
TRUY N THÔNG SỀ Ố
DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
Week 9

Reference
•“Digital communications: Fundamentals and Applications” by
Bernard Sklar
•Telecommunication Networks - Information Theory, Vinh
Dang
(*) H Văn Quân – Khoa CNTT – ĐH Bách Khoa TpHCMồ
[1]. R. E. Ziemer & W. H. Transter, “Information Theory and
Coding”, Principles of Communications: Systems,
Modulation, and Noise, 5th edition. John Wiley, pp. 667-720,
2002.
[2]. A. Bruce Carlson, “Communications Systems”, Mc Graw-
Hill, 1986, ISBN 0-07-100560-9
[3]. S. Haykin, “Fundamental Limits in Information Theory”,
Communication Systems, 4th edition, John Wiley & Sons Inc,

Tu n tr cầ ướ
•B gi i mã Maximum likelihoodộ ả
•Quy t đ nh m m / c ng (soft decisions ế ị ề ứ
and hard decisions)
•Gi i thu t Viterbiả ậ
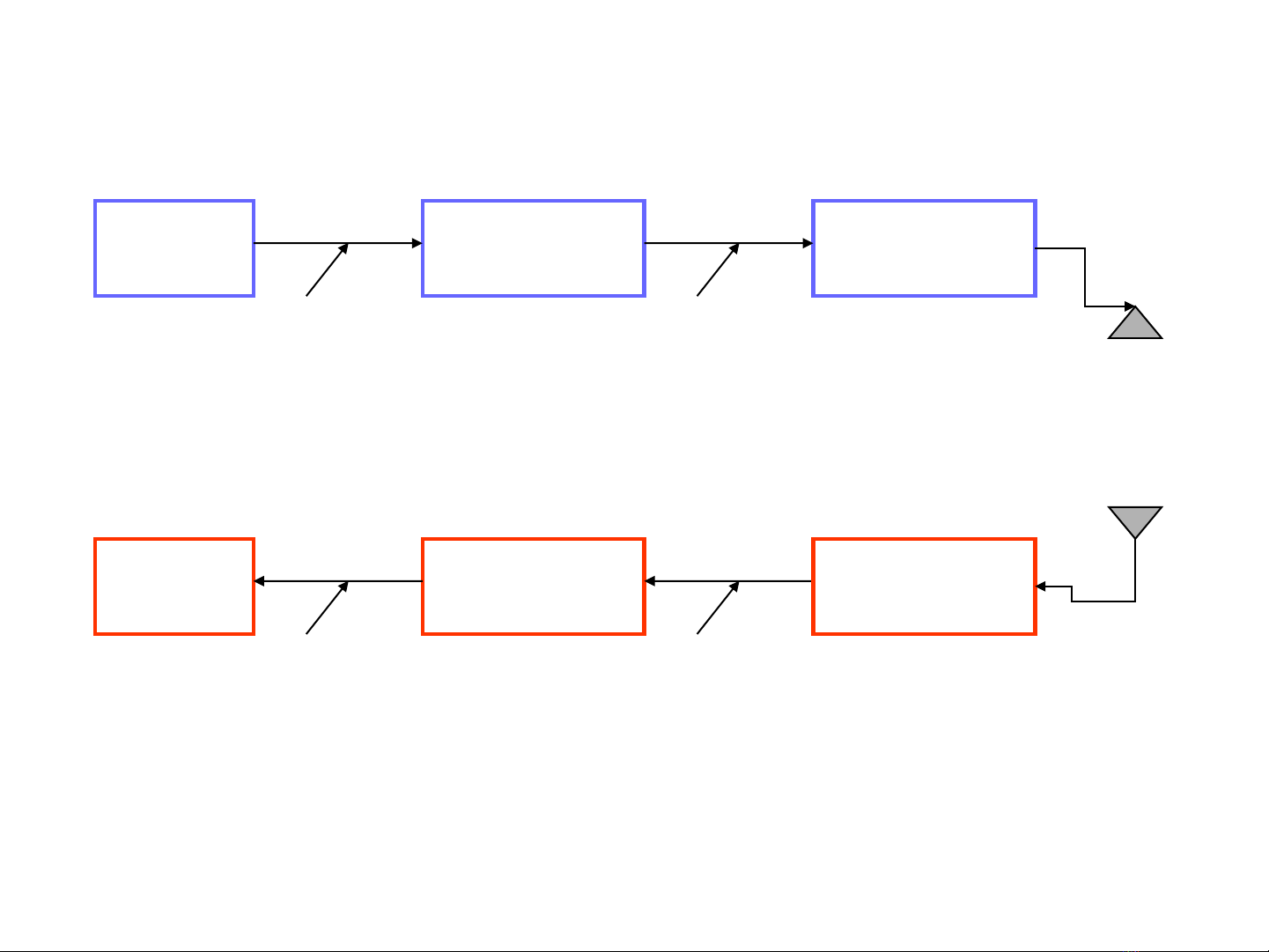
Block diagram of the DCS
dBranch worper outputs
1
dBranch worfor
outputsr Demodulato
sequence received
321
,...),...,,,(
n
nijii
i
i
i
,...,z,...,zzZ
ZZZZ
=
=Z
Information
source
Rate 1/n
Conv. encoder Modulator
Information
sink
Rate 1/n
Conv. decoder Demodulator
sequenceInput
21
,...),...,,(
i
mmm=m
bits) coded ( rdBranch wo
1
sequence Codeword
321
,...),...,,,(
n
nijiii
i
,...,u,...,uuU
UUUU
=
=
=G(m)U
,...)
ˆ
,...,
ˆ
,
ˆ
(
ˆ
21 i
mmm
=
m
Channel
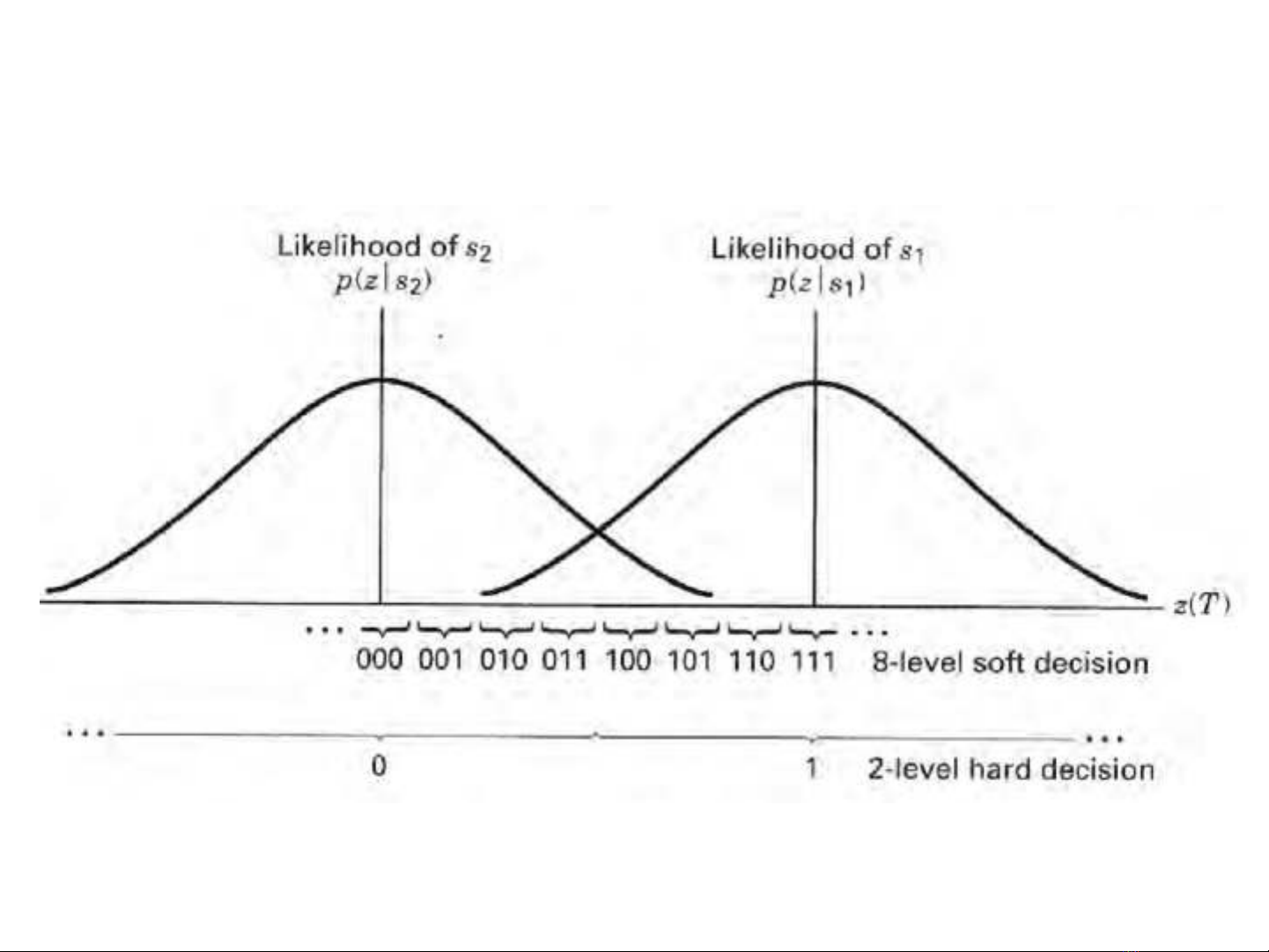
Quy t đ nh m m / c ngế ị ề ứ

![Câu hỏi ôn tập môn Truyền thông số [năm hiện tại]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250704/kimphuong1001/135x160/51751592781.jpg)





![Đề kiểm tra cuối kỳ môn Thu trong truyền thông số [năm]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2020/20200906/tamynhan4/135x160/3471599383353.jpg)




![Đề thi kết thúc học phần môn Truyền thông trong kinh doanh [năm học mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251015/dilysstran/135x160/93281760499390.jpg)


![Bài tập nhóm truyền thông marketing tích hợp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250904/hakanami1502@gmail.com/135x160/90671756969236.jpg)





![Định vị doanh nghiệp: Bài thuyết trình [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250813/vuthuhuyen1407/135x160/6261755072381.jpg)



