
1/3/2017
1
Chapter 9
Pricing in Business Marketing
www.dinhtienminh.net
DINH Tien Minh (Ph.D.)
University of Economics HCMC
Objectives
2
Examine the special meaning of price.
Understand and analyze the factors influencing
the pricing decisions.
Study the different price-setting methods and
pricing strategies.
Learn pricing policies for different types of
customers
Examine the practical aspects of commercial
terms and conditions.
Describe the role of leasing in business
Marketing.
Content
9.1 Special Meaning of Price
9.2 Factors influencing Pricing Decision
3
9.3 Pricing Methods and Strategies
9.4 Pricing Policies
9.5 Commercial Terms and Conditions
9.6 Role of Leasing

1/3/2017
2
4
9.1 Special meaning of Price
What do you think when a business
buyer buys a product from XYZ
supplier which is in competition
with several other suppliers of the
similar product?
5
9.1 Special meaning of Price (con’t)
Perception
of Value
Production
Manager
Quality of materials
Reliability of delivery
Financial
Manager
Lowest cost
Liberal payment
Purchase
Manager
Reputation
Dependable
salesperson
Krishna K Havaldar (2010), Business Marketing, McGraw Hill, 3rd edition, p313.
6
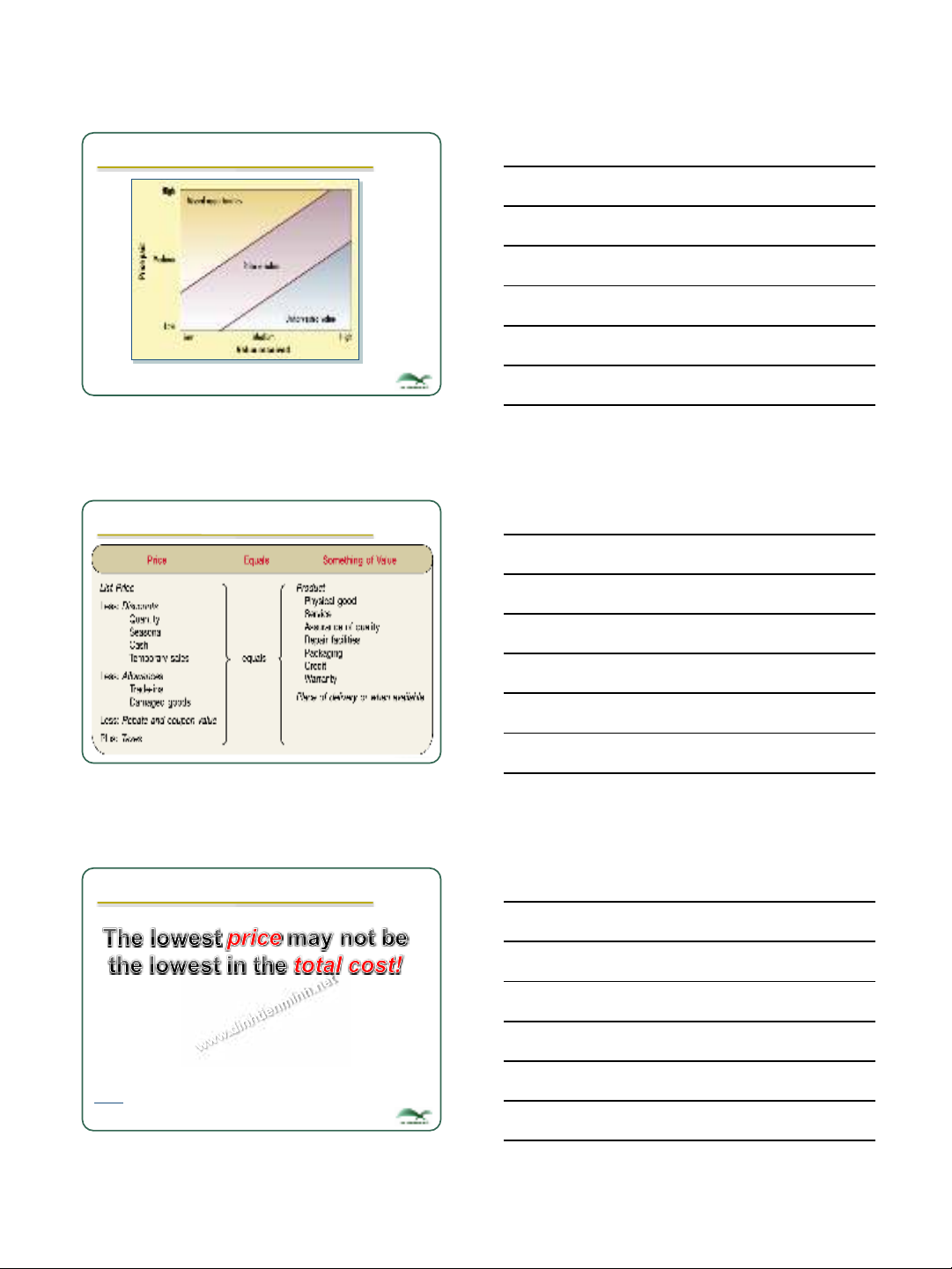
9.1 Special meaning of Price (con’t)
Total cost
Price
Transportation
cost
Transit insurance
cost
Installation cost
Risk cost
Product failure
Late delivery
Poor technical
support
Krishna K Havaldar (2010), Business Marketing, McGraw Hill, 3rd edition, p313.
1/3/2017
3
7
Price Should Align with Value
9.1 Special meaning of Price (con’t)
8
9.1 Special meaning of Price (con’t)
9
9.1 Special meaning of Price (con’t)
In out of over 100 purchase decisions, the lowest price
bidder was not selected in over 40%of the cases*.
Source: J. Patrick Kelly and James W. Coaker, “Can we generalize about choice
criteria for industrial purchasing decisions?”, in Kenneth L. Bernhardt, ed.,
Marketing: 1776-1976 and beyond (Chicago: AMA, 1976), pp330-33.
1/3/2017
4
10
9.2 Factors influencing Pricing Decision
Customer
perceptions of
value
Other Internal &
External
considerations
Product costs
Price ceiling
No demand above
this price
Price floor
No profits below
this price
Source: Philip KOTLER, Gary AMSTRONG (2008), Principle of Marketing, 12th edition,
Pearson Education International, Prentice Hall, p.267
11
9.2 Factors influencing Pricing Decision
Pricing
decision
1. Pricing objectives
2. Demand analysis
3. Cost analysis
4. Competition analysis
5. Government regulations
Krishna K Havaldar (2010), Business Marketing, McGraw Hill, 3rd edition, p313.
12
9.2 Factors influencing Pricing Decision
1. Pricing
objectives
Survival
Maximum short-term
profits
Product-Quality
leadership
Superior
quality
Slightly higher
price
Market penetration
Market skimming
Other pricing
objectives
Be regarded fair
by customers
Try to stabilize the
market
Meeting the
competition
Krishna K Havaldar (2010), Business Marketing, McGraw Hill, 3rd edition, p314.

1/3/2017
5
13
9.2 Factors influencing Pricing Decision
P’2
P2
P’1
P1
Q’1Q’2
Q1Q2
Elastic demand
Inelastic demand
2. Demand analysis
14
9.2 Factors influencing Pricing Decision
Example 1: If a manufacturer of steel sheets increases
the price by 2% and the demand (quantity sold) falls by
5%, what is the price elasticity of demand in this case?
Example 2: If a machine tools manufacturer decreases
the price by 10% and the demand (quantity sold) rises by
5%, what is the price elasticity of demand in this case?
15
9.2 Factors influencing Pricing Decision
Conditions determining price elasticity of demand:
There are few competitors.
No availability of substitute products from other
industries.
The buyers think the higher prices are justified by
normal inflation or change in government
policies.
The products are technically sophisticated,
customized, or important for buyer’s operation.

![Đề cương bài giảng Kỹ năng hoạt động công nghiệp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250715/kimphuong1001/135x160/76971752564028.jpg)
![Bài giảng Kỹ thuật điều độ trong sản xuất và dịch vụ [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250630/dcbaor/135x160/13121751251866.jpg)















![Bài giảng Quản lý sản xuất cho kỹ sư: Chương 3 - Đường Võ Hùng [Chuẩn Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250812/oursky02/135x160/10441768298495.jpg)







