
1
INTRODUCTION
1. Rationale
Institutions is an important factor in promoting business development in general, and
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) in particular. Research on institutions cannot
fail to mention North (1990, 1991), who laid the foundations for the first theories of
institutions. Then, inheriting the research of North, Alexiou et al (2014) showed that:
institutional quality is one of the most important factors protecting the prosperity of Sudan's
economy. North (1990) shows that: Institutional quality leads to differences in the efficiency
of different economies. In a good economic institutional environment, businesses will be
provided with maximum conditions for production and development. According to Porter
(2008), the institutional environment is a direct factor affecting firm productivity, which is a
condition that helps businesses achieve the highest level of productivity and level. According
to Acemoglu and Johnson (2005) these formal institutions are reflected in North (1981) with
"contract theory". State contract theory regarding the legal framework provided by the state
and various institutions will facilitate and support private contracts to reduce transaction
costs in economic transactions and consulted, Acemoglu and Johnson (2005).
Thus, economic institutions play a very important role in the productivity and
efficiency of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs). In recent years, Vietnam has
been fully aware of the role of economic institutions in the economy and enterprises, and
has been thoroughly grasped by the Government in Documents of the XI National Party
Congress. Specifically, the Government has implemented Resolution No.19/CP from 2014,
2015 to 2020, in order to fundamentally change economic institutions and management
mechanisms in the direction of creating good conditions. Most businesses, in recent years
marked important turning points marking the reform of economic institutions, including the
Enterprise Law and the Investment Law (2014) with issues of investment promotion and
establishment, enterprises or the Law on Anti-Corruption 2005, amended and supplemented
in 2012, Commercial Law, ... Institutional reform has achieved significant positive results in
reducing trade risks, legal risks, the business environment is more transparent, open and
autonomous, opening up new opportunities for SMEs.
The institutional changes have encouraged the development of the business sector,
especially the private sector. Central Conference 5, term IX on March 18, 2002 passed
Resolution 14-NQ/TW on "continuing to renew mechanisms and policies, to encourage and
facilitate private economic development". Following that, the 5th Central Conference
session XII on June 3, 2017 on "private economic development becomes an important
2
driving force of the economy", which motivated the private sector to thrive. strong in both
quantity and quality.
Experimental research on the model on the impact of institutions on the performance
of enterprises in general and Small and medium-sized enterprises in particular has been
studied by many authors. However, previous studies mostly study the impact of institutions
on the performance of enterprises in general or Foreign Invested Enterprise in particular as
in Anh and Phuong (2016) or local institutional studies, productivity growth like Thang
(2016) or studying the effects of individual actors in institutions - that is, corruption on
performance like Tuyen et al (2016)... Moreover, previous studies only research on the
direct impact of economic institutions on business in general.
But according to Agosin and Mayer (2000), Harrison and Mc Millan (2001), and
Ramirez and Ling (2004), Thang (2009) pointed out that State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs)
and Foreign Invested Enterprises (FIEs) have effects that prevent small and medium-sized
domestic private enterprises from developing by privileged preferences in access capital,
land access together with tax incentives. This shows that the impact of economic institutions
on Small and Medium-sized Enterprises performance depends not only on institutional
reforms, but also on the spillover effects of State-Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested
Enterprises on Small and Medium-sized Enterprises, especially non-state sector. Therefore,
Postgraduate chooses the project title "The impact of institutional quality on the
performance of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam", to do my doctoral thesis.
2. Research objectives
The thesis analyzes the impact of institutional quality on the performance of Small and
Medium-sized Enterprises, and focuses on the impact of institutions on the spillover
channel from State-Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises to small and
medium-sized domestic private firms. The empirical research results will provide sufficient
and reliable evidence to help policy makers to come up with solutions to continue to reform
and further improve the quality of institutions to create a fair business environment.
between business sectors, promoting Small and Medium-sized Enterprises to improve their
performance even more. Specifically, the thesis answers the following research questions:
(i) How do institutions impact the performance of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises?;
(ii) How do institutions affect the spillover effect from Foreign Invested Enterprises to
small and medium-sized domestic private firms?; (iii) How do institutions affect the
spillover effect from State-Owned Enterprises to small and medium-sized domestic private
firms?

3
3. Research subjects and scope
- Research subjects: The thesis focuses on assessing the impact of institutional quality
on the spillover effects from State-Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises to
small and medium-sized private firms. Since Small and Medium-sized Enterprises in
Vietnam are mainly non-state enterprises (accounting for more than 90%), all Small and
Medium-sized Enterprises in this study are non-state sector.
- Research scope:
+, In terms of content: Small and Medium-sized Enterprises performance is considered
under two angles of labor productivity (VA/ L) and profitability rate (ROA).
+, In terms of space: The thesis studies the impact of institutional quality on the
performance of domestic private firms on a small and medium scale across the country.
+, About time: The thesis studies the impact of economic institutions on Vietnamese
SMEs using the General Statistics Office's annual business survey data set from 2010-2018
and the IO data set of the General Department of Statistics to calculate spillover channels,
but since there is no new IO data, the thesis uses IO of 2012 to calculate spillover channels
from State-Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises for all years.
4. Research Methodology
To solve the research objectives, the thesis uses the following research methods: (i)
Methods of synthesizing, analyzing and evaluating research on the impact of institutions on
the performance of enterprises, also like Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. After doing
the research review, the postgraduate found research gaps and from there, built an analytical
framework for the thesis on the impact of institutions on the performance of Small and
Medium-sized Enterprises. (ii) Statistical analysis method: Based on secondary data, the
postgraduate assesses the current status of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises operations,
the current institutional and business environment in Vietnam, the status of the spillover
link between the enterprise sector. (iii) Quantitative research method: The PhD student uses
array data regression to estimate the impact of institutions on the performance of small and
medium-sized private firms. The thesis uses the array data percentile regression method to
estimate the impact of the institution on the financial performance of private firms ROA of
small and medium scale.
5. New contributions of the dissertation
The thesis studies the impact of institutional quality on the performance of Small and
Medium-sized Enterprises in Vietnam. Besides the inheritance, the thesis will overcome a
4
number of limitations of previous studies. Specifically, the thesis has some theoretical and
experimental contributions as follows:
Theoretically: The thesis has built a theoretical framework on the impact of
institutional quality on the performance of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)
most fully when considered in both direct effects and indirects effects throgh spillover from
State-Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises. Since then, the thesis has
experimentally demonstrated that the impact of institutional quality on SMEs' performance
depends on the spillover effects from State-Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested
Enterprises
In terms of experiment:
• The thesis has experimentally proven on a whole sample of Vietnamese SMEs, by
each size group, by each economic sector.
• Institutions have a positive impact on the performance of small and medium-sized
private firms in Vietnam. At the same time, institutions also have a spillover effect from
State-Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises on the performance of small and
medium-sized private firms, so the impact of institutions on the performance of large
private firms. Small and medium size depends on the spillover effects from State-Owned
Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises.
• The impact of institutions on the performance of private firms on a small and
medium scale varies across economic sectors.
• Transparency and legal institutional norms play an important role in promoting the
performance of small and medium-sized private firms. Market entry quotas affirm an
important role in promoting horizontal spillovers and downstream spillovers from State-
Owned Enterprises.
6. The structure of the dissertation
In addition to the Index, List of abbreviations, List of tables, List of figures, List of
references and Appendices, the thesis is structured into 4 chapters. Specifically:
Thesis structure
Chapter 1: Theoretical basis of the institution and its impact on the performance of
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises.
Chapter 2: Overview of research on the impact of institutions on the performance of
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises(SMEs).
Chapter 3: Research method on the impact of institutions on the performance of Small
and Medium-sized Enterprises in Vietnam.
5
Chapter 4: Institutional reality and operational efficiency of Vietnamese Small and
Medium-sized Enterprises.
Chapter 5: The impact of institutions on the performance of Small and Medium-sized
Enterprises in Vietnam.
Chapter 6: Policy recommendations.
CHAPTER 1
THEORETICAL BASIS OF INSTITUTIONAL QUALITY AND IMPACTS OF
INSTITUTIONAL QUALITY TO OPERATION OF SMALL AND MEDIUM
ENTERPRISES
1.1. Institutional fundamentals and institutional role
1.1.1. The concept of economic institutions
Economic institution is a set of rules of the game that includes parts:
- First, official sets of rules such as the constitution, laws and regulations are
promulgated by the State.
- Second, informal constraints: such as traditional customs, customs, and social norms
of conduct about the behavior of subjects ...
- Third, the enforcement mechanism of the rules: policies, support mechanisms,
sanctions, ...
1.1.2. Classification of economic institutions
Institutions can be classified according to many different criteria:
Firstly, in terms of field of activity: Institutions include political institutions, economic
institutions, cultural institutions, educational institutions, environmental institutions ...
Secondly, in terms of the degree of legalization.
Institutions are divided into formal institutions and informal institutions. Formal institutions
are those established by the State, including the constitution, laws, decrees, and regulations
from the central to local levels, up to the rules ratified and applied by public organizations
and privately operated within the legal framework. Informal institutions are rules,
regulations, and standards set by the community and people: customs, practices, agreements
... often operate outside of the formal institutional system.
Thirdly, in terms of institutional characteristics.
According to Acemoglu and Robinson (2012), institutions are of two basic types:
fusion institutions and appropriation institutions.
1.1.3. The role of the institution in economic activities
6
Firstly, the institution plays a role of orientation, creating a framework for the
organization and operation of the society.
Secondly, institutions create the economic, political and social foundation of the
country.
Thirdly, institutions play the role of social management and establish effective social
management tools.
Fourthly, the institution maintains a good government and limits corruption.
Fifthly, institutions contribute to creating the premise and conditions to limit the
disabilities of the social development process.
Sixthly, institutions control resources in society.
Seventhly, the institution guarantees social actors to exercise their rights and
obligations.
1.1.4. Institutional measurement
Institutions reflect the political level, the political nature of the country. Institutional
quality assessment is the process of examining and evaluating an institutional system to find
out the conformity or non-conformities in the system of a country.
Specific indicators measuring institutional quality are as follows: Economic freedom
index, IQ institutional quality index, Global Competitiveness Index (GCI - Global
Competitiveness Index), business facilitation index (EDBI - Ease of Doing Business Index),
provincial competitiveness of PCI.
In Vietnam, institutional quality is used by many studies as measured by the Provincial
Competitiveness Index (PCI). This is an index measuring and practical assessment of the
quality of economic governance of the provinces and cities in Vietnam. In other words, the
PCI is the index that speaks to businesses about the quality of the operations of the
Vietnamese government.
1.2. Enterprise efficiency
1.2.1. Concept and nature of the business performance
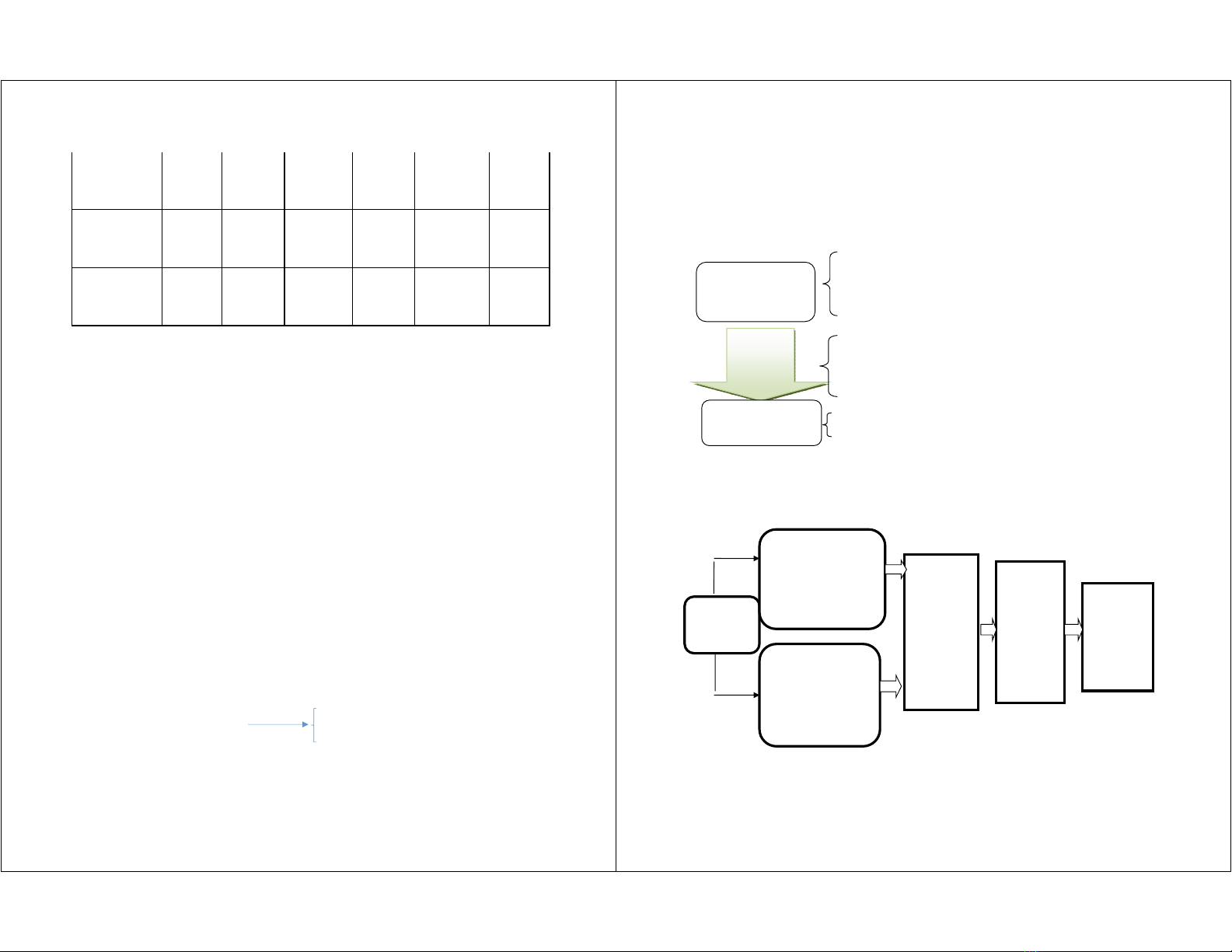
Table 1.1: Classification of SMEs in Vietnam according to Decree 39/2018/ND-CP
Very Small Business
Small Business Medium Business
Total
Capital
Number of
employees
Total
Capital
Number of
employees
Total Capital
Number of
employees
7
1.Agriculture,
forestry and
fisheries
≤3
billions
dong
≤10
people
3 - ≤20
Billions
dong
10 – ≤100
people
20 - ≤100
Billions
dong
100 –
≤200
people
2. Industry and
construction
≤3
billions
dong
≤10
people
3 - ≤20
billions
dong
10 – ≤100
people
20 - ≤100
billions
dong
100 –
≤200
people
3. Trade and
services
≤3
billions
dong
≤10
people
3 - ≤ 50
billions
dong
10 – ≤50
people
50 - ≤100
billions
dong
50 –
≤100
people
Source: Decree No. 39/2018 / ND-CP
The concept of SMEs' performance
Currently, there are still many different views on business performance of enterprises.
Công (2007) shows that: performance of enterprises include three level: (i) Labor efficiency
represents activity intensity - reflects the correlation between outputs and input costs. (ii)
Performance, showing the ability that businesses can achieve when using input factors
(indicators reflect the rotation speed of the inputs). (iii) The highest variable is operational
efficiency, which is the final result the business brings, measured by profit per input unit.
1.2.2. Indicators measuring the performance of SMEs
The view to evaluate the performance of enterprises according to Cong (2007) is a
comprehensive evaluation. However, according to Tien (2015), performance and
performance indicators have overlapping contents. That means performance is also just
showing the operational capacity of resources. Productivity is a sign of business efficiency.
The second cornerstone of efficiency is financial performance. The indicators reflecting the
profitability include: rate of return on total revenue (ROS), rate of return on assets (ROA),
rate of return on equity (ROE), ...
1.3. The impact of institutional quality on SMEs' performance
1.3.1. Direct impact of institutional quality on SME performance
Research by Acemoglu et al. (2005b) together with North (1990) has shown the role of
economic institutions in the following model:
Institutions
Economic efficiency
t
Economic
Distribution of resources
t+1
This model is the basis of institutional research for many later studies when studying
the role of institutions as well as the impact of institutions on economic growth and business
8
performance. According to Russell (2008), institutions that provide property rights, a fair
justice system, and effective contract enforcement will help businesses participate in
economic activities easily and effectively. He affirmed, in places where institutions are not
effective, the rate of inefficient enterprises. He gives a model of the impact of institutions
on business performance as follows:
Capital
Labor
The infrastructure
Available resources
Policy of tax
Business rules
Legal system
Free business / property protection
New business formation
New products and services
Figure 1.1. Institutional impact model on enterprise performance
Source: Russell Research (2008)
1.3.2. The impact of institutional quality on efficiency spillovers from State-Owned
Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises to domestic private firm.
Figure 1.2. Diagram showing the institutional impact on operational efficiency through
the spillover channel from State-Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises.
Production inputs
Institutions
Business
performance results
Institutions
FDI enterprises
- Increase K
- Increase industrial
investment
- Improve production
capacity
SOEs
- Increase K
- Increase industrial
investment
- Increase production
capacity
Spillover
- Horizontal
spread
-
Spread down
the afternoon
-
Spread in the
opposite
direction
Change
-Technology
level,
parameter
A
- Quality of
capital
- Quality of
labor
Change
-Output
-Productivity
-Effective

9
Source: Author's synthesis
All economic theories show that technology is an important factor for long-term
growth (Solow, 1956, 1957). Investing in research and development and technological
knowledge will increase productivity and drive economic growth (Romer, 1990). State-
Owned Enterprises and Foreign Invested Enterprises were the sectors with higher
investment capital than the small and medium-sized domestic private private sector. The
ability to invest in R&D activities and import machinery and equipment will be higher than
domestic private firms with small and medium scale.
CHAPTER 2
OVERVIEW OF RESEARCH ON IMPACT OF INSTITUTIONAL QUALITY ON
SMALL AND MEDIUM BUSINESS OPERATION
2.1. Factors affecting the business performance of the business
Research overview of factors influencing SMEs' performance is divided into two main
groups: (i) External factors, such as: institutional quality, State policies, system law,
customer and market or enterprise's raw material source. (ii) Factors within the enterprise,
including: production technology level, labor, management capacity, average labor income,
financial access, operating policies of the enterprise . These are factors that the business can
control to some degree.
2.2. The impact of institutions on the performance of Small and Medium-sized
Enterprises (SMEs)
Institutional impacts on SMEs' performance have two opposite conclusions: First,
institutions have a positive impact on business performance such as Johan (2015), Tran
Quang Tuyen et al (2016). , Bach Ngoc Thang (2017), Pham The Anh and Chu Thi Mai
Phuong (2016). Second, the opposite effect in the study of Tran Quang Tuyen et al (2016)
when studying the impact of corruption on corporate performance, the author uses the
variable ROA (return on assets) to research and show that institutions have opposite effects
with ROA.
However, there are studies that do not support a positive relationship of institutions and
enterprise efficiency such as Joseph et al (2013) when studying the effects of institutions on
export efficiency. He said that there are only a few institutions that positively affect small
and new enterprises, he finds uncertainty about the direct relationship between institutions
and enterprise efficiency, saying that: Return to enterprises performance. It is possible that
10
this study lacks geographic data such as urban and rural areas, and has not yet controlled
intermediate variables such as centralized business zones.
Thus, the impact of economic institutions on business performance is different in
previous studies, possibly due to studies conducted in different types of enterprises such as
Pham's research. The Anh and Chu Thi Mai Phuong (2016) researched on Foreign Invested
Enterprises, while the research by Tran Quang Tuyen et al (2016) was on SMEs (mainly
non-state enterprises). Also, according to Yi Che et al. (2011) pointed out that institutional
quality positively affects the survival of Private Enterprises. He said that the economic
institutional impact on business performance different between types of enterprises.
Bhaumik et al (2012) also showed different results when studying from an industry
perspective, or between countries, there may be different results when studying in
developed countries and countries with new economies, floating like Vietnam. Therefore,
the results have not really been consistent in previous studies.
2.3. Institutional impacts on spillovers from State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) and
Foreign Invested Enterprises (FIEs) to Private Firms
2.3.1. Factors affecting the ability to spread
FIEs has the ability to spread to business performance, Nguyen Khac Minh (2014).
However, spillovers are dependent on many factors, which can either promote the spillover
capacity to increase or possibly reduce the spillover effect. The empirical studies on the
spillover effects from FIEs to domestic firms have shown that: the spillover effect of FIEs
to domestic firms depends on many factors related to the characteristics of multinational
companies and foreign investment, as well as host country characteristics, industries and
businesses. These factors include: absorption capacity of the firm, R&D activities and
cooperation in research, linkages between input suppliers and customers.
2.3.2. The impact of institutional quality on SMEs performance
There are very few previous studies on the impact of institutions on the spillover
effects of Foreign Invested Enterprises on domestic enterprises as well as the impact of
State-Owned Enterprises on small and medium-sized domestic private firms that the thesis
researches. Some previous studies have not shown the impact of institutions on full
spillover efficiency through spillover channels from SOEs and FIEs, Wang and Chen
(2014) only assesses the of FIEs, institutional quality as measured by the NERI index
published annually by the China National Institute of Economic Research. The PhD student
studied the impact of the institution on the performance of Vietnamese SMEs in the non-
state sector, but this enterprise sector is subject to the spillover effects of the SOEs and


























