1
Activity-Based Cost Systems
Nguyen Phong Nguyen
1
•TCS are systems that allow assigning
indirect/overhead costs to cost objects based on
volume-based measures.
•Plant-wide and departmental rates based on direct
labor hours, machine hours, or other volume-based
measures are used successfully by many
organizations.
–However this approach to costing is equivalent to an
averaging approach and may produce distorted, or
inaccurate costs.
Traditional Cost Systems (TCS)
2
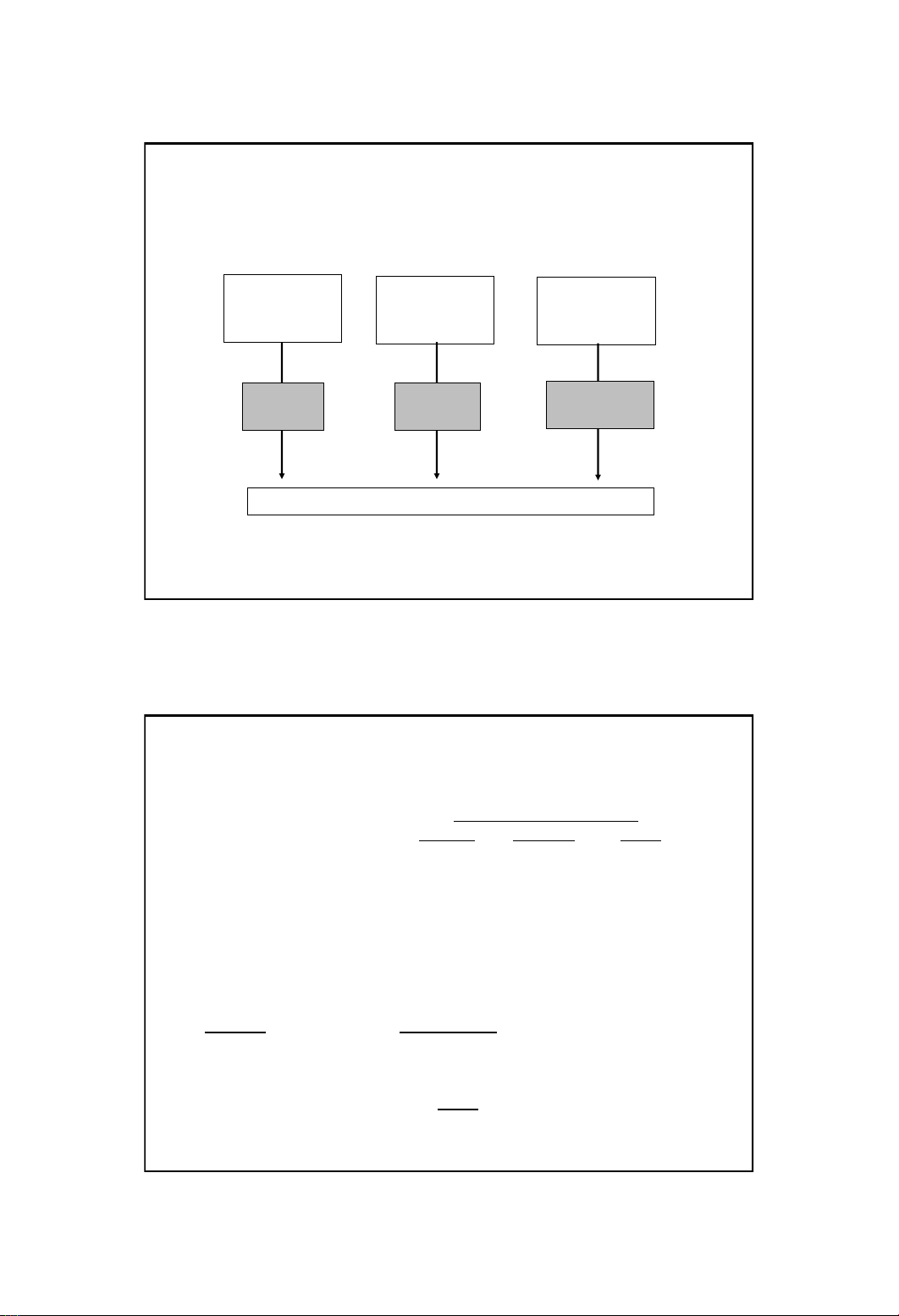
Traditional Cost Systems
Direct
Material
Costs
Direct
Labor
Costs
Overhead
Costs
Direct
Trace
Direct
Trace
DLH
Allocation
Cost objects
Example: Tan Thanh Corporation
Activity Usage Measures
Deluxe Regular
Total
Units produced
10
100
Prime costs
800
8,000
8,800
Direct labor hours
20
80
100
Machine hours
10
40
50
Setup hours
3
1
4
Number of moves
6
4
10
Activity Cost Data (Overhead Activities)
Activity
Activity Cost
Setting up equipment
1,000
Moving goods
1,000
Machining
1,500
Assembly
500
Total
4,000
3
Tan Thanh Corp: Traditional Cost Systems
•Plant-wide overhead rate =…………………
………………............................../DLH
•Overhead cost allocated to
oDeluxe = …………………………………………….
oRegular =…………………………………………….
•Unit cost of
oDeluxe = …………………………………………….
oRegular =…………………………………………….
Continuous
Improvement Total Quality
Management
Product cost distortions
can be damaging,
particularly for those
firms whose business
environment is
characterized by:
Limitations of Traditional
Cost Systems
4
Limitations of Traditional
Cost Systems (continued)
•The need for more accurate product costs has
forced many companies to take a look at their
costing procedures.
•Two major factors impair the ability of unit-
based plant-wide and departmental rates to
assign overhead costs accurately:
–The proportion of nonunit-related overhead costs
to total overhead costs is large.
–The degree of product diversity is great.
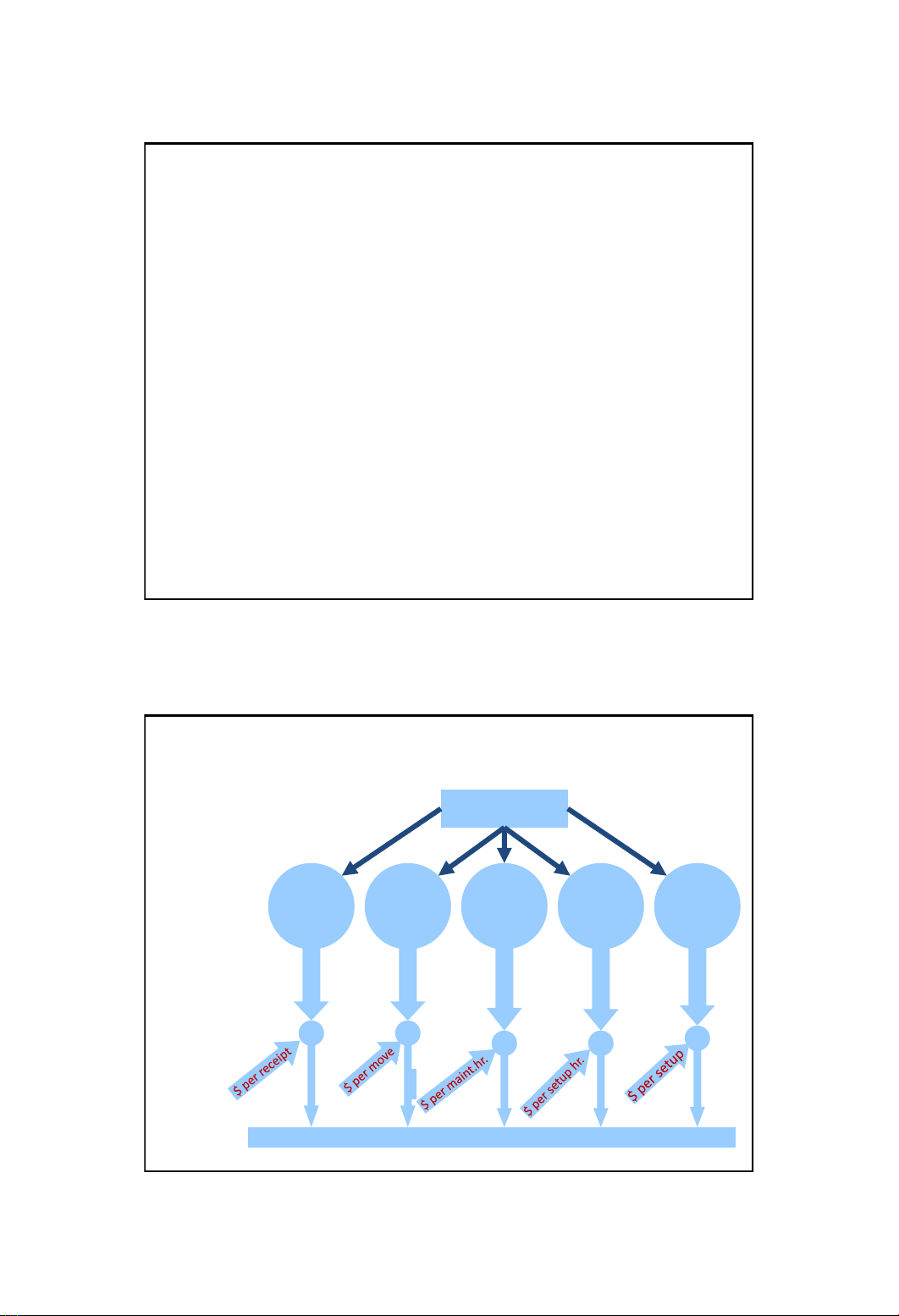
Activity-based Costing: the basic idea
8
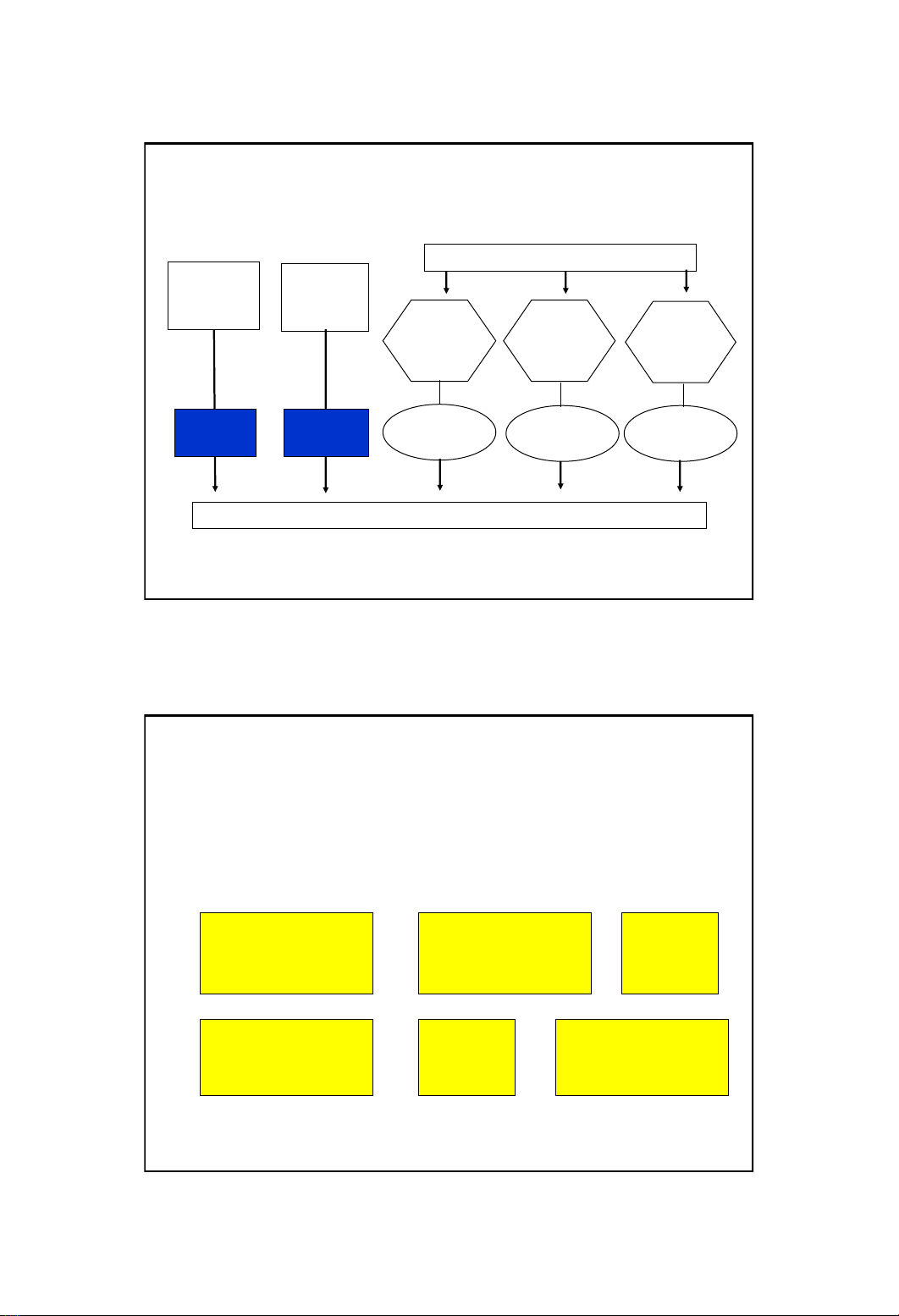
Resource: Indirect labor
Inspect
incoming
materials
Activity: Move
materials
Maintain
machines
Set up
machines
Prepare
tooling
Activity
cost driver:
Cost driver
rate
Product,
Customers
# receipts
# moves
# maint. hrs.
# setup hrs.
# setups
5
ABC Cost Systems
Direct
Material
Costs
Direct
Labor
Costs
Overhead Costs
Direct
Trace
Direct
Trace
Cost objects
Machining
activity
costs
Assembly
activity
costs
Inspection
activity
costs
# of parts
Processing
Hours
# of
inspections
10
ABC systems refine costing systems by focusing on individual
activities as the fundamental cost object
they measure utilization of each activity by cost objects and assign
the cost of the activity accordingly
total cost of activity
per period
(“cost pool”)
÷ total utilization of
activity per period
= Cost driver
rate
cost driver units
used by cost object
× Cost driver
rate
= overhead cost
assigned
to cost object
ABC Cost System









![Bài giảng Chuẩn mực kiểm toán Việt Nam [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2022/20220606/charaznable/135x160/2241654490097.jpg)






![Bài giảng Kế toán quốc tế: Chuẩn mực TSCĐ (Tài sản cố định) - [Nội dung chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251020/vitobirama/135x160/32311768303697.jpg)



![Bài tập Tổ chức công tác kế toán doanh nghiệp [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250613/laphong0906/135x160/69341768292575.jpg)
![Bài tập Kế toán quản trị: Tổng hợp 89 câu [kèm đáp án]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250612/minhquan0690/135x160/41641768201852.jpg)

![Tài liệu ôn tập Kế toán quản trị và chi phí [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250612/minhquan0690/135x160/26871768201854.jpg)


