
Smart cards
a fascinating and fruitful adventure
Gemalto Technology & Innovation
Nguyen Quang Huy
3
No internal timer, battery
No keyboard, display, network interface
Current generation
µ-processor: 16-bits, <=10MHz
RAM: 4K
ROM: 100K for code storage
E2PROM (105 updates ): 64K for data storage
I/O: serial (9600 bps),
–Contactless protocols: MiFare, FeliCa, Calypso
Next generation
µ-processor: 32-bits, up to 100MHz
Flash memory: more durable and more rapid
I/O: USB (12 Mbps)
–Contactless open protocols: NFC, ZigBee
25 mm
25 mm2
2
Smart Card HW
4
Smart Card SW
Proprietary architecture
Undisclosed specification
Tedious application development
Closed configuration: no application can be added after issuance
Open architecture
Open specification
High-level programming languages
Post-issuance applications are available
Some open architectures
Java Card
MULTOS
.NET Card
Basic Card
5
Example: Java Card
Introduced by Schlumberger in 1996
Leading open multi-applicative architecture
>5 billions Java-embedded cards issued
Applications (applets) developed in Java
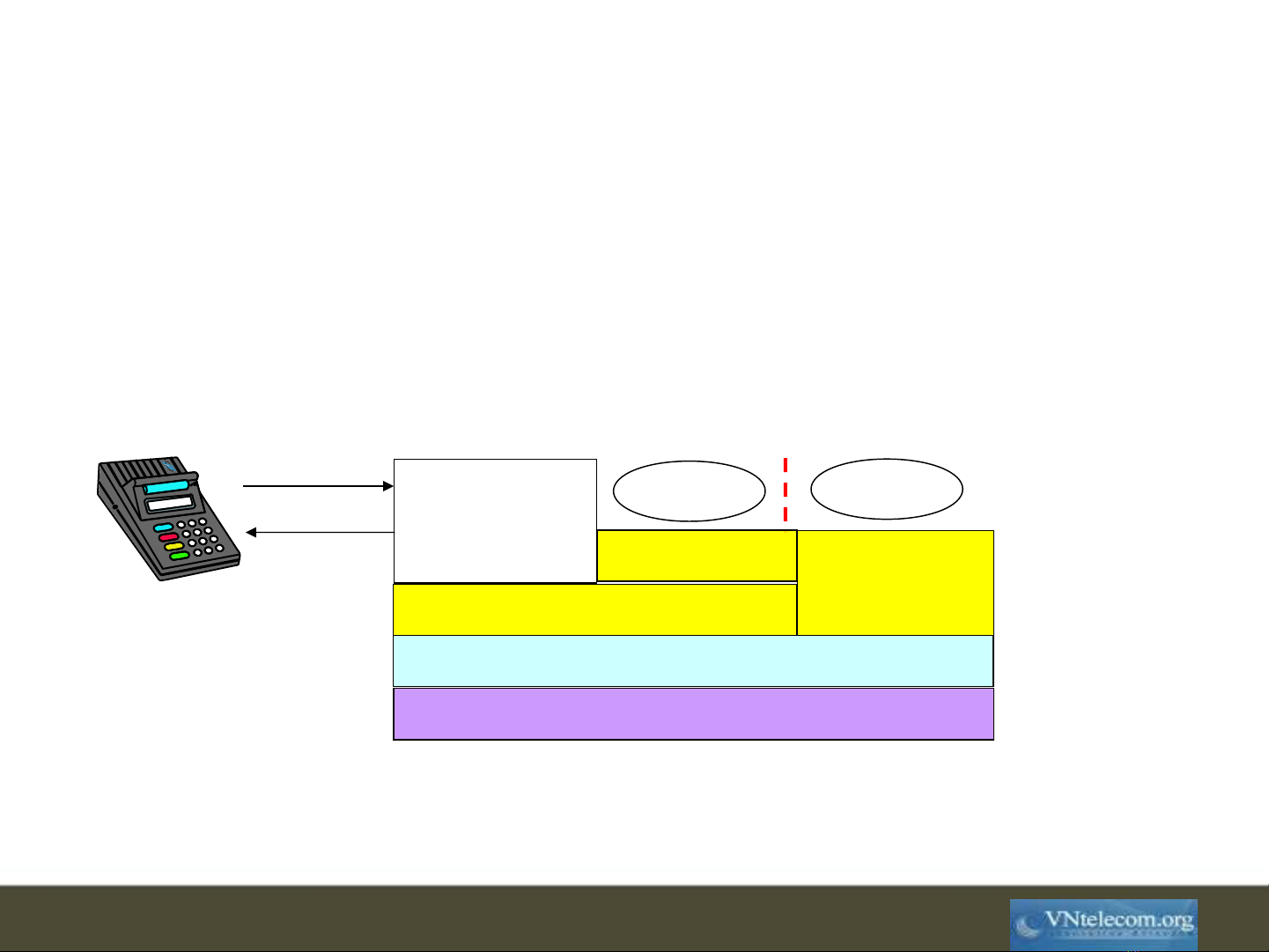
Integrated Circuit
Operating System
Java Card Virtual Machine
API in Java Native
API
Card
Manager
Applet 1 Applet 2
JC Firewall
I/O command




![Giáo trình lý thuyết kỹ thuật điều khiển tự động 20 [Năm xuất bản]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2011/20110119/cindy03/135x160/lythuyetdieukhientudong_20__17.jpg)


![Giáo trình lý thuyết kỹ thuật điều khiển tự động 17: [Mô tả/Định tính - ví dụ: Kinh nghiệm, Mới nhất...]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2011/20110119/cindy03/135x160/lythuyetdieukhientudong_17__5288.jpg)
![Giáo trình lý thuyết kỹ thuật điều khiển tự động 16: [Mô tả/Định tính thêm nếu cần]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2011/20110119/cindy03/135x160/lythuyetdieukhientudong_16__6022.jpg)
![Giáo trình lý thuyết kỹ thuật điều khiển tự động 15: [Mô tả/Định tính - Ví dụ: Tổng quan, Chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2011/20110119/cindy03/135x160/lythuyetdieukhientudong_15__542.jpg)
![Giáo trình lý thuyết kỹ thuật điều khiển tự động 14: [Mô tả/Định tính]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2011/20110119/cindy03/135x160/lythuyetdieukhientudong_14__585.jpg)














![Đề cương đề tài nghiên cứu khoa học [chuẩn nhất/mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251117/duong297/135x160/26111763433948.jpg)

