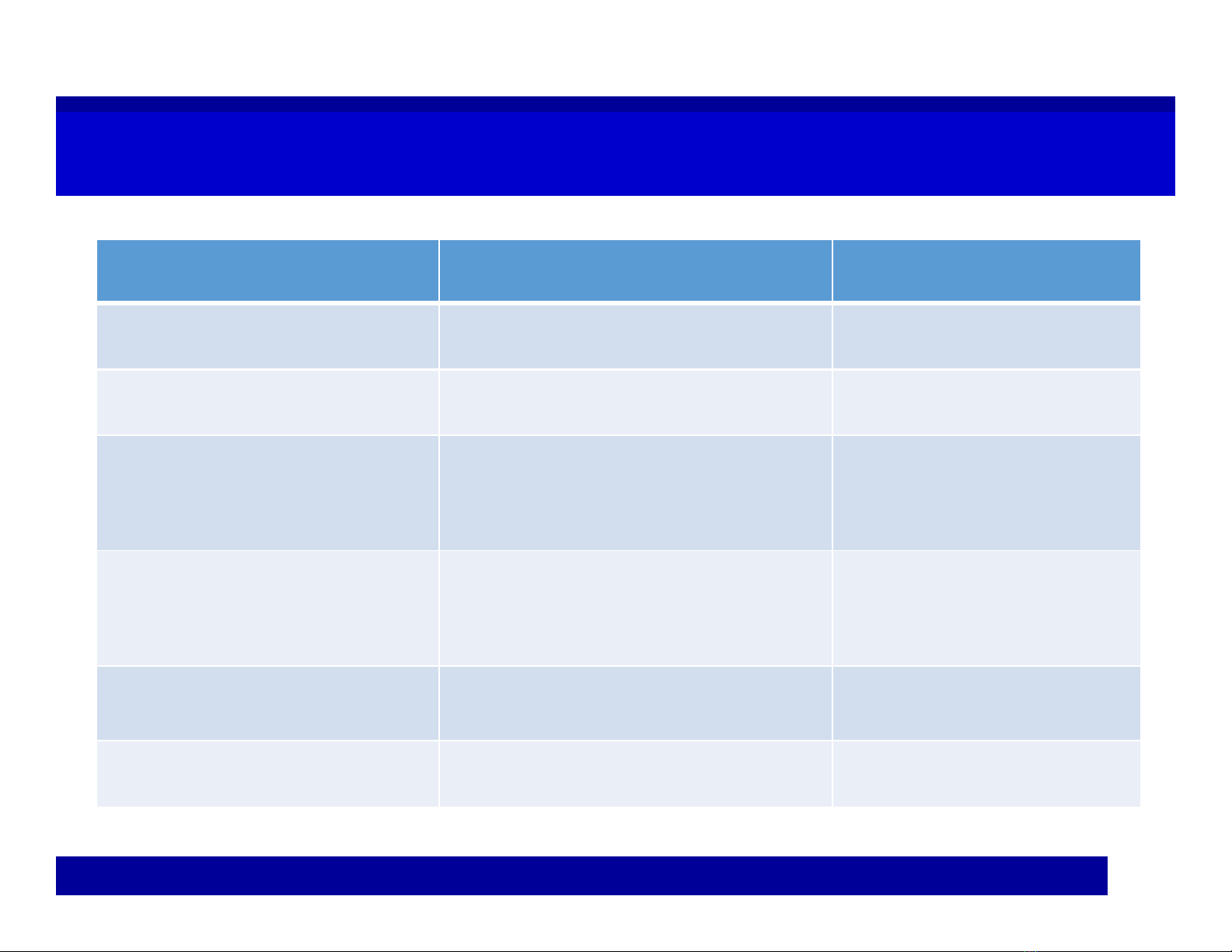
Experiment – Outcome - EventExperiment – Outcome - Event
Experiment Outcome Event
Flip a coin Head, tail ‘Head’, ‘tail’
Toss a die 1,2,3,4,5,6 dot(s) ‘greater than 3’
Do an exam Score = 0, 1, 2,…, 10 ‘pass’;
‘excellent’
Invest in a project Profit: (+), (–), zero ‘Non negative’
‘profitable’
Apply for a job Pass, fail
Do a job Salary = …
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS– Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 4

Classical ProbabilityClassical Probability
Sample space: all basic outcomes, denoted by Ω
Assumes all basic outcomes in the sample space are
equally-likely to occur
Number of basic outcomes:
Number of basic outcomes for event A:
Probability of event A:
=
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS – Bui Duong Hai – NEU – www.mfe.edu.vn/buiduonghai 5





![Bài giảng Tính toán tiến hóa: Bài 6 - TS. Huỳnh Thị Thanh Bình [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2023/20230211/kimphuong1001/135x160/8401676110802.jpg)




















