
1
PREFACE
1. Urgency of the thesis
Reinforcement of thermoplastic by using particle has studied in few decades ago. Until now, it
plays an important role in as well [1]. The flexibility of thermoplastic composite materials expands the
scope of application in the life and research field. When the materials are reinforced by fillers, their
properties are changed. Typically, the filler impacts in hardness, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion.
However, they improve strength and elasticity as well because of the filler properties and the changing of
morphology matrix. The inorganic filler are used wide in thermoplastic such as CaCO3, talc, SiO2, mice
and Mg(OH)2.
Most of the researches carried paying attention on the factors such as (i) component; (ii) shape and
size; (iii) composition; (iv) compatibility of matrix and filler. Some of them showed a polymer layer
locating aninteraction phase between filler surface and matrix which have special property. However, the
role, influenceand a parameters relationship ofthe phase interaction betweenthe filler and the matrix on
the mechanical properties (i.e. tensile strength, impact resistance) is not determined clearly.
Thus, supervisor and PhD student carried on a thesis:” Effect of surface fillers modification on
phase interaction and mechanical properties of thermoplastic materials”
2. The aim of thesis
To study relation of molecular structural changing between polypropylene microcomposite system
and the particle fillers with varies phase interactions by using solid-state NMR(ss-
NMR) spectra.Therein,emphasizing the molecular flexibility on mechanical properties of materials.
3. Main contents of thesis
a. Preparing polypropylene composites materials by using the filler was modified/unmodified
surface at varies contents.
b. Research phase interaction morphology, determine the mechanical properties of materials
including tensile strength and impact resistance (integral J).
c. Application of solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (ss-NMR) method to determine molecular
mobility in polymer composite materials, study the relation of mechanical properties of material.
Outline of the thesis: The thesis has 24 pages including introduction, 4 chapters of content, contributions
and a list of publication.
The main results of the thesis are published in:
- 01 article in an international journal in the ISI list (IF = 3.7)
- 04 articles in national journal
- 05 reports in the International Science Conference (1 international conference to publish
ISBN)

2
Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1. Thermoplastic polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP) was invented by research groups in the United States and Europe in the early
1950s. The commercial production of PP began in 1957 in the US and in 1958 in Europe. On the other
hand, PP ranks first in the largest volumes group of thermoplastic products used such as: polyethylene
(PE), polyvinylchloride (PVC) and polystyrene (PS). Average consumption of PP increases about 10%
per year and the trend will keep increasing in future.
The flexibility is important property of PP. The structure and characteristics (including processing)
of PP can be adjusted according to usage requirements. Polypropylene has many advantagedproperties
such as low density, chemical resistance, easy processing and recyclability. In addition, its mechanical
properties are well suited to engineering plastics. Besides, PP also has some disadvantages such as
deteriorationin properties at low temperatures and low impact resistance. Thus, PP copolymers and their
blendsare studied to develop in commercial fields.
1.2. Polymer composite materials base on fillers reinforced PP
Fillers reinforced PP composite materials have been used in large quantities in many different
fields such as automotive, furniture, electrical equipment, etc. Because of the relation between cost and
achieved properties, filler reinforced PP composites are used widely and gradually replaced ABS inthe
traditional fields. Other materials like. Many efforts have been made to expand its scope of application in
engineering thermoplastic materials
There are many types of reinforced fillers using in PP, however, CaCO3, talcand fiber glass play the
most important role and will keep it in the near future including. In thermoplastic market, CaCO3
consumptionmakes up a majority of the filler field. However,talc mineral ranks first inthe PP market,
CaCO3 only ranks second and glass fiber follow. Hence, glass fiber reinforced PP is studied to improve its
capabilities and expand its scope of application. In despite of many efforts,they are still potential and
expectant researches. In reality, application and the growth rate of fiber glass for PP are lower than that of
particle fillers.
Nowadays, not only the technical and aesthetic requirements but also the costs of processing and
raw materialsare increasing. To meet these requirements, the researchers need understanding the relevant
properties of fillers as well as their influence on the structure and properties of composite materials touse
all the advantages of fillers or just use them as diluents forreducing costs.
1.3 . Solid state magnetic resonance spectroscopy and its application for molecular mobility in
polypropylene composites
Today, the high-resolution 13 C NMR spectrum is a common tool for studying the structure of
polymers. 1 H-NMR isa standard technique in structural analysis of liquid-state substances, but in solid-
state substances. Isotactic polypropylene isa polymorphic material due to a modifying arrangement of
polymer chains. Hence, ss-NMR spectroscopy technique showed complicatedanalysis for
polypropylene.It is more complicated particularlyif the composition of these components that plays a
decisive role changing the properties of polymer is significantly lower than composition of the matrix.
This difference prevents the use calibration curve analysis. Therefore, special method must be used to

3
describe the small differences between the amorphous and crystals disordering in the phase interaction
region.
However, the less attention has been paid to the multi-molecular analysis of the ss-NMR spectrum
for amorphous or disordered solids, which can be considered an extreme limit due to the frequency range
being too much for signals for which only one signal is available are defined. Therefore, the thesis also
demonstrates that 13 C MAS ss-NMR spectrocopy is a fast, reliable tool for describing extremely
complex crystal forms in PP material for clarifying the relationship between spectral data at the
molecular level and the macroscopic properties of materials such as mechanical properties.
1.4 . These studies were carriedon in Vietnam
The basic researches in Vietnam on thermoplastic composite materials in general and
polypropylene in particular were studied by Hoang Thai and et al at the Institute of Tropical Technology
and Dieu Tran Vinh and et al at Hanoi University of Technology.
Hoang Thai et al treated titan dioxide or nano BaSO4 surface by silane coupling agent for studying
mechanical properties and morphological structure of titan dioxide or nano BaSO4 filled polypropylene
composites. This surface modification process improved significantly the mechanical properties of
composite materials. Tensile strength and elastic modulus of PP composite materials with 2% of surface-
modified nanoparticles are 42 Mpa and 979 Mpa, respectively. Based on results of the cumulative module
(G ') and phase interaction from X-ray diffraction analysis and FE-SEM, they showed that the properties
and phase interaction of the material containing modified nanoparticle are better than these of the material
containing unmodified nanoparticle. .
Besides, the research team of Prof. Hoang Thai mixed melting polypropylene and vinysilane
modified fly ash particles. The effect of fly ash content on viscosity, mechanical properties and material
morphology was determined. The results indicated that the viscosity of the mixture decreased with
increasing fly ash content. Tensile strength and elongation at break of the material with different loading
of untreated fly ash are lower than the original PP. After modifying by vinyl silane,PP / fly ash composite
material showed higher tensile strength and elongation at break while viscosity of the mixture was lower.
The research team of Prof. Dieu Tran Vinh had many studies on composite materials based organic
fibers reinforced polypropylene . They was considered that the adhesion between the plastic substrate and
polar organic fiber affects incredibly the properties of the composite. Thus, maleic anhydride–
grafted polypropylene (MA-g-PP) compatibilizer or acetic anhydride and acrylonitrile was used.
Comparing the mechanical properties of polypropylene composite materials containing jute fibers and
glass fibers, although tensile strength and elastic modulus of jute were lower than that of fiberglass, the
specific module of jute was higher than glass fiber, and the module cost of jute is much higher than that of
fiberglass. The effect of jute and MAPP on PP tensile and flexural strength were determined. When 50%
weight of jute is loaded, the flexural strength of PP increases from 31.33 Mpa to 49.97 Mpa and increases
sharply to 87.66 Mpa when adding 3% of MAPP weight. Tensile strength does not increase much without
MAPP. However, when MAPP has tensile strength, composites increase about 2 times (from 28.92 MPa
to 59.12 MPa).
Similarly, composite is reinforced with NaOH solution treated short bamboo fiber adding 0.6% of
MAPP compatibilizer, its tensile strength, flexural strength and impact strength are respectively increased
by 24%; 23% and 40% compared with its of raw PP. The team also carried on the acetylation of bamboo

4
fibers and determined the effect of this process on the reinforcement of polypropylene based composite
material. Acetylation reduces the hygroscopic of bamboo fibers, increases the adhesion between bamboo
fibers and PP resin. 50% of short bamboo fibers reinforced PP composites has the highest tensile strength
(36.45 MPa), increase of 2% compared with its raw PP.
Chapter 2. EXPERIMENTAL
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Polymer
Isotactic polypropylene homopolymer Mosten 52.412 (Chemopetrol, Czech Republic) was used
as a matrix in this study.
2.1.2. Fillers
Glass beads, average size ~ 20 µm supplied by SOVITEC, France.
Calcium carbonate, average particle size ~ 1.7 µm (1VA) and ~ 12 µm (15VA), supplied by
Omycarb, Switzerland.
Talc mineral originated from Thanh Son district, Phu Tho province, Vietnam. The main
components of this mineral are SiO2 (60,82 %) and MgO (32,16 %). Average particle size ~ 6,58 µm.
2.1.3. Surface modification agents
Vinyltriethoxysilane supplied by Momentive (Switzerland) and methacryloxy
propyltrimethoxysilane supplied by DowCorning (USA). Oleic and stearic acids (technical grade products
supplied by Sigma-Aldrich) were used for calcium carbonate surface modification.
2.1.4. Other materials
Dicumyl peroxite (technical grade ) supplied by Sigma-Aldrich.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Surface modification
The surface modification of filler particles is carried out in 96% ethanol solution containing 2%
of the surface modification agent.
2.2.2. Composite preparation
Polypropylene and fillers were been compounded in the twin-screw compounder (extruder)
Brabender DSE and subsequently injection-molded into form of specimens (dog-bone) by ENGEL Spex
victory 50 machine.
2.3. Properties assessment
2.3.1. Morphology
The morphology was assessed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) taken on impact fracture
cross-section of composites.
2.3.2. Tensile properties
Tensile mechanical tests were carried out on Instron 5800 material tester at room temperature and
cross-head speeds alternating of 1 mm/min and 50 mm/min.
5
2.3.3. Impact properties
An instrumented Charpy impact tester Ceast Resil Impactor with 7,5J work capacity was used for
the J-integral evaluation.
2.3.4. ss-NMR
The ss-NMR experiments were performed using a Bruker Avance 500 WB/US NMR (Karlsruhe,
Germany, 2003; B0 ¼ 11.7 T) with 4 mm ZrO2 rotors at a MAS frequency of 6 kHz. The 13C
crosspolarization (CP) MAS NMR spectra were measured with a B1(13C) field nutation frequency of 62.5
kHz, a contact time of 1.75 ms and a recycle delay of 2 s. To record the T1-filtered, domain-selective
spectra of the highly mobile components, the single-pulse 13C MAS NMR spectrawere measured with a
repetition delay of 2 s. The VT experiments were performed in the temperature range from 295 to 355 K.
The frictional heating of the sample was compensated, and the sample temperature was calibrated using
the 207Pb chemical shift in Pb(NO3)2.
2.3.5. Factor analysis (FA)
FA is a method that uses the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) algorithm to extract specific
information from experimental data. This technique allows visualization and distinguishing subtle
differences between the prepared PP/CaCO3 microcomposites in 2D or 3D maps.
Chapter 3: RESULS AND DISCUSION
3.1. Composite based on polypropylene and glass beads
3.1.1. Morphology observation
The introduction of inorganic filler into a polymer matrix results in a heterogeneous system.
Adhesion among different materials is created by physical or chemical bonds between the adhesive and
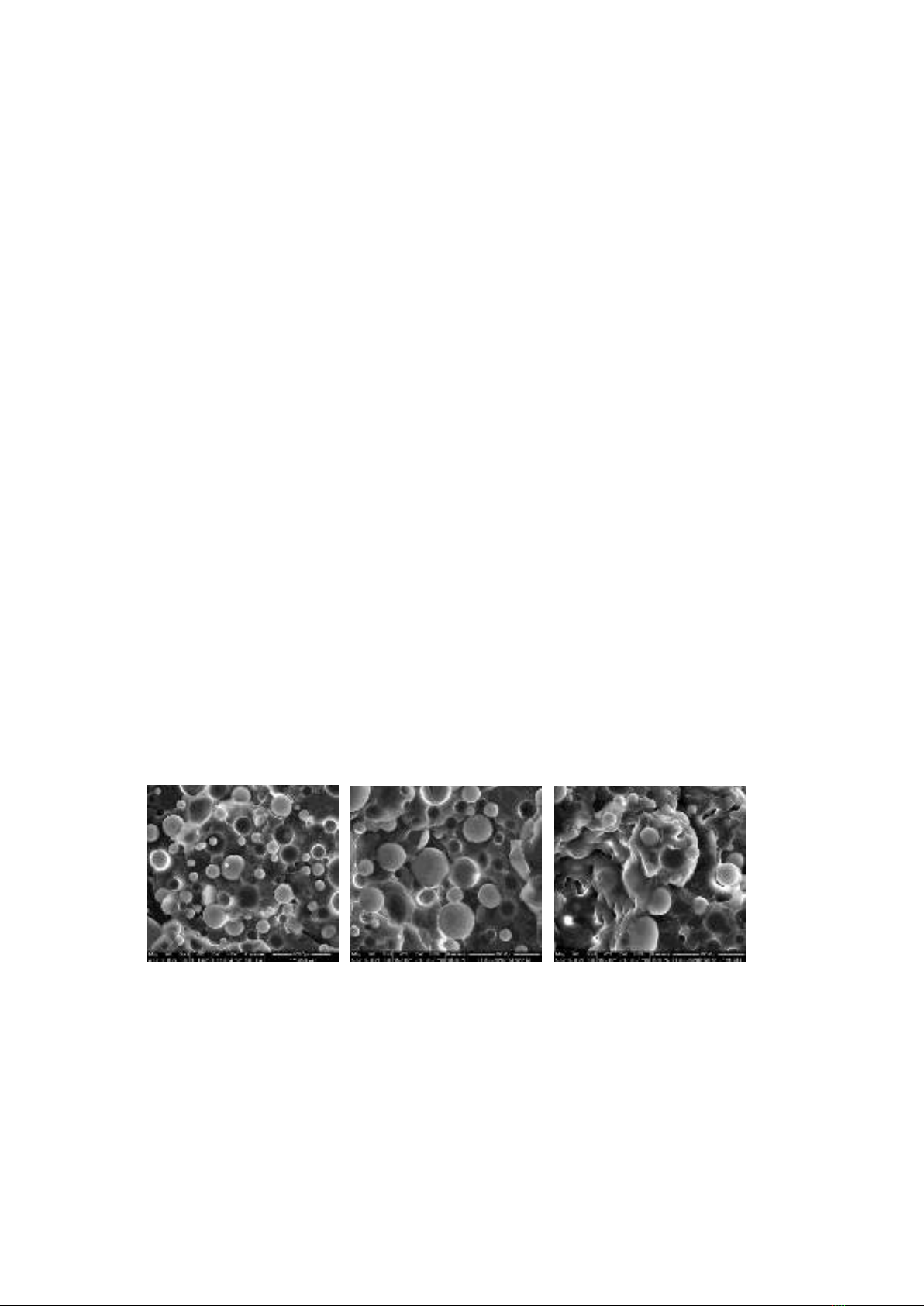
the substrate, and this depends on the selection of coupling agent. Figure 3.1 presents structure
morphology taken of the impact fracture cross section of PP/glass beadcomposites with 20% of filler
content.
a) b) c)
Fig. 3.1. Degree of interfacial adhesion between glass bead and PP matrix.
As revealed by SEM in the cases of non-treated and NO adhesion, there was a poor interfacial
with the strong debonding of particles. While in case of GOOD adhesion, a strong bonding achieved
between glass bead particles and PP matrix, coated spheres adhere to the matrix.
3.1.2. Tensile properties
The effects of glass bead with different surface properties on the mechanical properties of
composites are showed in Fig. 3.2. It can be sheen that the tensile moduli in all cases of composites





![Luận văn Thạc sĩ: Tổng hợp và đánh giá hoạt tính chống ung thư của hợp phần lai tetrahydro-beta-carboline và imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250816/vijiraiya/135x160/26811755333398.jpg)




















