ECONOMICS - SOCIETY https://jst-haui.vn HaUI Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 60 - No. 11E (Nov 2024)
126
P
-
ISSN 1859
-
3585
E
-
ISSN 2615
-
961
9
STUDYING THE INFLUENTIAL FACTORS ON STUDENTS' ENTREPRENEURIAL INTENTIONS IN HANOI: THE ROLE OF CREATIVE INNOVATION CAPABILITY
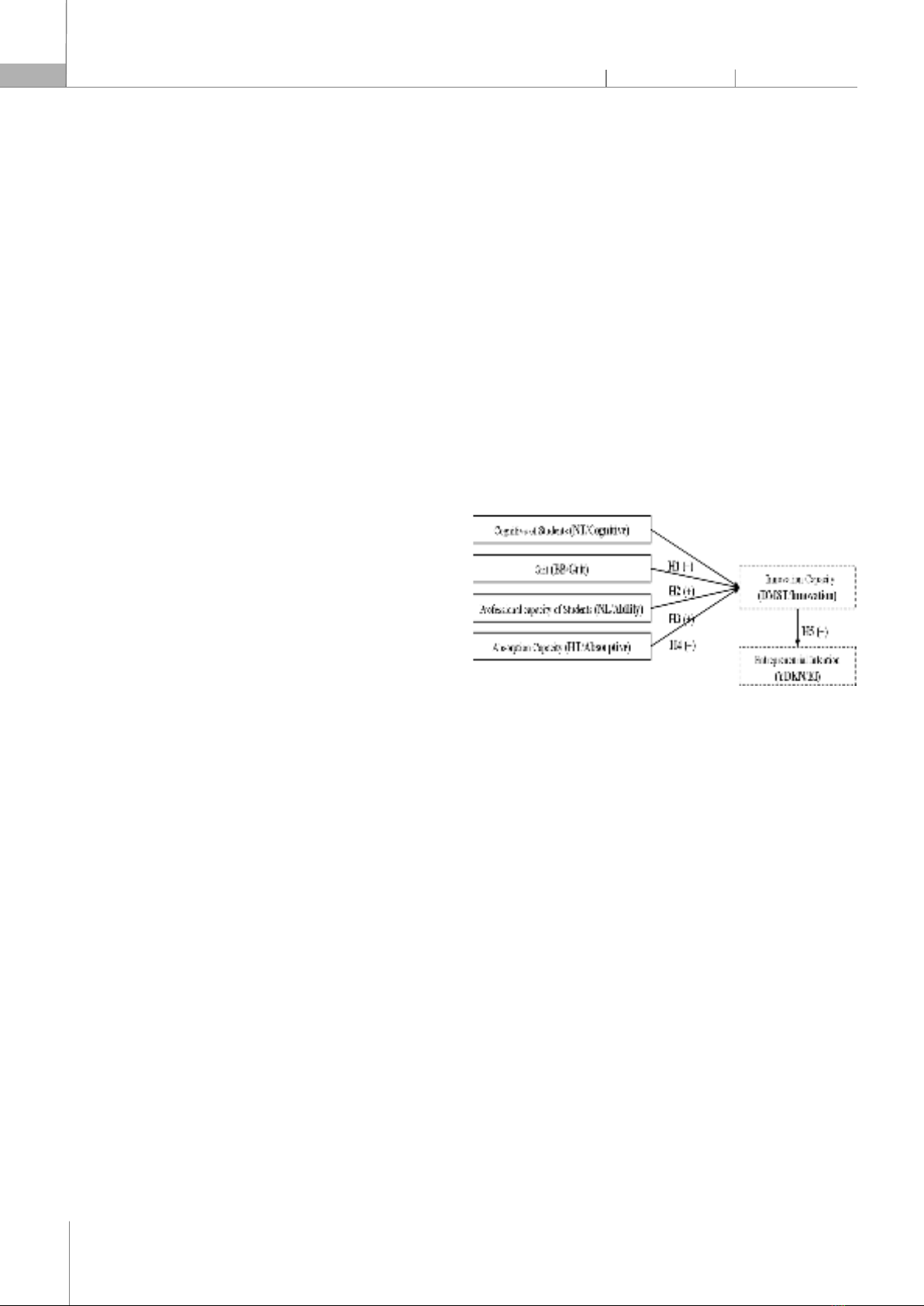
Do Thi Ngoc Lan1,*, Nguyen Anh Linh1 DOI: http://doi.org/10.57001/huih5804.2024.351 ABSTRACT
The study aims to determine the role of innovation capacity in students'
entrepreneurial intention, case study in Vietnam. The author uses qualitative
and quantitative research methods to determine the research model as well
as determine and
measure the inuence of factors on students'
entrepreneurial intentions. Research data was surveyed by the author from
1642 students currently studying in Vietnam. The results of linear structural
modeling (SEM) research show that factors that positively
inuence students'
entrepreneurial intention through innovation capacity include: (1) Grit, (2)
Cognitive of Students, (3) Absorptive capacity, (4) Students' professional
capacity. Thereby, the study proposes some management implications to
improve the entrepreneurial intention of Vietnamese students in the future. Keywords:
Startup, entrepreneurial intention, innovation capacity,
students.
1Hanoi University of Industry, Vietnam *Email: dothingoclan@haui.edu.vn Received: 14/5/2024 Revised: 21/7/2024 Accepted: 28/11/2024 1. INTRODUCTION Startup businesses not only create new dynamism for the economy but also bring new directions and creative methods. Therefore, governments around the world often apply support policies to encourage the development of businesses, especially those that advocate science and technology, production and business, and development. economy based on application and innovation in the eld of science and technology. According to the General Statistics Office, in 2022, Vietnam will have 148,500 newly registered businesses, an increase of 27.1% compared to the previous year. Although the registered capital decreased slightly, the signicant increase in the number of businesses shows the excitement and potential of the startup market in Vietnam. Vietnam has recognized the importance of entrepreneurship and applied support policies to promote this development. According to the 2023 Global Innovation Index (GII) Report, Vietnam has increased 2 places compared to 2022, from position 48 to 46 out of 132 ranked countries. This shows an improvement in creating favorable conditions for start-up businesses. Building startup programs not only provides opportunities for young people and students to promote their creative spirit, but also helps them apply learned knowledge into practice and create successful startup projects. likelihood of success. At the same time, building a comprehensive startup support program also plays an important role in promoting the development of young businesses. Especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, promoting the entrepreneurial spirit and "ownership mindset" among students has become more urgent than ever. Providing solutions to reduce employment pressure and promote economic and social development has become necessary and urgent. However, in Vietnam, the startup rate among students is still low at 7%, and the innovative startup ecosystem is still in the process of formation and development. To promote the spirit of entrepreneurship in society, enhancing entrepreneurial intention among young people, especially the student generation, is extremely urgent. To promote the spirit of entrepreneurship in society, raising the intention to start a business among young people, especially the student generation, is of decisive signicance. According to research by [1], students are a group of potential creative start-ups because they are an elite group, knowledgeable, well-trained, and especially those who are on the threshold of choosing a job.