
CHƯƠNG 7 XÁC ĐỊNH GIÁ TRỊ DOANH NGHIỆP BẰNG
CÁC PHƯƠNG PHÁP DỰA TRÊN THU NHẬP
1. Phương pháp chiết khấu dòng tiền
(Discounted future economic income method)
Chiết khấu dòng cổ tức (DDM) và chiết khấu
dòng tiền FCF
2.
Phương pháp dòng tiền thặng dư (capitalized
146
2.
Phương pháp dòng tiền thặng dư (capitalized
excess earnings method)- doanh nghiệp tạo ra
lợi thế thương mại, vốn hoá dòng tiền lợi thế
thương mại này + tài sản hữu hình của doanh
nghiệp

PHƯƠNG PHÁP DỰA TRÊN THU NHẬP – CÔNG
THỨC TỔNG QUÁT
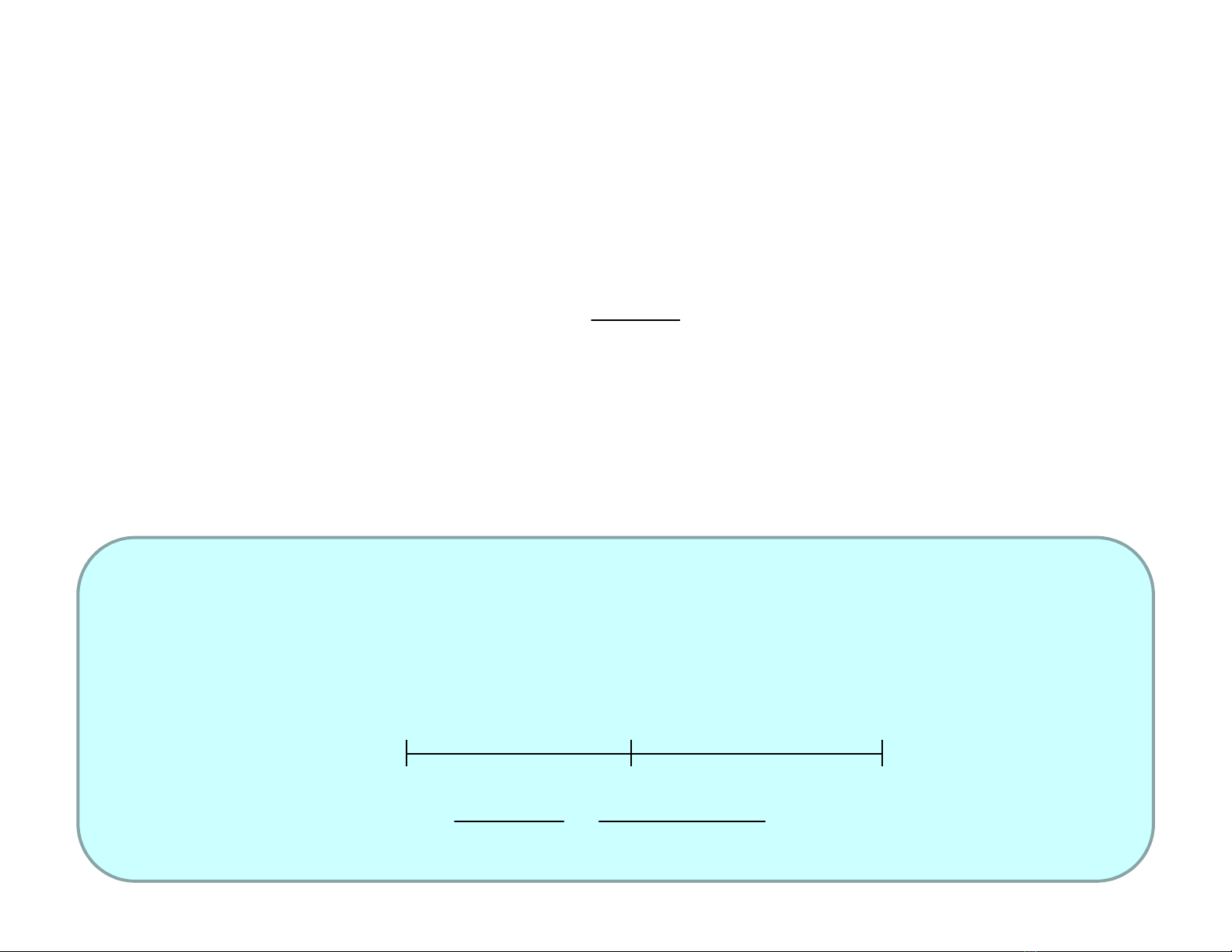
Giá trị doanh nghiệp = Giá trị của tất cả các tài sản
kinh tế = Giá trị các tài sản kinh doanh + giá trị các
tài sản tài chính
Công thức tính tổng quát
AF
n
n
t
t
V
k
VR
k
CF
V
+
+
+
+
=
−−
∑
)
1
(
)
1
(
147
• V = Giá trị doanh nghiệp
• CFt= Free cash flow của tài sản kinh doanh
• VR = Giá trị bán lại tại thời điểm cuối chu kỳ
• VAF = Giá trị hiện tại của tài sản tài chính
• k = WACC, CAPM
• n = Số năm dự tính của chu kỳ kinh doanh
AF
t
t
V
k
VR
k
CF
V
+
+
+
+
=
=
∑
)
1
(
)
1
(
1

DDM or FCF
•DDM Model
–Use the Dividend Discount Model
• (a) For firms which pay dividends (and repurchase stock) which are
close to the Free Cash Flow to Equity (over a extended period)
• (b) For firms where FCFE are difficult to estimate (Example : Banks and
Financial Service companies)
•DCF Models
–Use the FCFE Model
• (a) For firms which pay dividends which are significantly higher or lower
than the Free Cash Flow to Equity. (What is significant ? ... As a rule of
thumb, if dividends are less than 80% of FCFE or dividends are greater
than 110% of FCFE over a 5-year period, use the FCFE model)
• (b) For firms where dividends are not available (Example : Private
Companies, IPOs)
148
DDM Model
• As with any other security, the first step in valuing common stocks is to determine
the expected future cash flows.
• Finding the present values of these cash flows and adding them together will give
us the value :
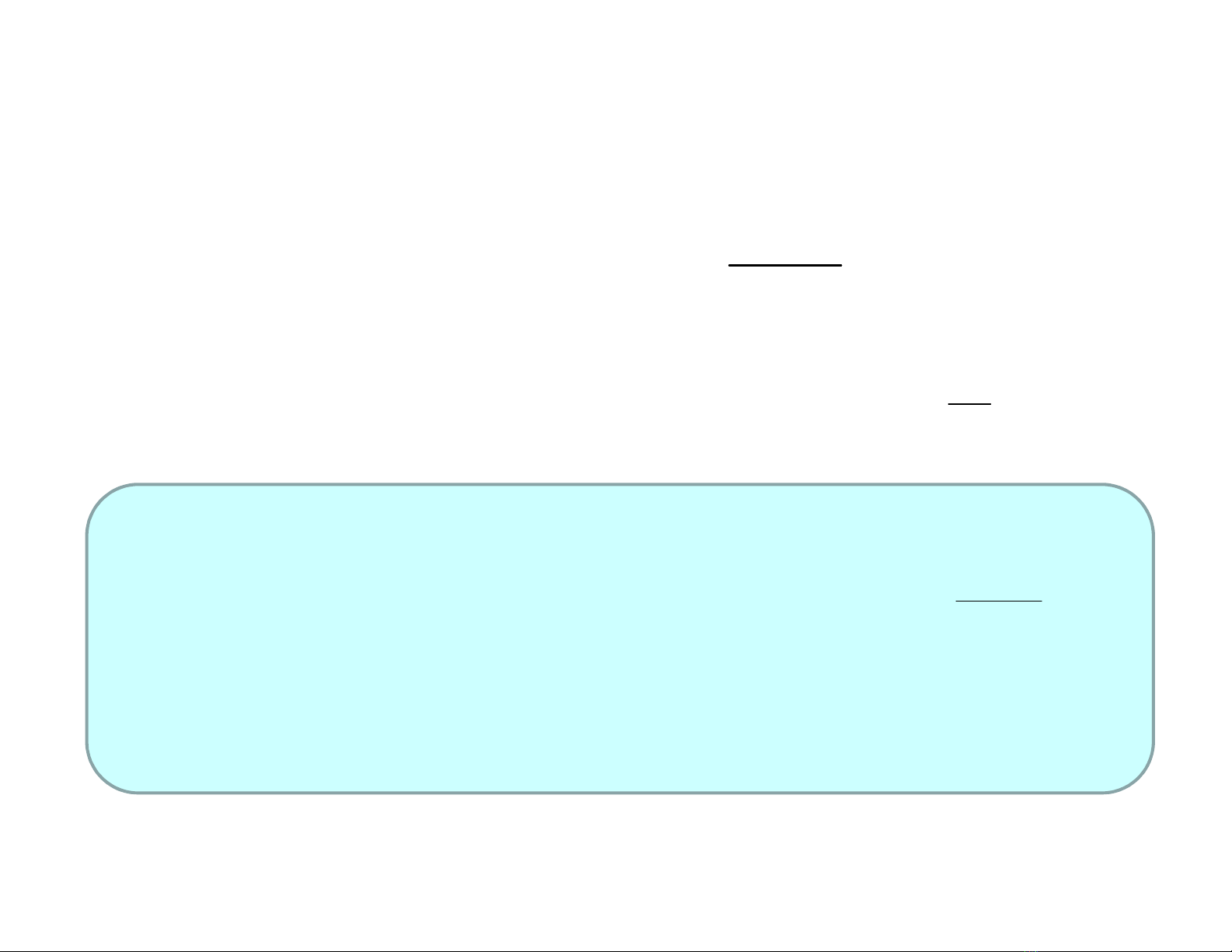
• For a stock, there are two cash flows :
– Future dividend payments
( )
∑
∞
=
+
=
1
1
t
t
t
CS
r
CF
V
– The future selling price
Assume that you are considering the purchase of a stock which will pay dividends of $2
(D1) next year, and $2.16 (D2) the following year. After receiving the second dividend,
you plan on selling the stock for $33.33. What is the intrinsic value of this stock if your
required return is 15%?
2.00 2.16
33.33
?
(
)
(
)
V
C S
=+++
+=
2 0 0
1 1 5
2 1 6 3 3 3 3
1 1 5 2 8 5 7
1 2
.
.
. .
..
A. Gordon Constant DDM
• If Dtis constant, then it is an ordinary perpetuity :
r
D
V
1
0
=
lStock pricing relationship :
∑
∞
=
+
=
1
0
)1(
t
t
t
r
D
V
150
The current (annual) dividend is: $0.28
According to the constant dividend (zero growth) model :
The price of Wal-Mart was actually $52.83
Can you explain the difference?
41
.2$
1162
.
0
28.0$
0
==
W M
P
Example : Wal-Mart











![Bài giảng Marketing căn bản Trường CĐ Phương Đông Quảng Nam [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260124/lionelmessi01/135x160/30531769270692.jpg)
![Câu hỏi trắc nghiệm Nguyên lý Marketing: Tổng hợp [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260124/hoahongxanh0906/135x160/37491769228050.jpg)













