1
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION
AND TRAINING
VIETNAM ACADEMY OF SCIENCE
AND TECHNOLOGY
GRADUATE UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
……..….***…………
DAO THI THUY QUYNH
IMPROVE THE EFFICIENCY OF
CONTENT-BASED IMAGE RETRIEVAL THROUGH
WEIGHT ADJUSTMENT TECHNIQUE OF THE
DISTANCE FUNCTION
Major: Computer Science
Code: 9 48 01 01
SUMMARY OF PHD THESIS
Ha Noi – 2019
2
The thesis has been completed:
Graduate University Of Science And Technology - Vietnam Academy Of
Science And Technology
Supervisor 1. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ngo Quoc Tao
Supervisor 2. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen Huu Quynh
Review 1:
Review 2:
Review 3:
The thesis will be defended at the Board of Examiners of Graduate
University Of Science And Technology - Vietnam Academy Of Science
And Technology, at……………….on………………………….
The thesis can be explored at:
- Library of Graduate University Of Science And Technology
- National Library of Vietnam

1
PREFACE
1. Motivation of the thesis
Image database is becoming more and more popular in various application
fields such as remote sensing, crime prevention, medicine, education ... The
evolution of image acquisition, transmission and storage techniques has allowed
the construction of very large image databases. These factors have prompted the
attention of the image retrieval community to propose ways to effectively exploit
this image database.
Content-based image retrieval techniques are time-consuming, costly, and
depend on the subjective perception of the descriptors. Moreover, when changes
are needed, this system is difficult to implement.
To overcome this problem, in the early 1990s, content-based image retrieval
(CBIR) was launched. The basic idea of this approach is to use automated visual
feature extraction techniques to produce content descriptions from images, such
as color, texture, and shape characteristics. These content descriptions are used
for indexing images. There are many content based image retrieval systems that
have been proposed. However, many experiments on CBIR systems indicate that
low-level content often fails to describe high-level semantic concepts that appear
in the user's mind. The performance of CBIR systems is still far from the users'
expectations.
Therefore, the thesis chooses the topic of "Improve the efficiency of content-
based image retrieval through weight adjustment technique of the distance function" to
contribute to solving existing problems.
2. The objective of the thesis
The thesis proposes a number of image retrieval methods to improve image
retrieval accuracy. These methods will address issues of reducing semantic gaps
between low-level features and high-level concepts of images.
3. The major contributions of the thesis
Propose SRIR method (Semantic–Related Image Retrieval method),
AWEIGHT method (An efficient image retrieval method using adaptive
weights).
4. Thesis organization
The contents of the thesis are presented in three chapters.
Chapter 1 introduces the fundamentals of content-based Image retrieval.
Chapter 2 presents the semantic-related image retrieval method.
Chapter 3 presents an efficient image retrieval method using adaptive
weights.
Final, the thesis presents conclusions and future research.
2
Chapter 1. OVERVIEW OF CONTENT-BASED
IMAGE RETRIEVAL
1.1. Introduction
Various types of multimedia sources are increasing rapidly, such as visual data
in smartphones, 2D / 3D applications, web content, etc. Therefore, the need for
image applications is more important than ever. However, visual media requires a
significant amount of processing and storage. It requires efficient methods to
index, store, analyzes and retrieval visual information from image databases.
Therefore, retrieval images to ensure quickness, accuracy, and efficiency
becomes one of the challenging tasks.
1.1.1. Text-based image retrieval
The original approach for image retrieval is based on the text that describes the
image, in which the images are indexed by keywords, topics or classification
codes. These keywords, topics or classification codes are used in the retrieval
process. However, with large image databases, the difficulties faced by the text-
based retrieval approach are becoming more serious, for example: this process is
labor-intensive, time-consuming and subjectivity of the description. To overcome
these problems, a content-based image retrieval approach was born. In CBIR, the
image contents are automatically extracted from the images themselves used for
retrieving the image.
1.1.2. Content-based image retrieval
In CBIR, images can be searched either using low-level features (ie colors,
shapes, and textures) or using high-level semantic concepts.
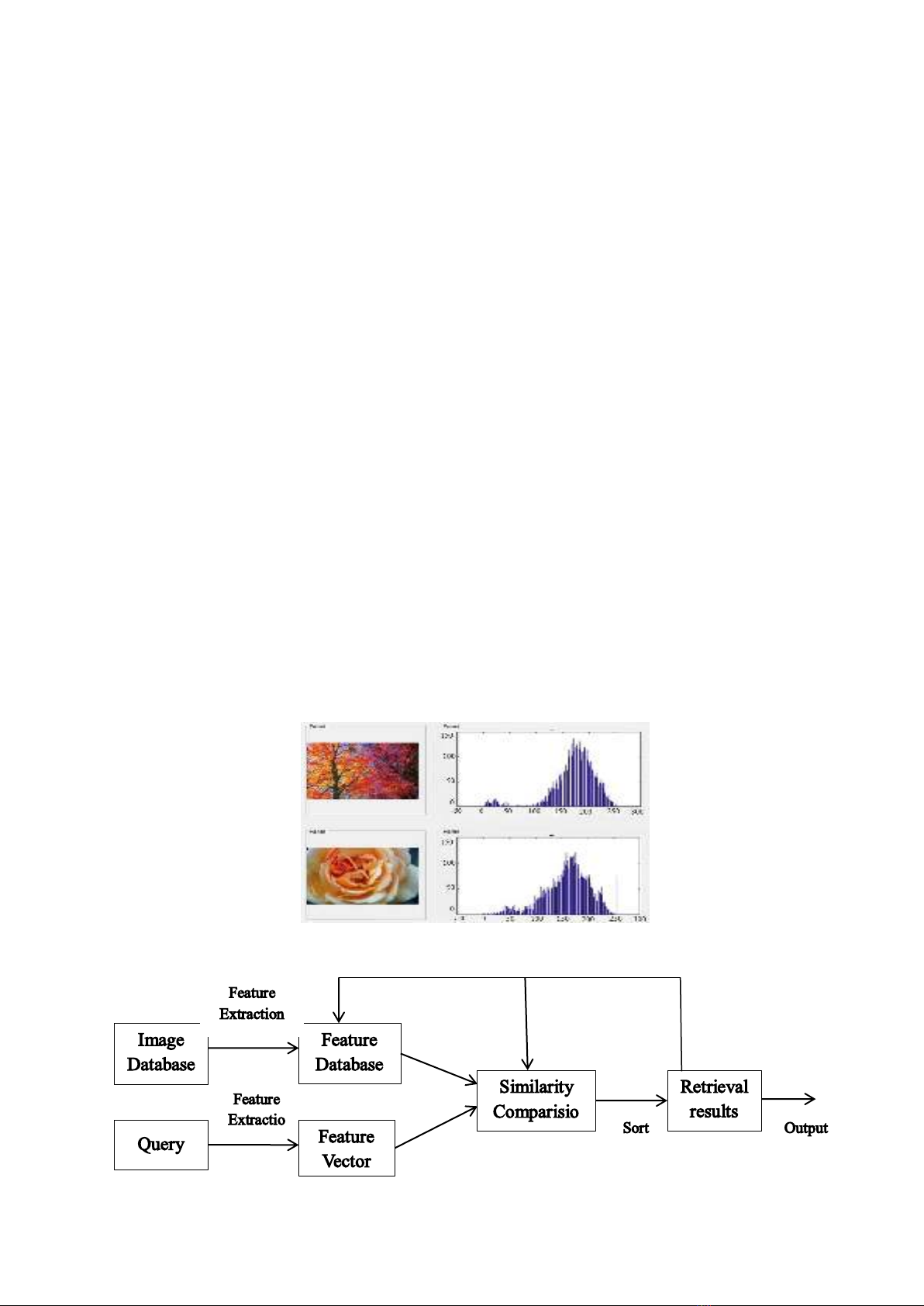
Figure 1.1. Illustration of semantic distance.
The architecture of the image-based retrieval system is shown in Figure 1.2.
Figure 1.2. The architecture of content-based image retrieval system.
3
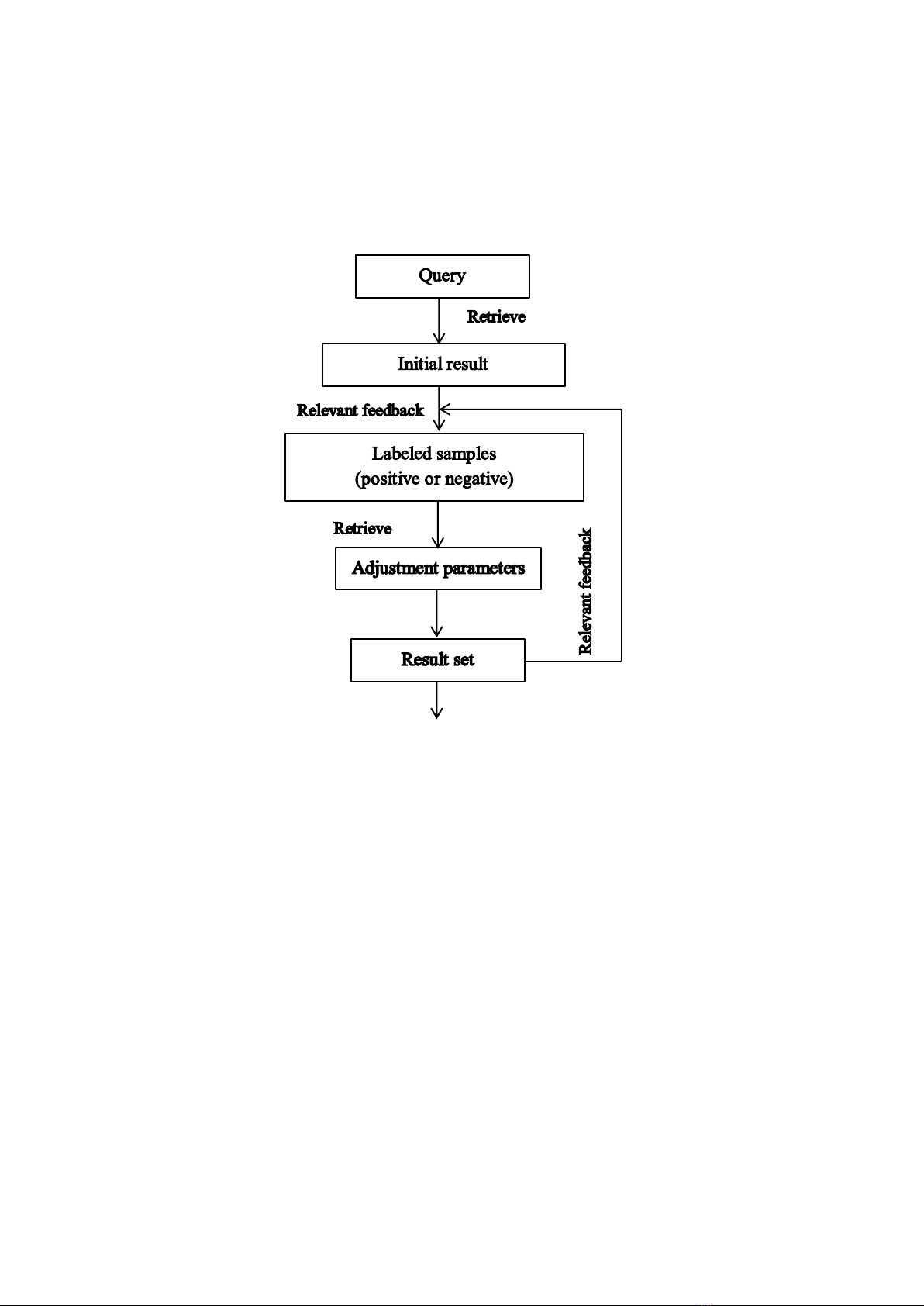
Figure 1.3 shows the implementation mechanism of the relevant feedback in
CBIR. When the initial retrieval results are available, the user selects the related
images in this list of results as labeled samples (positive or negative). Based on
this training set, a machine learning algorithm is implemented to adjust the
parameters. Based on the parameters that have just been learned, image retrieval
is performed. The process is repeated until the user is satisfied.
Figure 1.3: Image retrieval diagram using machine learning with relevance
feedback.
1.1.3. Related works
Several CBIR methods have been proposed, which are the core of the systems,
such as: VisualSeek, SIMPLicity, Blobwworld, WebSeek, Image Rover….
1.2. Feature extraction
1.2.1. Color feature
The color feature is used very effectively for retrieving color images in the
image database. Color descriptions are extracted and compared effectively, so
they are suitable for visual characteristics based retrieval.
1.2.2. Texture feature
Image texture is an important feature of an image to describe the surface
properties of an object and its relationship to surrounding areas.
1.2.3. Shape feature
The shape features of images carry semantic information and can be classified
into two categories: contour-based and region-based.


























