http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 281 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 7, Issue 7, November–December 2016, pp.281–287, Article ID: IJM_07_07_031
Available online at
http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=7&IType=7
Journal Impact Factor (2016): 8.1920 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
COGNIZANCE AND INGESTING PRACTICE OF
SMALL MILLETS IN VILLUPURAM DISTRICT
– AN EXAMINATION
Dr. N. Srividhya
Professor, SMVEC, Pondicherry, India
ABSTRACT
Millets are grown expansively in different areas of India as a staple crop to feed a huge section
of the inhabitants. In India, its production holds the sixth position after wheat, rice, maize, sorghum
and bajra. The most important cultivated species of millets in India are foxtail millet, finger millet,
pearl or cattail millet, brown millet etc., It offers high nutritional supplement food and acts as an
antioxidant properties contained food. India is a country needs such type of food grain needs to
supplement all nutrition’s to the ever-growing population. To facilitate an improved and healthy
food supply the Government along with the farmers need to produce various small millets and
supply to the general public. This should be the right option for the farmers and it will definitely
provide a rich place for India’s growth. The planned cultivation of these millets will have provided
a very nutritious and economical food for a large proportion of poor people.
Key words: Small millets, Nutritional value, Diabetics
Cite this Article: Dr. N. Srividhya, Cognizance and Ingesting Practice of Small Millets in
Villupuram District – An Examination. International Journal of Management, 7(7), 2016, pp. 281–
287. http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=7&IType=7
1. INTRODUCTION
Today almost 8 out of 10 people facing a major problems Diabetes. What is the root cause for this
deficiency? Is it because of our food, or food habits, or culture. May be any one reason but now-a-days
there is a major awareness among people to use small millets, because it reduces the problem of Diabetes
and usage of more millets than regular rice helps them to reduce fat content, reduces cholesterol level.
Millets have wonderful in their nutrient content. Every millet has highly recommended fiber, protein,
minerals and vitamins. Today physicians also recommend their patients to take millets more for their
health and safety life. All millets have high anti-oxidants. Moreover, millets need little water to grow, and
it is not dependent on any fertilizers or pesticides. The consumption of millets is increasing day by day, but
the production is very limited. Farmers are hesitant to produce these types of products. This article
analyses the awareness and consumption practice of millets among Villupuram district people.
In India, lack of dietary diversity is one of the key factors behind malnutrition and the prevalence of
non-communicable diseases such as Blood pressure, Diabetes etc., Small millets are the great supplement
to current crops.
Dr. N. Srividhya
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 282 editor@iaeme.com
“The rice eater is weightless like a bird; the one who eats Jowar is strong like a wolf: one who eats
Raagi remains ‘nirogi’ [illness free] throughout his life - An old Kannada saying”
2. NUTRITION BENEFITS OF SMALL MILLETS
Millet is so important because of its uniquely high content of nutrients, including impressive starch levels,
very high B-vitamin content, as well as calcium, iron, potassium, zinc, magnesium, not to mention being a
healthy source of essential fats in the body. Furthermore, there are significant levels of protein and dietary
fiber in millet as well, which contribute to even more health benefits of this important grain.
3. HEALTHY BENEFITS OF SMALL MILLETS
• Beneficial in detoxifying body.
• Lowers bad cholesterol level.
• Prevents onset of breast cancer.
• Helps to prevent type 2 diabetes.
• Effective in reducing blood pressure.
• Helps to protect against heart diseases, optimize kidney, liver and immune system health.
• Eliminates problems like constipation, asthma, excess gas, bloating and cramping.
• Reduces risk of gastric ulcer or colon cancer.
3.1. Small Millets and its Nutritious Value
Name Energy value (Kg., Calorie)
Kambu 361
Maize (Solam) 222
Ragi 328
Thinai 331
Varagu 309
Nutrients – Carbohydrates 27%, protein 26%, Calories 18% and Dietary fiber 11%
Vitamins – Thiamin 26%, Niacin 22%, Folate 20%, Vitamin B6 18%
Minerals – Copper 35%, Phosphorous 27%, Magnesium 26%, Iron 16%
4. REASONS FOR LESS PRODUCTION OF SMALL MILLETS IN INDIA
• Millets are grown on poor shallow and marginal soils under rain fed conditions. The soils on which these
crops are cultivated have low moisture retention capacity.
• The mixed cropping practices adopted by the farmers are mostly suited to sustenance agriculture and many
of them are not remunerative.
• It is frequently cultivated under unmanured and unfertilized conditions. Improved crop management
practices are not adopted by the farmers due to socio economic constraints.
• There is no ready market for the disposal of surplus produce at a remunerative price. There is a lack of
extension and development support.
5. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
• To find the awareness and consumption practice of small millet users in Villupuram District.
• To analyze the reasons for usage of small millets in Villupuram District.
• To rank the dominating factor that forces the respondents for the usage of small millets.
Cognizance and Ingesting Practice of Small Millets in Villupuram District – An Examination
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 283 editor@iaeme.com
• To make an economic analysis of small millets with that of predominant rice.
• To find the purchasing frequency of small millets among the respondents in Villupuram District.
6. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
SHOBANA ET AL., 2013 WHISPERED "Finger millet grains can be processed in several ways
depending upon the ultimate utilization. In order to develop consumable products, the different processing
techniques include milling, malting, popping, puffing, flaking, debarring. They are crushed in a roller mill,
like wheat, and WINMOWED, to give coarse flour which is utilized as porridge.
Dr. Rama Naik emphasized the point that millets are among the most nutritious food grains available
in India and that the people who consume millets on a regular basis are decidedly healthier than those who
do not. Those who consume millets are found to be fit even in their old age.
7. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This research study is conducted in Villupuram District. The methodology used for this research is
Descriptive in nature. A structured questionnaire was framed. Primary data was collected with the help of
questionnaire from 100 respondents. Convenience sampling is used for this research. Statistical tools like
frequency analysis, chi square analysis, cross tabulation analysis, Factor analysis are used.
7.1. Hypotheses of the Study
H1 – There is no significant relationship between the income and acquisition habit of small millets.
H2 – There is no significant relationship between the respondent’s age and amount spent for purchases of
small millets.
H3 – There is no statistical relationship between respondent’s education, occupation and awareness of
small millets.
The sample size taken for the study is restricted to 150 respondents.
8. ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATIONS
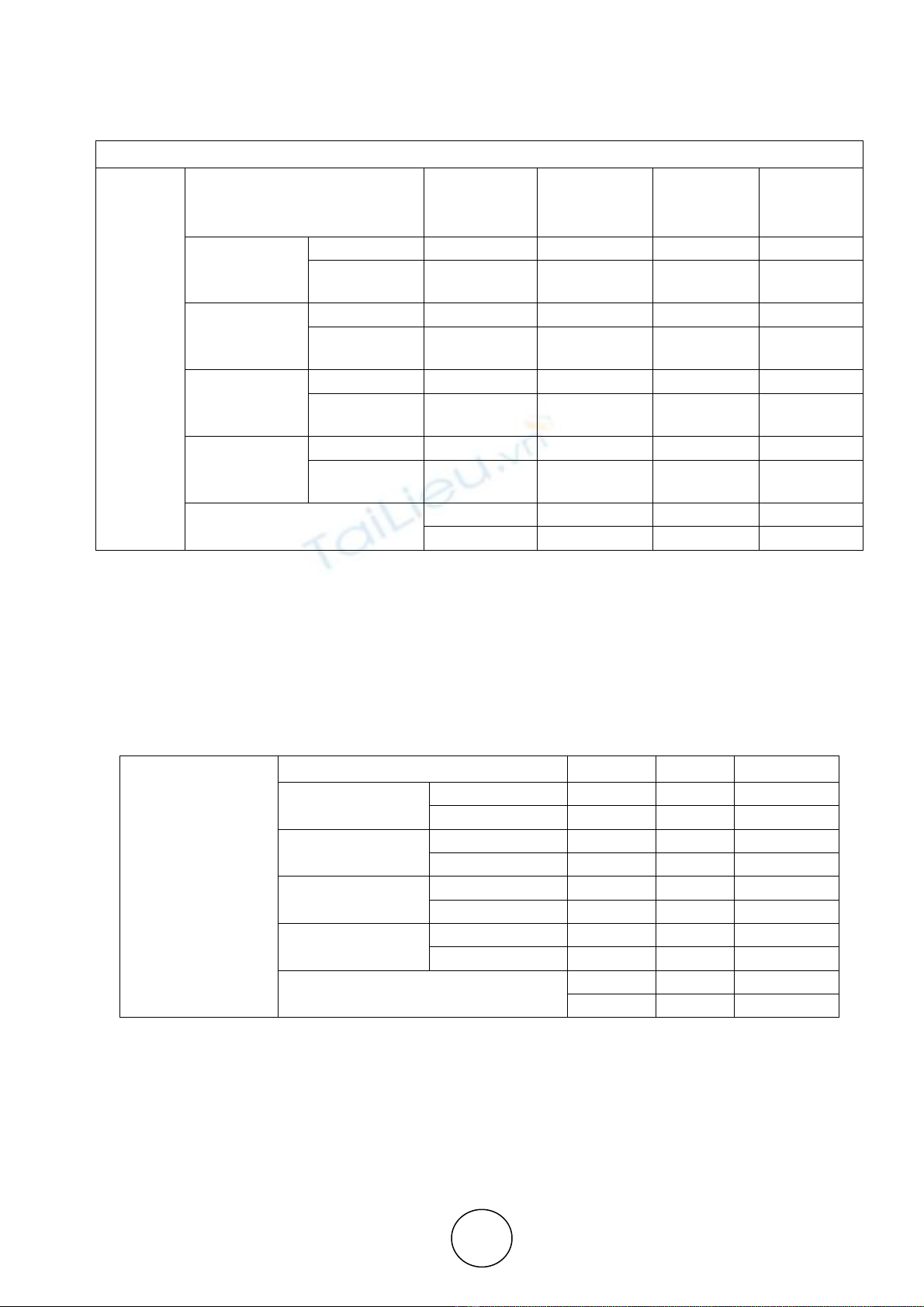
Table 1 Socio Economic Status of the Respondents
SL. NO STATUS NUMBER OF
RESPONDENTS
PERCENTAGE CUMULATIVE
PERCENTAGE
I AGE OF RESPONDENTS
25 - 35 YEARS 66 44% 44
36 – 45 YEARS 67 45% 89
45 – 55 YEARS 10 7% 96
ABOVE 55 YEARS 7 4% 100
II. EDUCATIONAL QUALIFICATION
ILLETERATE 14 10% 10
SCHOOL LEVEL 33 22% 32
COLLEGE LEVEL 47 31% 63
PROFESSIONALS 56 37% 100
III. OCCUPATION
GOVERNMENT SECTOR 86 57% 57
PRIVATE SECTOR 12 8% 65
SELF EMPLOYED 39 26% 91
HOMEMAKER/OTHERS 13 9% 100
Dr. N. Srividhya
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 284 editor@iaeme.com
1V. MONTHLY INCOME
LESS THAN RS. 20000 53 35% 35
RS. 20001 – 30000 70 47% 82
RS. 30001 – 40000 18 12% 94
ABOVE RS. 40000 9 6% 100
V. NATURE OF FAMILY
JOINT FAMILY 40 27% 27
NUCLEAR FAMILY 110 73% 100
VI. NO. OF MEMBERS IN THE
FAMILY
2 – 4 MEMBERS 80 53% 53
4-6 MEMBERS 60 40% 93
6 AND ABOVE 10 7% 100
VII. FREQUENCY OF PURCHASES OF
MILLETS
MONTHLY ONCE 90 60% 60
ONCE IN 3 MONTHS 35 23% 83
RARELY 25 17% 100
Source: Primary Data
H1 – There is no significant relationship between the income of the respondents and the acquisitions of
millets for their use.
Table 2 Cross tabulation showing the relationship between the income and the acquisitions of millets.
ACQUISITIONS OF SMALL MILLETS
MONTHLY
INCOME
Monthly
once
Once in 3
months
Rarely Total
Less than Rs.
20000
COUNT 35 10 8 53
% OF
ACQUISITION
39% 29% 32% 34%
Rs. 20001 –
Rs. 30000
COUNT 42 16 12 70
% OF
ACQUISITION
47% 46% 48% 46%
Rs. 30001 –
Rs. 40000
COUNT 8 6 4 23
% OF
ACQUISITION
9% 17% 16% 15%
RS. 40000
AND ABOVE
COUNT 5 3 1 9
% OF
ACQUISITION
5% 8% 4% 6%
Total 90 35 25 150
100% 100% 100% 100%
Source: Primary data
The above table shows clearly the relationship between the income and acquisition of small millets for
their use. By applying the p value is significant and at 5% level. Hence it is proved that there is a
relationship between the income and acquisition of millets. Respondents who are in the income category II
purchase more than people who earn more. The P value is 74.65 and it is statistically significant that there
is a relationship between the income and the acquisition of millets.
Cognizance and Ingesting Practice of Small Millets in Villupuram District – An Examination
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 285 editor@iaeme.com
Table 3 Cross tabulation showing the relationship between the age and the amount spent on purchases of millets.
AMOUNT SPENT ON PURCHASES OF MILLETS PER MONTH
AGE
RS. 100 - 200
RS. 201 - 300
RS. 301 -
400
Total
25 – 35
YEARS
COUNT 21 23 22 66
% OF
PURCHASES
68% 39% 37% 44
35 – 45
YEARS
COUNT 7 33 27 67
% OF
PURCHASES
23% 56% 45% 45
45 - 55
YEARS
COUNT 0 0 10 10
% OF
PURCHASES
0% 0% 17% 8
ABOVE 55
YEARS
COUNT 3 3 1 4
% OF
PURCHASES
9% 5% 1% 3
TOTAL 31 59 60 150
100% 100% 100% 100%
Source: Primary data
The above cross tabulation explains the relationship between the age and the acquisition of millets.
Now a day’s people in the age group of 25 to 35 got more awareness about the benefits of small millets
and they use more than others. Now people are more conscious about their health, fear about some
common diseases etc., by applying chi square the P value is statistically significant at 5% level with a
value of 92.64. So it is proved that there is a statistical relationship between the age and amount spent on
purchases of millets.
Table 4 Table showing relationship between educational qualification and awareness of millets of the respondents.
EDUCATIONAL
QUALIFICATION
AWARENESS OF MILLETS YES NO TOTAL
ILLITERATE COUNT 11 3 14
PERCENTAGE 9% 11% 9%
SCHOOL LEVEL COUNT 32 1 33
PERCENTAGE 26% 3% 22%
COLLEGE
LEVEL
COUNT 32 15 47
PERCENTAGE 26% 54% 32%
PROFESSIONALS
COUNT 47 9 56
PERCENTAGE 39% 32% 37%
Total 122 28 150
100% 100% 100%
Source: Primary data
The above table presents the relationship between the educational qualification and awareness of
millets among the respondents. While applying the p, value is statistically significant and 5 df. The p value
is 28.031. It clearly explains the qualified people better know about the millets than the illiterate. In order
to create awareness among the illiterate the Government can conduct awareness campaign in villages. That
will motivate them to understand better about the medicinal benefits of small millets.

























![Nội dung ôn tập Tâm lý học lứa tuổi học sinh trung học [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251016/phuongnguyen2005/135x160/8151768537367.jpg)
