
1/2/2017
1
Chapter 3
Organizational Buying &
Buying Behavior
www.dinhtienminh.net
DINH Tien Minh (Ph.D.)
University of Economics HCMC
Objectives
2
Understand organizational buying objectives.
Gain knowledge organisational buying process
including the types of buying situation.
Identify the members of decision making unit.
Understand some of models of organizational
buying behavior.
Outline
3.1 Purchasing Objectives
3.2 Organisational Buying Process
3.3 Types of Purchase or Buying Situations
3.4 The Buying Center
3
3.5 Models of Organisational Buying Behavior
3.6 Questions and Homework

1/2/2017
2
4
3.1. Purchasing Objectives
Buying the right item in the right quantity,at
the right price, for delivery at the right time
and place.
What’s right for each dimension?
Delivery/ Availability
Product quality
Lowest price
Services
Supplier relationship
5
3.1. Purchasing Objectives (cont’)
© 2002 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., McGraw-Hill/Irwin
The Firm and Personal objectives.
More complex than the consumer decision process
and takes place within formal organization’s budget,
cost, and profit considerations.
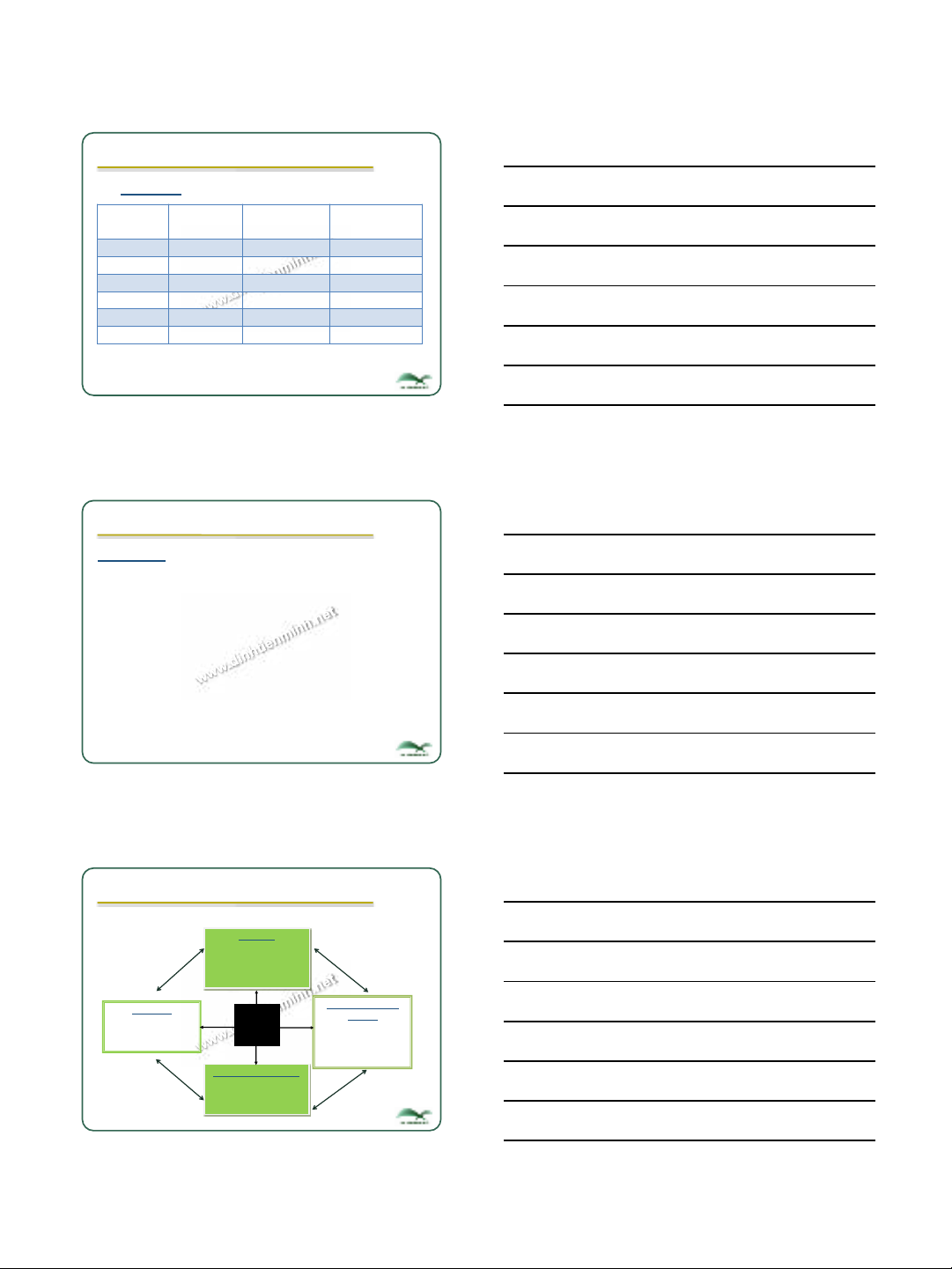
3.2. Organisational Buying Process
6
Source: Krishna K Havaldar (2010), Business Marketing, McGraw Hill, 3rd edition.
6

1/2/2017
3
Stage 1: Anticipate a problem/need and a
general solution
Need to provide employees with a good cup of coffee
to enhance productivity.
Stage 2: Determine the characteristics and
quantity of a needed good or service
Offering a coffee system that brews one cup of coffee
at a time according to each employee’s preference.
7
3.2. Organisational Buying Process (cont’)
7
Stage 3: Describe characteristics and the
quantity of a needed good or service
Firms need a simple system for
brewing a good cup of coffee; quantity
requirements are easily correlated to the
number of coffee drinkers.
Stage 4: Search for and qualify potential
sources
Choice of supplier.
8
3.2. Organisational Buying Process (cont’)
8
Stage 5: Acquire and Analyze proposals
May involve competitive bidding, especially if the
buyer is the government or a public agency.
Stage 6: Evaluate proposals and Select
suppliers
Buyers choose proposal best suited to their needs.
Final choice may involve trade-offs between feature
such as price, reliability, quality, and order accuracy.
9
3.2. Organisational Buying Process (cont’)
9
1/2/2017
4
10
Krishna K Havaldar (2010), Business Marketing, McGraw Hill, 3rd edition, p42.
Method: A Supplier Evaluation System
3.2. Organisational Buying Process (cont’)
Attribute
(or Factor)
Weight
(Important)
Supplier
Performance*
Supplier Rating
(or Score)
Quality
30 0.8 30 x 0.8 = 24
Delivery
25 0.4 25 x 0.4 = 10
Price
15 0.6 15 x 0.6 = 09
Service
20 0.6 20 x 0.6 = 12
Flexibility
10 0.2 10 x 0.2 = 02
Total
100 57
* The information on the existing supplier’s performance is obtained from departments.
10
11
Method 2: Use the concept of Balanced Scorecard
(BSC) to evaluate Suppliers’ performance
Translate a company’s mission and strategy into a
set of performance measurements,in which the
Internal-business-process is relevant for evaluating
supplier performance.
Find additional measurements (timely delivery)
that create superior value beside the traditional
factors (price, quality).
3.2. Organisational Buying Process (cont’)
11
12
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Framework
3.2. Organisational Buying Process (cont’)
Robert S. Kaplan & David P. Norton, The Balanced Scorecard, Harvard Business School Press, 1996.
Financial
To success financially,
Company should focus on
financial objectives that will
satisfy shareholders.
Customer
Which customer value
company should focus on,
to achieve its mission
Internal-Business-
Process
To satisfy shareholders
and customers, what
business process company
must excel at?
Mission
&
Strategy
Learning and Growth
How can company improve
and change to achieve its
mission
12
1/2/2017
5
13
Internal-Business-Process
3.2. Organisational Buying Process (cont’)
Krishna K Havaldar (2010), Business Marketing, McGraw Hill, 3rd edition, p43.
Identify
Customer
needs and
Market
Design,
Develop
Product/
Service
Make/
Buy
Product/
Service
Market
Product/
Service
Satisfy
Customer
Needs
Innovation
Processes
Operations
Processes
13
Stage 7: Select an order routine
Buyer and Vendor work out best way to process
future purchases.
Stage 8: Obtain feedback and Evaluate
performance
Buyers measure vendors’ performance.
Larger firms are more likely to use formal evaluation
procedures.
Some firms rely on outside organizations to gather
quality feedback and summarize results.
14
3.2. Organisational Buying Process (cont’)
14
18
3.3. Types of Purchase or Buying Situations
Source: Krishna K Havaldar (2010), Business Marketing, McGraw Hill, 3rd edition.
18

![Đề cương bài giảng Kỹ năng hoạt động công nghiệp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250715/kimphuong1001/135x160/76971752564028.jpg)
![Bài giảng Kỹ thuật điều độ trong sản xuất và dịch vụ [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250630/dcbaor/135x160/13121751251866.jpg)















![Bài giảng Quản lý sản xuất cho kỹ sư: Chương 3 - Đường Võ Hùng [Chuẩn Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250812/oursky02/135x160/10441768298495.jpg)







