
Tập 18 Số 4-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
10
UTILIZATION OF SOYBEAN RESIDUE BY PRODUCT FOR BIOPRODUCTION OF
1-HYDROXYPHENAZINE - A POTENTIAL FUNGICIDAL COMPOUND
Nguyen Van Bon1
Received Date: 05/8/2024; Revised Date: 14/8/2024; Accepted for Publication: 15/8/2024
ABSTRACT
1-Hydroxyphenazine (HP) is a heterocyclic nitrogenous compound which reported various potential
bioactivities. The current work aimed to utilize soybean residue by-product (SRBP) as a C/N source
for the biosynthesis of HP via fermentation and investigated its potent inhibition against some plant
pathogen fungi. The novel medium for effective HP production by P. aeruginosa TUN03 was investigated
comprising 1.75% C/N source (SRBP/Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) ratio of 8/2), 0.05% FeSO4, and 0.05%
K2HPO4 to obtain a high yield of HP at 19.23 μg/mL in a small flask. HP was pathogen using a 14
L-bioreactor and achieved higher productivity (32.01 μg/mL) in a shorter fermentation time (10 h)
compared to its fermenting at a small scale in flask. In anti-fungal tests, this compound showed potential
inhibition against Fusarium oxysporum F10 with a high inhibitory value of 65% and moderate effect
against Gongronella butleri F07 (35%) and Fusarium incarnatum F13 (30%). HP was further evaluated
for its effect against spore germination of F. oxysporum F10 and showed high inhibition value of 75%.
The result of this work suggested that SRBP is a suitable C/N source for the production of HP with
potential use a fungicidal agent.
Keywords: soybean residue by- product, 1-Hydroxyphenazine, bioreactor, anti-fungal activity.
1. INTRODUCTION
Phenazine - a nitrogenous and heterocyclic
compound has the formula of (C6H4)2N2. More
than 100 phenazine compounds have been found
in nature and their chemical structures are formed
from the basic chemical structure of phenazine
(Cimmino A. et al., 2012). Almost all the
natural phenazine derivatives are biosynthesized
via microbial fermentation, and more than 50
phenazines were reported being produced by
Pseudomonas species (Liu H. et al., 2007), of
which Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a major
phenazines-producing bacterial strain, as such
this bacterium has been extensively used in the
biosynthesis of phenazines.
In various earlier reports, commercial media
were used as a C/N source for P. aeruginosa
fermentation to produce phenazines, and the culture
processes were mainly performed on a minor scale
of flasks (Nguyen T.H. et al., 2022a). Concerning
eco-friendly and cost-effective production, we
established the fermentation process using some
organic by-products, such as squid pens (Nguyen
T.H. et al., 2022a), cassava residue (Phan T.Q. et
al., 2024), and groundnut cake (Nguyen V.B. et al.,
2023). In this study, soybean residue by-product
(SRBP) was considered used for fermentation.
Soybean is a species of legume, which is
native to East Asia, widely grown for harvesting
its edible bean. Soybean has been widely used for
oil extraction, production of soymilk, and other
products (Riaz M.N. et al., 2023). soybean residue
by-product (SRBP) is the main by-product from
oil extraction and soymilk manufacturing with a
reported highest residue yield of nearly 90% (Sun
Y. et al., 2021). This residue was found rich in
protein (16.1-33.4%), fat (8-22.3%), carbohydrates
(under 53.6%), and total minerals (0.2-5.3%) in
a survey by Shuhong Li et al 2013. Thus, SWRP
has been utilized for many purposes. In this work,
SWRP was used as a C/N source for fermentation
to produce 1-hydroxyphenazine (HP) – a phenazine
compound with potential fungicidal effects.
To date, phenazines have been reported for their
potential fungicidal effects against pathogenic
fungi in human (Zahraa J.J. et al., 2017; Sudhakar
T. et al., 2017), and toxigenic fungi in food (Zahraa
J.J. et al., 2017; Mohamed N.F.H. et al., 2020;
Hina S. et al., 2021). Notably, phenazines showed
inhibition against various plant pathogenic fungi,
including Botrytis cinerea, Alternaria alternate,
Fusarium graminearum, Fusarium oxysporum,
Magnaporthe grisea, Rhizoctonia solani,
Sitophilus oryzae, Macrophomina phaseolina,
Colletotrichum capsici, Colletotrichum
gloeosporioides, Comastoma falcatum,
Phaeosphaerella theae based on our recent survey
(Nguyen T.H. et al., 2022b). Recently, HP was
found as a potential fungicide against Fusarium
oxysporum with the anti-mycelial growth and anti-
1Institute of Biotechnology and Environment, Tay Nguyen University;
Corresponding author: Nguyen Van Bon; Tel: 0842458283; Email: nvbon@ttn.edu.vn.

Tập 18 Số 4-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
11
spore germination activity of 68.7% and 98.4%,
respectively (Phan T.Q. et al., 2024). In this study,
we evaluated the potential fungicidal effects of HP
against some plant pathogenic fungi collected in
the Central Highland of Vietnam.
Fermentation in
Small Scale
Soybean residue
by-product Scale-up Production of HP
in a 14 L- Bioreactor
Extraction &
Isolation of PG
Testing
fungicidal
Effect of HP
Scheme 1. The steps and contents for performing experiments in this work
2. MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY
2.1. Study contents
- Establishment of the fermentation process for
the production of 1-hydroxyphenazine.
- Purification of 1-hydroxyphenazine from the
culture medium.
- Assessment of the potential fungicidal activity
of 1-hydroxyphenazine.
The contents and experimental stepts of this
study were illustrated in Scheme 1.
2.2. Materials
P. aeruginosa TNU03 was isolated from
the soil of Dak Lak province of Vietnam in the
previous work (Nguyen T.H. et al., 2022c).
Silicagel (Geduran® Si 60, size: 0.040-0.063 mm)
was purchased from Merck Sigma Chemical
Co. (St. Louis City, MO, USA). Some plant
pathogenic fungi were obtained from our earlier
report (Nguyen D.N. et al., 2021).
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. The effect of SRBP/TSB ratio and their con-
centration added in medium on HP yield
- The fermentation process: SRBP was
combined with TSB at several ratios (SRBP/TSB,
w/w) of 5/5, 6/4, 7/3, 8/2, 9/1, and 10/10 then
used as C/N sources for cultivation. 30 mL culture
medium in a 100 mL-flask containing 1% C/N
source, 0.05% K2HPO4, and 0.05% FeSO4, initial
pH 7 was fermented by P. aeruginosa TUN03 at
30°C with a shaking speed of 150 rpm for 3 days
(this fermentation process is denoted by *). The
supernatant was harvested by centrifugation at
10,000× g for 15 min and used to determine the
target compound (HP) concentration.
- Various concentrations of C/N source (SRBP/
TSB at the ratio of 8/2), including 0.5, 0.75, 1.0,
1.25, 1.5, 1.75, and 2.0% were prepared in a liquid
medium containing 0.05% K2HPO4 and 0.05%
FeSO4 with initial pH 7, then were fermented using
the above protocol (*) to investigate the suitable
C/N concentration.
- Scale-up production of HP in a bioreactor
system: bacterial strain TNU03 was pre-cultivated
in culture broth TSB in some 500 mL flasks at the
temperature of 30 °C for 1.5 days, then a total of
400 mL of fermented medium (bacterial inoculum)
was added to the reactor containing 4.6 L of the
newly investigated culture medium containing
1.5% C/N source (SRBP/TSB at the ratio of 8/2),
0.05% K2HPO4 and 0.05% FeSO4, initial pH 7.0
The fermentation was performed at 30°C, 250
rpm, and dissolved oxygen of 1.2 vvm for 12 h,
and the HP produced by TNU03 was determined
every 2 h.
2.3.2. The purification and evaluation of fungicid-
al activity of HP
HP was isolated from the culture broth in a
bioreactor according to the protocol previously
presented in our report (Nguyen T.H. et al., 2022c).
Its GCMS and HPLC profiles were conducted
following the method reported by Nguyen V.B. et
al. (2023).
The fungicidal activity was tested via mycelial
growth inhibition and fungal spore germination
inhibition, which were presented in detail in our
previous work (Nguyen T.H. et al., 2024).
2.3.3. Statistical Analysis
The experimental data were obtained and
analyzed via the simple variance (ANOVA)
Tập 18 Số 4-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
12
then Duncan′s multiple range tests (when the
experiment contains ≥ 6 items that need to be
compared) and Fisher’s LSD tests (when the
experiment contains ≤ 5 items that need to be
compared) at p = 0.01 were evaluated. Statistical
Analysis Software (SAS-9.4) purchased from
SAS Institute Taiwan Ltd (Taipei, Taiwan) was
used for statistical analysis.
3. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1. Establishment of the fermentation process
for the production of HP.
The effect of SRBP/TSB ratio and their
concentration added in medium on HP yield:
TSB was used as free protein for adding into
the culture medium. SRBP was combined with
this free protein at several ratios and used as a C/N
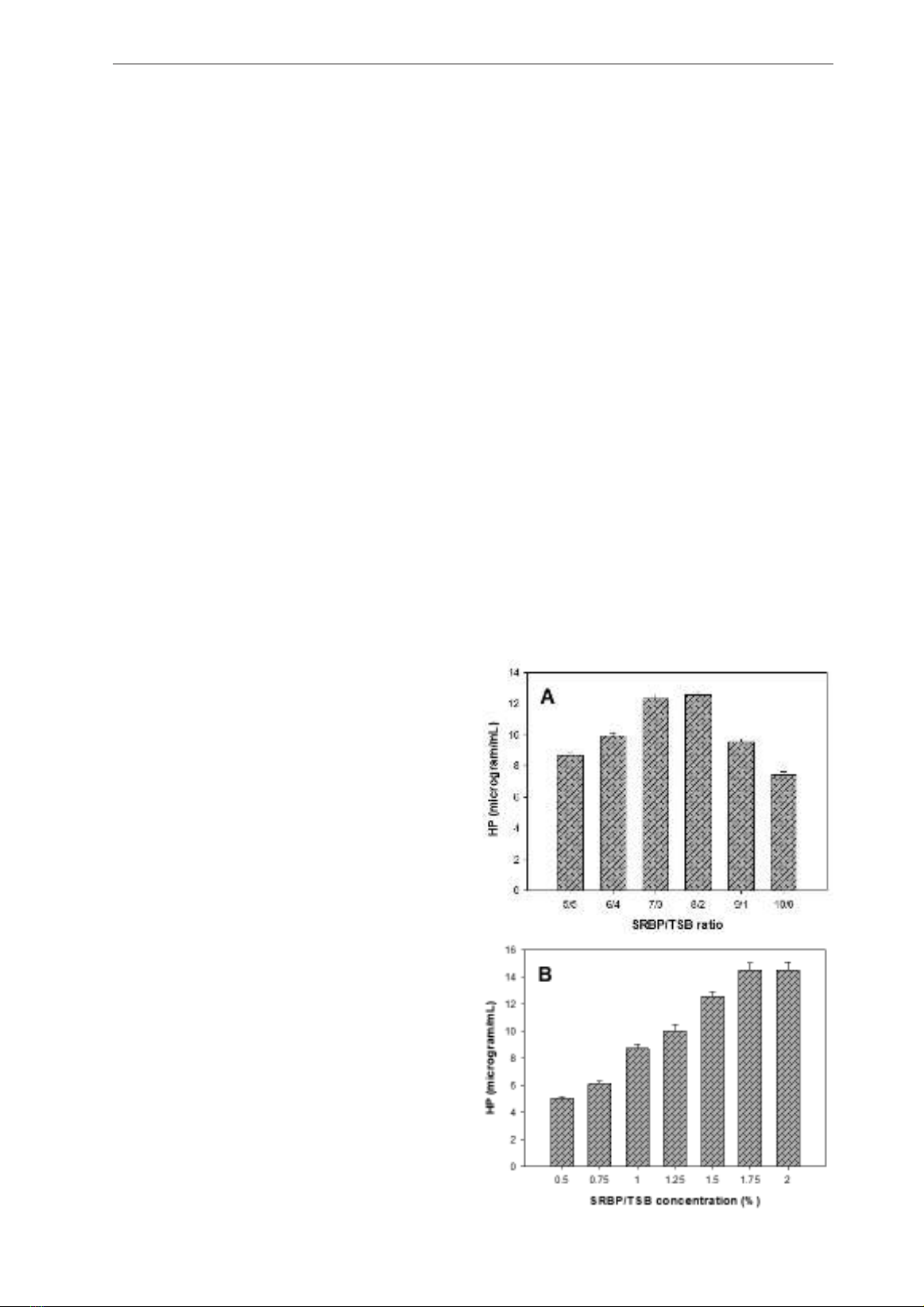
source for fermentation. As shown in Figure 1A,
the SRBP/TSB ratios of 7/3 and 8/2 gave the high
content of HP (12.3-12.5 μg/mL) in the fermented
medium. For cost-effectiveness, the ratio of 8/2
was chosen for further investigation to determine
the most suitable C/N source concentration.
The C/N source (SRBP/TSB at the ratio of 8/2)
was added into the cultured media with various
concentrations of 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75, and
2.0% then used for fermentation by P. aeruginosa
TUN03. As presented in the Figure 1B, the C/N
source at the concentration of 1.75-2% gave the
high yield of HP (14.50-14.52 μg/mL) in the
fermented media, and 1.75% C/N was chosen as
the suitable and cost-effective for fermentation to
produce HP.
Phenazine compounds were reported to
numerous bioactivities and as such received
much attention for their production. In many
previous reports, commercial media like King’s
B, King’s A, tryptone, peptone, and nutrient broth
for fermentation and phenazines were produced
at the content of 5.2-33.0 μg/mL (Elbargisy
R.M. 2021; Devnath P. et al., 2021; Ozdal M. et
al., 2019; Barakat K.M. et al., 2015; Ozdal M.
2019). For the lower cost of bioproduction of
phenazines, several low-cost organic materials
such as corn, cottonseed, sweet potato, soya
bean, groundnut, peat moss, and taro leaves
were investigated for phenazines producing by
fermentation, however, these compounds were
synthesized at low productivity under 4 µg/mL
mL (DeBritto S. 2020; El-Fouly M.Z. et al.,
2015).
Phenazines were also produced by using
some organic wastes, such as tea wastewater,
waste cheese whey, waste frying oil, olives
waste, maize wastewater, sugar beet molasses,
craft beer waste, peapods, and the phenazines
yield were obtained in the rang of 1.3-58 μg/
mL. Of these, craft beer waste was found as the
most potential C/N source for fermentation, and
phenazines were produced at a high of 21-58 μg/
mL according to a recent survey by Nguyen et al.
(2023). In this study, soybean residue by-product
(SRBP) combined with a minor amount of TSB
was first reported as being used as a potential
C/N source for fermentation to produce HP with
a high yield of 14.52 μg/mL.
Scaling up of 1-hydroxyphenazine production
using a 14 L-bioreactor system
In microbial fermentation technology,
bioreactor systems are considered valuable
quipment to effectively bio-produce secondary
metabolites with a high-level yield and reduce
the fermentation time (Nguyen, T.H. et al.
2021). In this work, HP was produced in mass
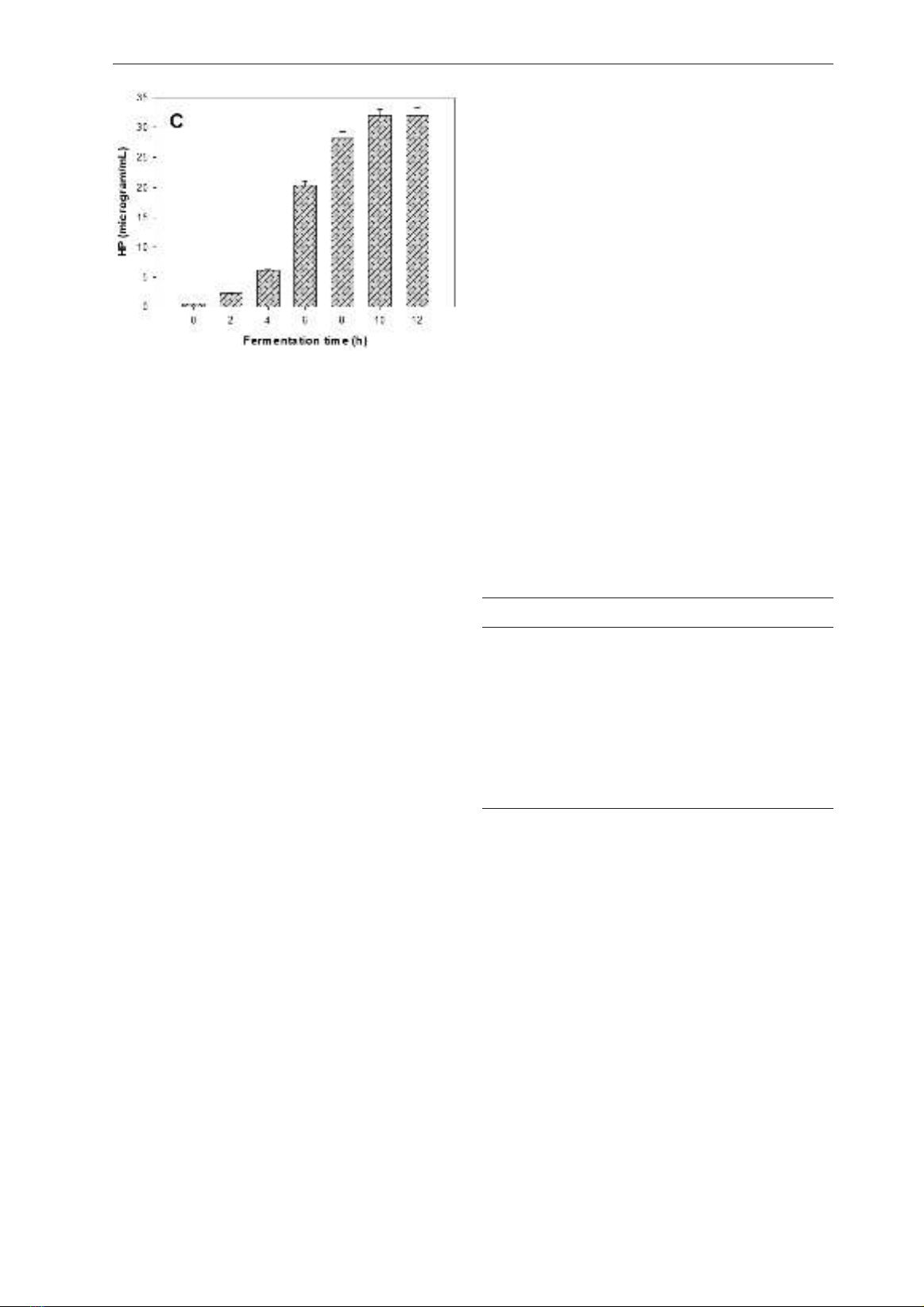
using a 14 L-bioreactor system. As illustrated in
Figure 1C, HP was synthesized by P. aeruginosa
TUN03 with a significant amount from 6 h
of cultivation. The HP yield was significant
enhanced till 10 h (reached the yield of 32.01
μg/mL), and no further HP was produced from
10-12 h of fermentation.
Tập 18 Số 4-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
13
Figure 1. Production of 1-Hydroxyphenazine
(HP) via fermentation.
Note: The effect of SRBP/TSB ratio (A) and
their concentration added in medium (B) on HP
yield. Scaling up of HP production using a 14
L-bioreactor system).
Recently, HP was produced in bioreactor
systems using peanut oil processing by-product
(Nguyen V.B. et al., 2023) and cassava starch
processing by-product (Phan T.Q. et al., 2024)
resulting in harvesting high productivity of 35.1
and 36.5 µg/mL, respectively.
3.2. The purification and evaluation of fungicidal
activity of HP.
The phenazine compound was isolated and
purified from the cultured broth in a bioreactor
system using the method presented in our
earlier report (Nguyen T.H. et al., 2022c). The
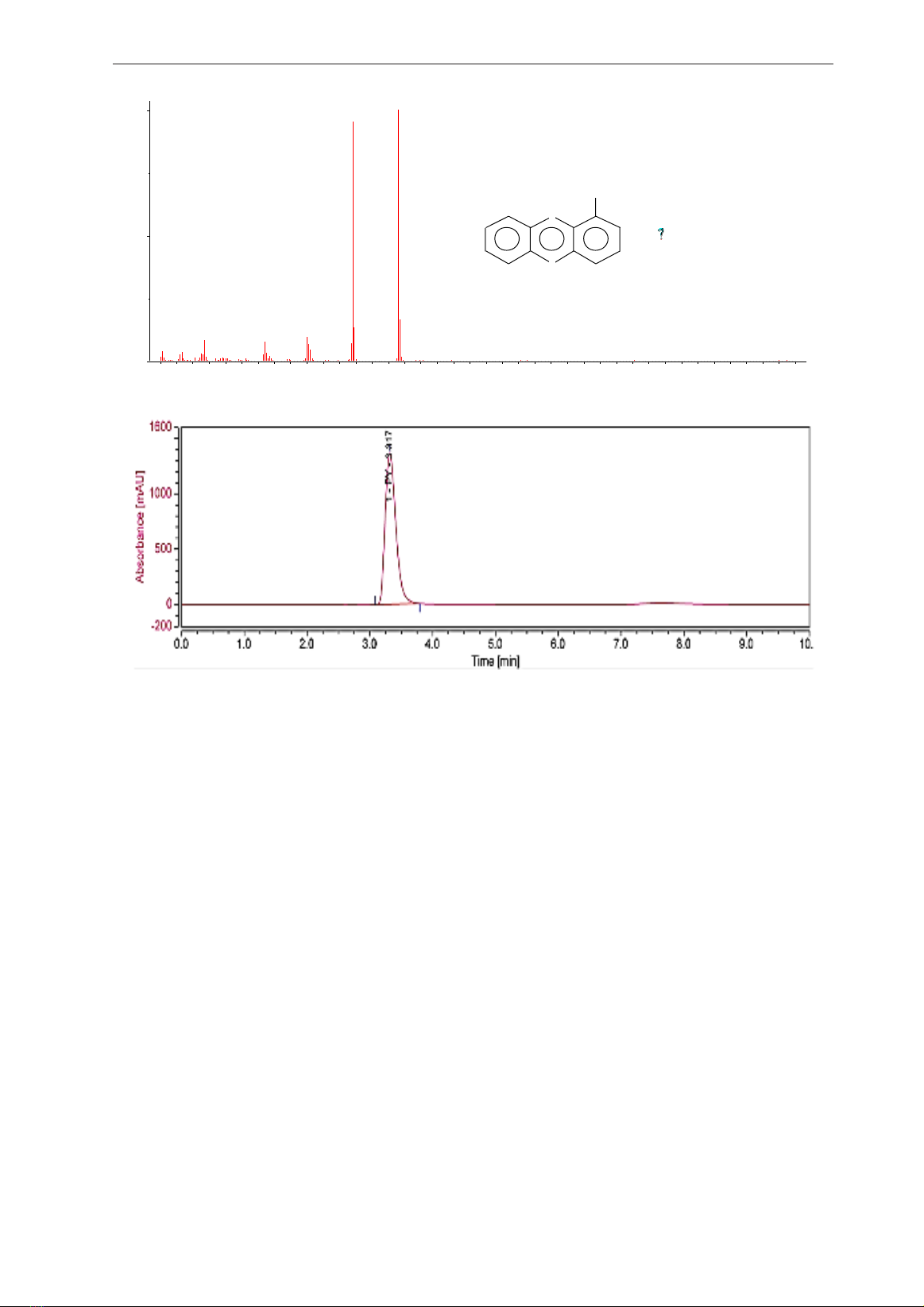
purified yellow compound was confirmed as
1-Hydroxyphenazine using GCMS analysis
(Figure 2). Based on the HPLC profile of HP
produced in this work, it was found to have a
high purity (Figure 3) as such it could be used for
further study in bioactivity tests.
To confirm the purified compound – HP
produced in this study is an active fungicidal
compound, various plant pathogenic fungal
strains obtained from the previous work (Nguyen
D.N. et al., 2021) were used for testing the
fungicidal effect of HP. As shown in Table 1, HP
shows inhibition against some fungal strains,
including Fusarium solani F02, Fusarium
solani F03, Fusarium solani F04, Gongronella
butleri F07, Fusarium oxysporum F10, and
Fusarium incarnatum F13 with the inhibition
values in the range of 7-65%. Of those, HP had a
weakly inhibition against Fusarium solani F02,
Fusarium solani F03, Fusarium solani F04 with
an inhibition of 7-16%, moderately effect against
Gongronella butleri F07 (35%) and Fusarium
incarnatum F13 (30%). This compound showed
the most effect against Fusarium oxysporum F10
with a high inhibitory value of 65%. The result of
this work suggested HP may be a high potential
candidate for management of Gongronella butleri
F07, Fusarium oxysporum F10 and Fusarium
incarnatum F13.
The fungal spores were reported to play an
important role in the pathogenesis of pathogenic
fungal strains, in addition, this is also recognized
as the most sensitive stage to inhibition, as
such, assessing the inhibitory effect of both
mycelial growth and spore germination is an
effective strategy for the phytopathogenic
fungi management (Phan T.Q. et al., 2024). To
futher characterize HP as a potential fungicide
against Fusarium oxysporum F10, the fungal
spore germination inhibition of HP was also
tested. The result showed that HP demontated
better inhibitory effect for spore germination
(75%) than inhibition against mycelial growth
(65%).
Table 1. Inhibitory effects of HP on some
pathogenic fungal strains
Fungal strains Anti-fungi (%)
Fusarium solani F02 7
Fusarium solani F03 16
Fusarium solani F04 11
Gongronella butleri F07 35
Fusarium oxysporum F10 65
Fusarium incarnatum F13 30
4. CONCLUSIONS
This study achieved finding a novel culture
medium comprising 1.75% C/N source (SRBP/
TSB ratio of 8/2), 0.05% FeSO4, and 0.05%
K2HPO4. HP was then scale-up produced using a
14-L bioreactor system resulting in a high HP yield
of 32.01 μg/mL. The purified HP demonstrated
potential inhibition against Fusarium oxysporum
F10 (65%) and a moderate effect against
Gongronella butleri F07 (35%) and Fusarium
incarnatum F13 (30%). In addition, HP also
demontated high effect against F. oxysporum F10
spore germination of (75%).
Tập 18 Số 4-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
14
(Text File) PYO01_120729234758#1070 RT: 13.47 AV: 1
50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 260 270 280 290 300 310 320 330 340 350 360 370 380 390 400 410 420 430 440
0
50
100
51 63
77
88 102
114
128
140
153
168
196
207 229 271 341 430
ine
N
N
OH
Figure 2. The GCMS profile of 1-hydroxyphenazine
Figure 3. The HPLC profile of 1-hydroxyphenazine purified in this work.

![Bài giảng Chế biến khoáng sản vô cơ [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251025/thanhvan173002/135x160/21521761538638.jpg)








![Bài giảng Giản đồ pha: Chương 2 - Nguyễn Văn Hòa [FULL]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2018/20180409/tieu_vu10/135x160/531523282915.jpg)















