Solids
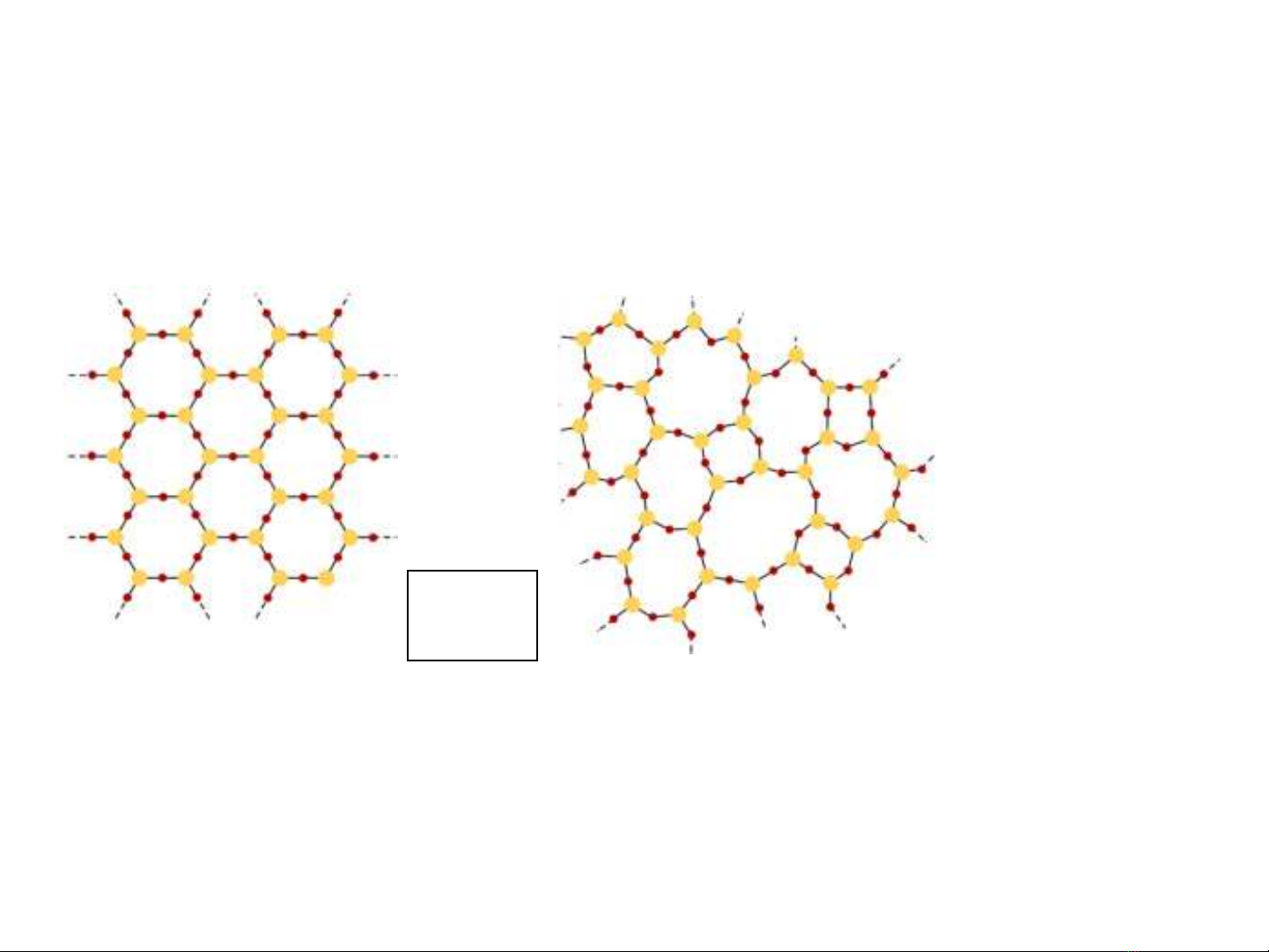
crystalline
amorphous
well defined structures
no orderly structure glass
quartz
SiO2
crystal lattice system of points
describes arrangement of particles
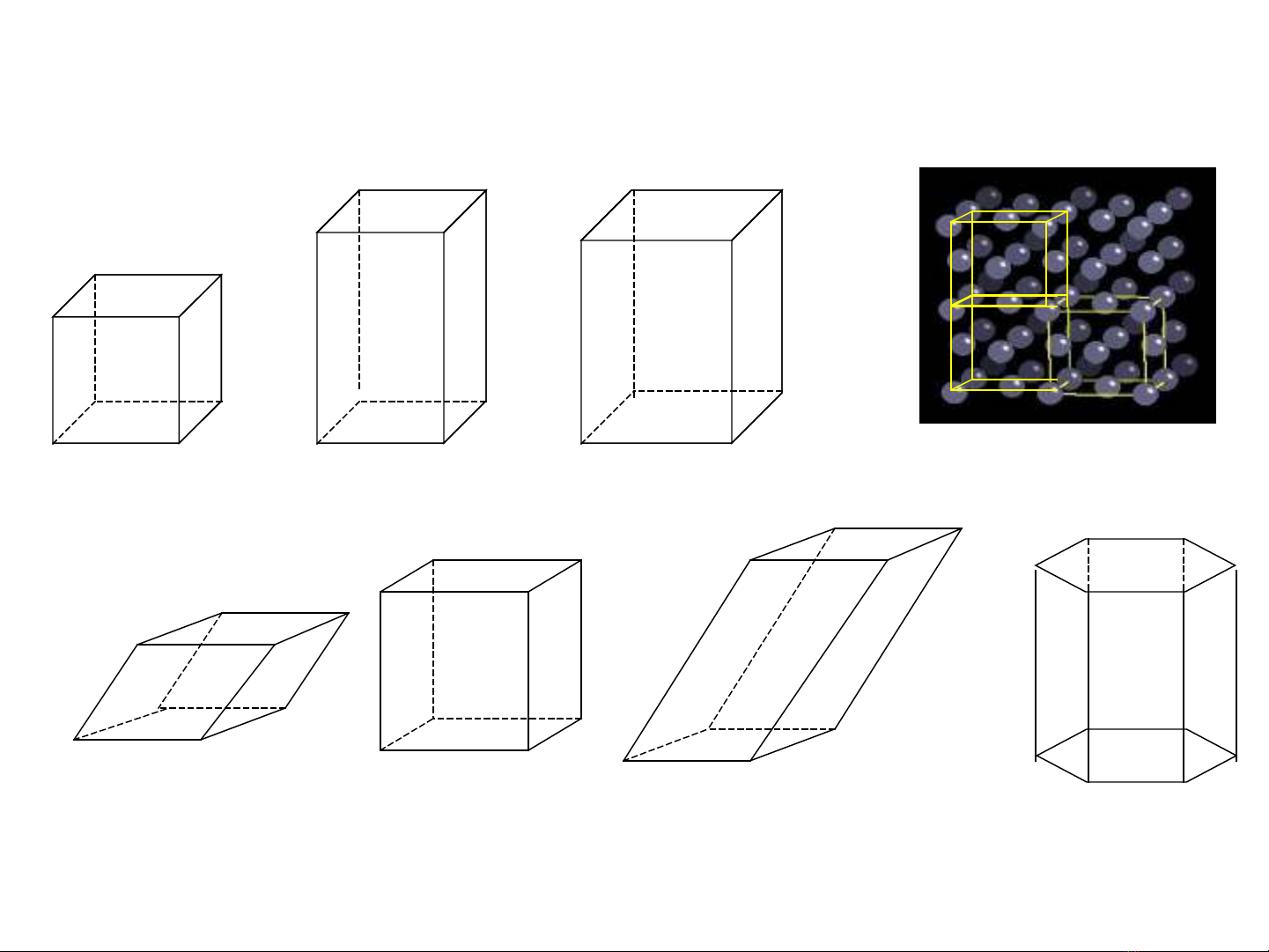
unit cell repeating structural unit lattice
7 unit cells
simple cubic
formed from packing spheres
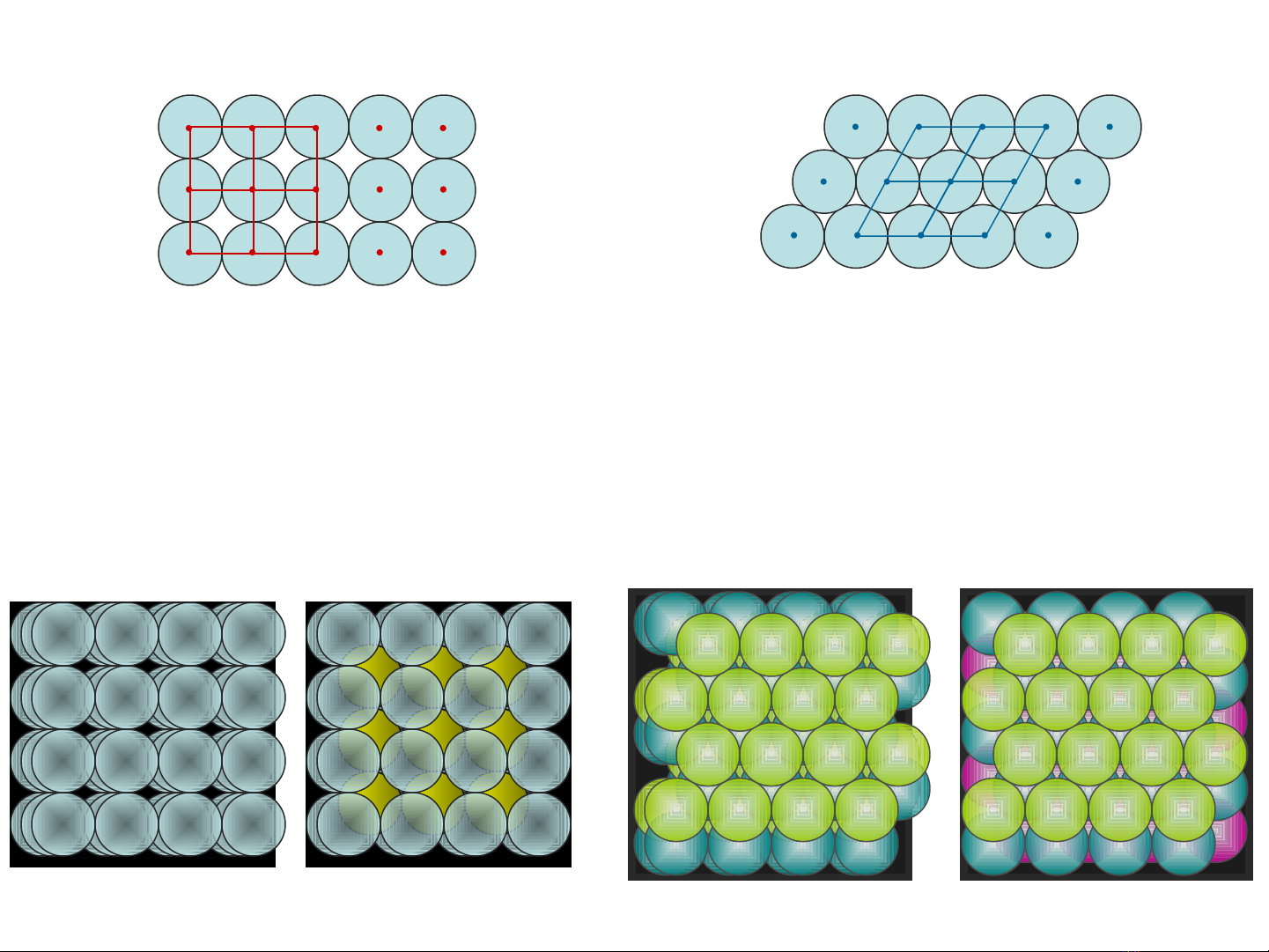
unit cells
crystalline solids
hexagonal closest packing
“abab” layers “abca” layers
cubic packing
“aaa” layers
in 3 dimensions
hexagonal closest pack cubic closest pack
“abab” layers
simple cubic body centered cubic
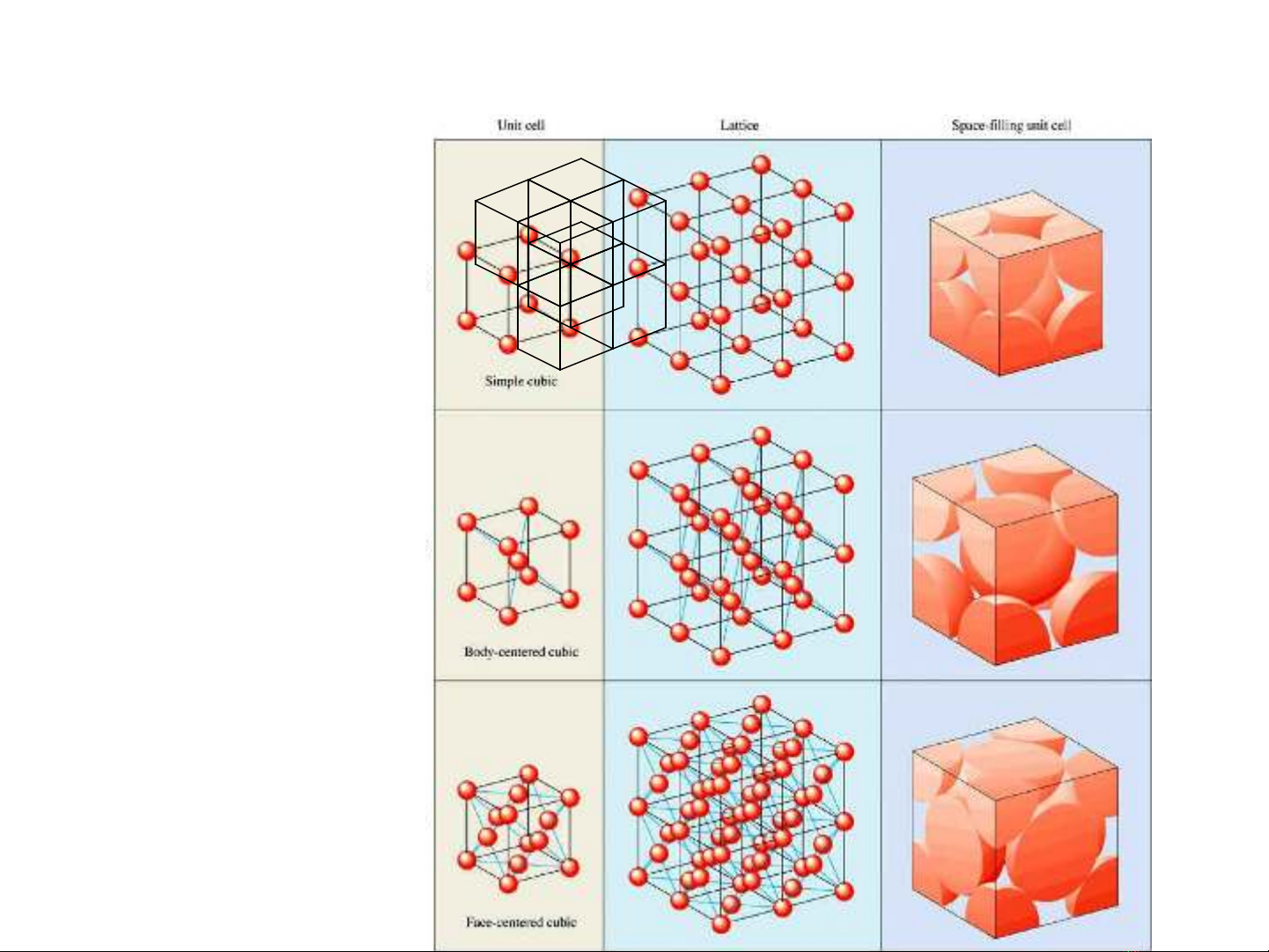
Three-Dimensional Cubic Lattices
Simple cubic
Face-centered cubic
Body-centered cubic
1/8x 8 =1 particle
(1/8 )x 8 + 1 = 2 particles
(1/8 )x 8 (1/2 )x 6+ = 4 particles
cubic closest pack
a a a
a b a b
a b c a b c
coordination number = 6
coordination number = 8
coordination number = 12
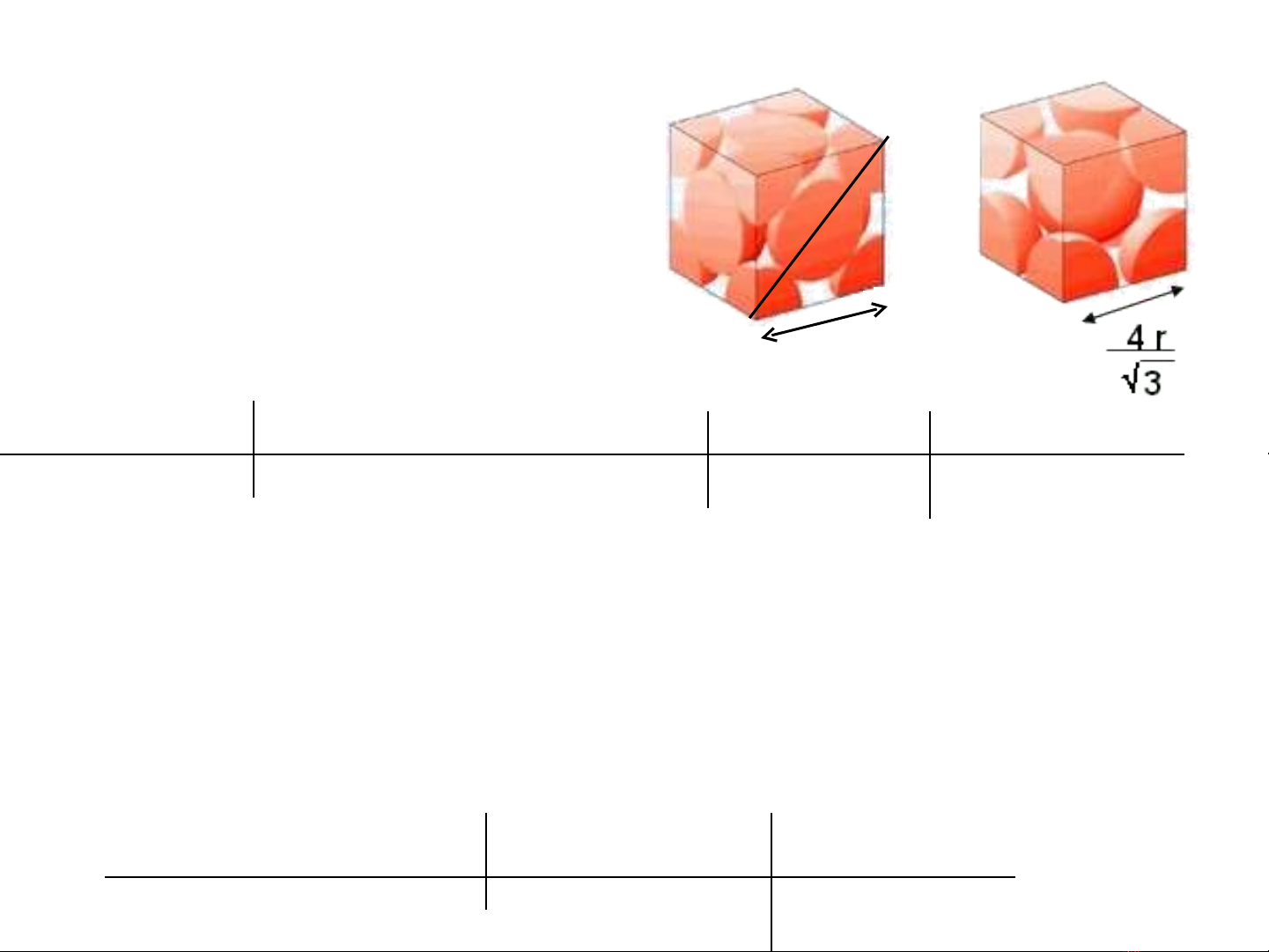
Calculation of atomic radii
Cu faced-centered cubic
density = 8.92 g/cm3
mass = 63.546 g/mol
63.546 g
mol
1 mol
6.022 x 1023 atoms
4 atoms
unit cell 8.92 g
cm3
4.732 x 10-23 cm3 / unit cell( )1/3
= 3.617 x 10-8 cm
(3.617 x 10-8)2 + (3.617 x 10-8)2
= (4r)2
r = 1.279 x 10-8 cm
1 cm
1 x 10-2 m
1 x 10-12 m
1 pm = 127 pm
r+2r+r
lattice parameter, a















![Đề thi kết thúc học phần Nguyên lí Hóa học 2 [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251014/anhinhduyet000/135x160/69761760428591.jpg)










