199
TÍNH CHẤT CƠ BẢN CỦA CKPS
PART
01
Thứ nhất, tài sản cơ sở của Chứng khoán Phái sinh được chia thành 02
dạng chính:
•Hàng hóa: thực phẩm (ngũ cốc, thịt, cà phê, hồ tiêu, v.v…), kim
loại (vàng, bạc, kẽm, v.v…), năng lượng (khí đốt, dầu, v.v…), khác (thời
tiết, kết quả bầu cử, v.v…).
•Công cụ tài chính: cổ phiếu (chỉ số cổ phiếu, cổ phiếu đơn lẻ), trái
phiếu (trái phiếu chính phủ, trái phiếu địa phương, trái phiếu doanh
nghiệp), Lãi suất (lãi suất ngân hàng, lãi suất ngoại tệ), Tiền tệ (USD, Yên
Nhật, Euro, v.v…), Chứng khoán phái sinh.
Thứ hai, giá trị của chứng khoán phái sinh phụ thuộc vào, hoặc bắt
nguồn từ của tài sản cơ sở.
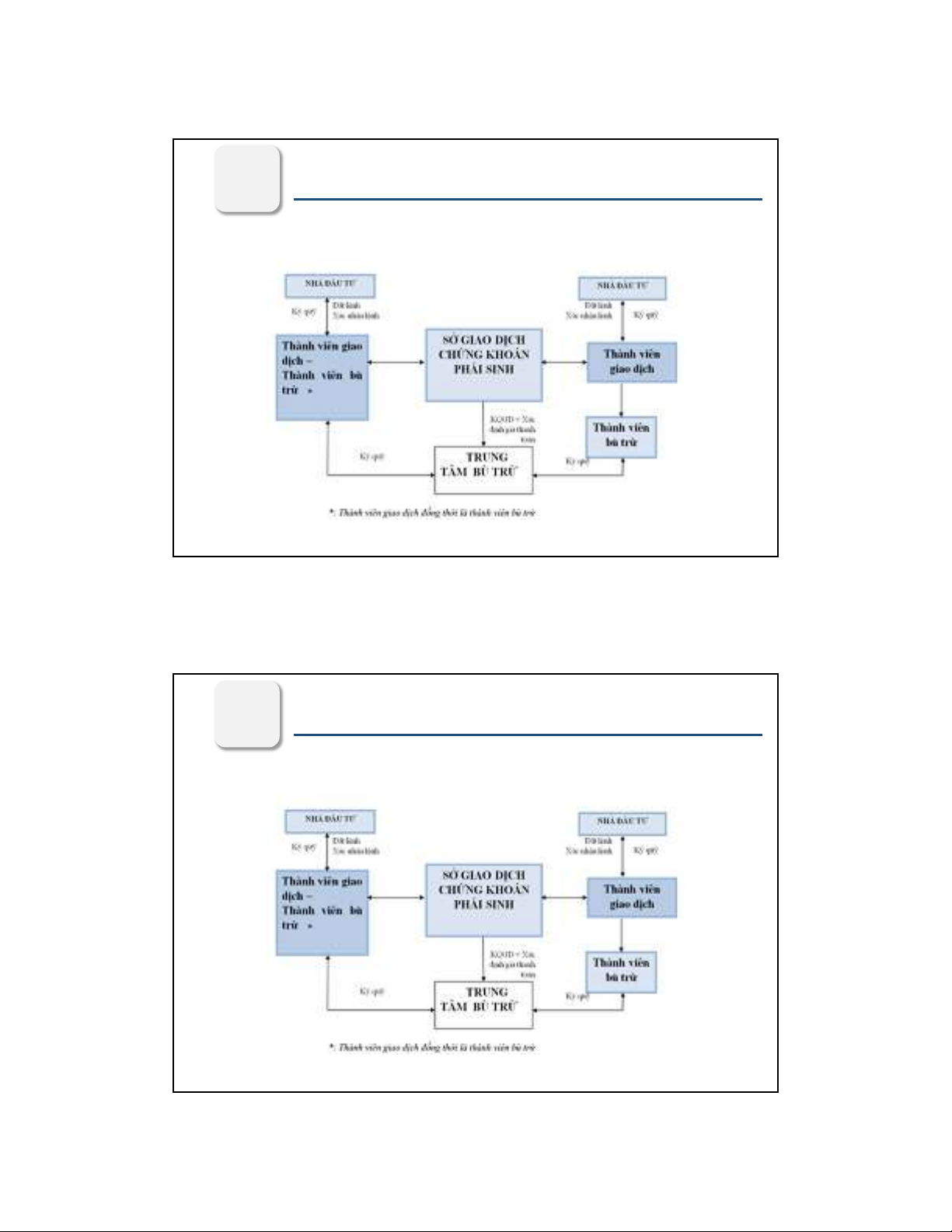
Thứ ba, các chứng khoán phái sinh giúp hạn chế và quản trị rủi ro trong
kinh doanh, đầu tư . 397
First, the underlying assets of derivative securities are divided into two
main types:
• Commodities: food (grain, meat, coffee, pepper, etc.), metals (gold,
silver, zinc, etc.), energy (gas, oil, etc.), others (time details, election
results, etc.).
• Financial instruments: stocks (stock index, single share), bonds
(government bonds, municipal bonds, corporate bonds), Interest rates
(bank interest rates, foreign interest rates) Currency), Currency (USD,
Japanese Yen, Euro, etc.), Derivatives.
Second, the value of the derivative security depends on, or is derived from,
the underlying asset.
Third, derivative securities help to limit and manage risks in business and
investment.
FEATURES OF DERIVATIVES
PART
01
398