http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 103 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 9, Issue 2, March–April 2018, pp. 103–111, Article ID: IJM_09_02_012
Available online at
http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=9&IType=2
Journal Impact Factor (2016): 8.1920 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
A STUDY ON POTENTIALITY OF VIRTUAL
SHOPPING CONCEPT FOR SELECTED FMCG
PRODUCTS IN BANGALORE
Saravana Kumar. S
Ramaiah Institute of Management studies, Bangalore
ABSTRACT
The recent development of technological wave, in particular to virtual technology,
has brought a new era in shopping activities. After, the successful business of e -
commerce the shopping is changing which results in the emergence of virtual
shopping using smartphones. Current research is chosen to investigate how
consumers adopt technology in diverse virtual environments. QR (Quick Response),
disseminate information about the products and services of the next step to bar code
and use them before they buy online. This research aims to discuss the future
directions for how virtual shopping using smartphones will change shopping
behaviour in Bangalore. Based on the scope of utilizing virtual technology in
shopping practices the concept is tested using a data from selected sample of
Bangalore population. Research shows that customer shopping is simple and
convenient. It also shows the concept is very useful for office goers and frequent
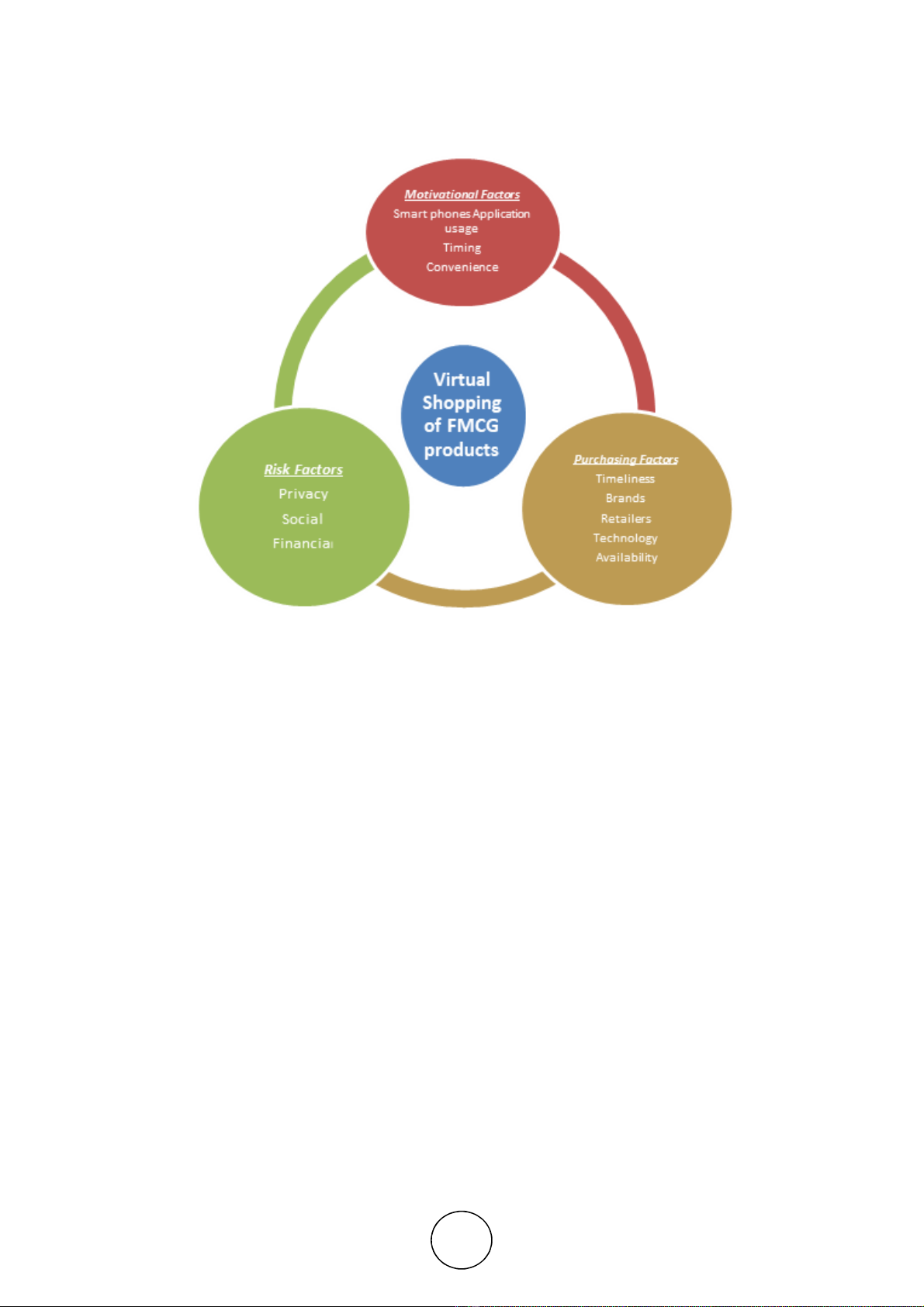
buyers which have great demand in Bangalore. Though buyers are interested still
sceptical with the issues faced when purchased online like, security, product quality,
originality, warranty etc. The future online shopping is bright especially of travel,
books, electronic gadgets, shoes, and gifts. On the basis of these findings, the younger
generation's virtual shopping idea and the profile of potential buyers are examined. It
id been concluded that middle-aged customers are more attracted for greater
shopping experience by scanning QR code which eliminates long-time standing for
groceries and saves money and time by simply scanning.
Keywords: Virtual Shopping, What is virtual shopping, Virtual shopping in India, Virtual
Shopping Strategies, Virtual Shopping 2018, Virtual shopping in Bangalore, Consumer
Behaviour towards Virtual Shopping.
Cite this Article: Saravana Kumar. S, A Study on Potentiality of Virtual Shopping
Concept for Selected FMCG Products in Bangalore, International Journal of
Management, 9 (2), 2018, pp. 103–111.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=9&IType=2