VIỆN CÔNG NGHỆ SINH HỌC & CÔNG NGHỆ THỰC PHẨM
SCHOOL OF BIOTECHNOLOGY AND FOOD TECHNOLOGY

Miễn dịch học
1.
Đề cương
1.1. Khái niệm cơ bản về đáp ứng miễn dịch
1.2. Các cơ quan và tế bào tham gia vào đáp ứng miễn dịch
1.3. Kháng nguyên
1.4. Đáp ứng miễn dịch dịch thể
1.5. Bổ thể
1.6. Tế bào T
1.7. Phức hệ phù hợp mô chủ yếu
2.
Giáo trình
- Miễn dịch học, Trường ĐH Y HN
- Miễn dịch học cơ sở, Đỗ Ngọc Liên
- Immunology – A short course,
Richard Coico, Geoffrey Sunshine

Khái niệm cơ bản về miễn dịch học
I.
Khái niệm cơ bản về đáp ứng miễn dịch
I.1. Khái niệm về miễn dịch
I.2. Lịch sử và hướng phát triển của miễn dịch
I.3. Miễn dịch tự nhiên
I.4. Miễn dịch thu được
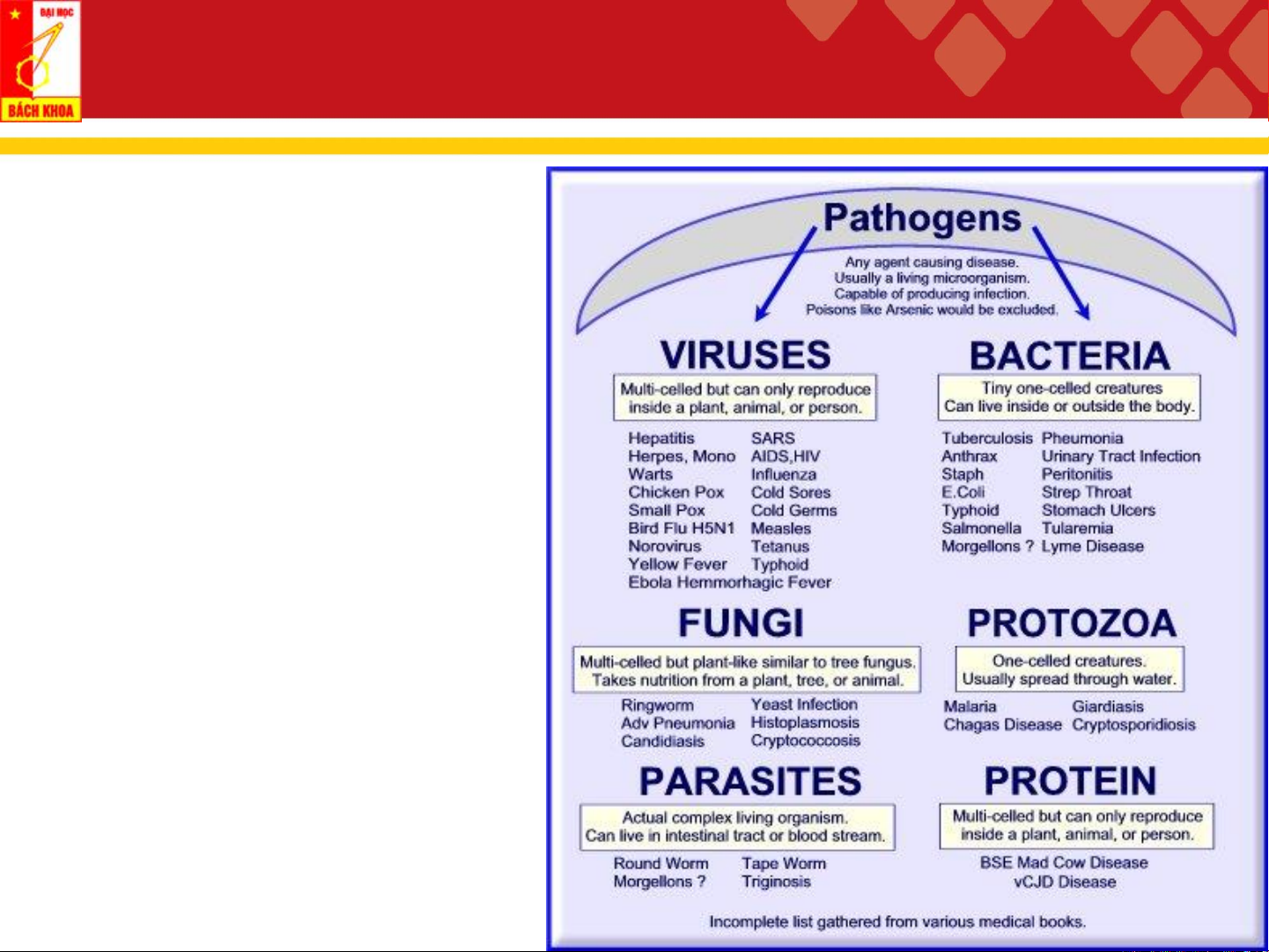
Hình ảnh: nguồn Internet

Khái niệm cơ bản về miễn dịch học
•Immunology: the study of how body components respond and interact
•Immunoglobulins: class of proteins that make up antibodies
•Phagocytosis: process where cells engulf and destroy foreign particles such
microorganisms or damaged cells. Macrophages and segmented
neutrophils are the most important phagocytic cells
•Immunogenicity: the degree to which an antigen elicits an immune
response
•Immunogen: antigen that stimulates an immune response
•Soluble antigen: free floating antigen recognized by B cell receptors
•Epitope: the small piece of an antigen that is bound by an antibody or a T
cell receptor
•Chemotaxis: release of substances which attract phagocytic WBC to
bacteria. Cells move from an area of low to high concentration of
chemokines.
•Immune System: cells in our bone marrow, thymus, and the lymphatic
system of ducts and nodes, spleen, and blood that function to protect us
Khái niệm cơ bản về miễn dịch học
Miễn
dịch là khả năng
của
cơ
thể kháng lại hoặc loại
bỏ
các
tác nhân ngoại lai
gây
hại
hoặc các tế bào
bất
thường
của cơ thể.

![Bộ câu hỏi trắc nghiệm môn Vi sinh vật [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251113/kimphuong1001/135x160/64181763025328.jpg)
![Bộ câu hỏi trắc nghiệm Vi sinh [năm] mới nhất](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251113/kimphuong1001/135x160/72591763025328.jpg)









![Bài giảng Vi sinh vật: Đại cương về miễn dịch và ứng dụng [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251124/royalnguyen223@gmail.com/135x160/49791764038504.jpg)