Ch1
Chapter 1
Chapter 1
Strategic Management and
Strategic Management and
Strategic Competitiveness
Strategic Competitiveness
Michael A. Hitt
Michael A. Hitt
R. Duane Ireland
R. Duane Ireland
Robert E. Hoskisson
Robert E. Hoskisson
©2000 South-Western College Publishing
Ch1
Sustained Competitive Advantage
Sustained Competitive Advantage
Above-Average Returns
Above-Average Returns
Returns in excess of what an investor expects to
Returns in excess of what an investor expects to
earn from other investments with similar risk
earn from other investments with similar risk
Occurs when a firm develops a strategy that
Occurs when a firm develops a strategy that
competitors are not simultaneously implementing
competitors are not simultaneously implementing
Provides benefits which current and potential
Provides benefits which current and potential
competitors are unable to duplicate
competitors are unable to duplicate
Strategic Competitiveness
Strategic Competitiveness
Achieved when a firm successfully formulates
Achieved when a firm successfully formulates
and implements a value-creating strategy
and implements a value-creating strategy
Ch1
which are required for firms to achieve:
which are required for firms to achieve:
Above-Average Returns
Above-Average Returns
Strategic Competitiveness
Strategic Competitiveness
Sustained Competitive Advantage
Sustained Competitive Advantage
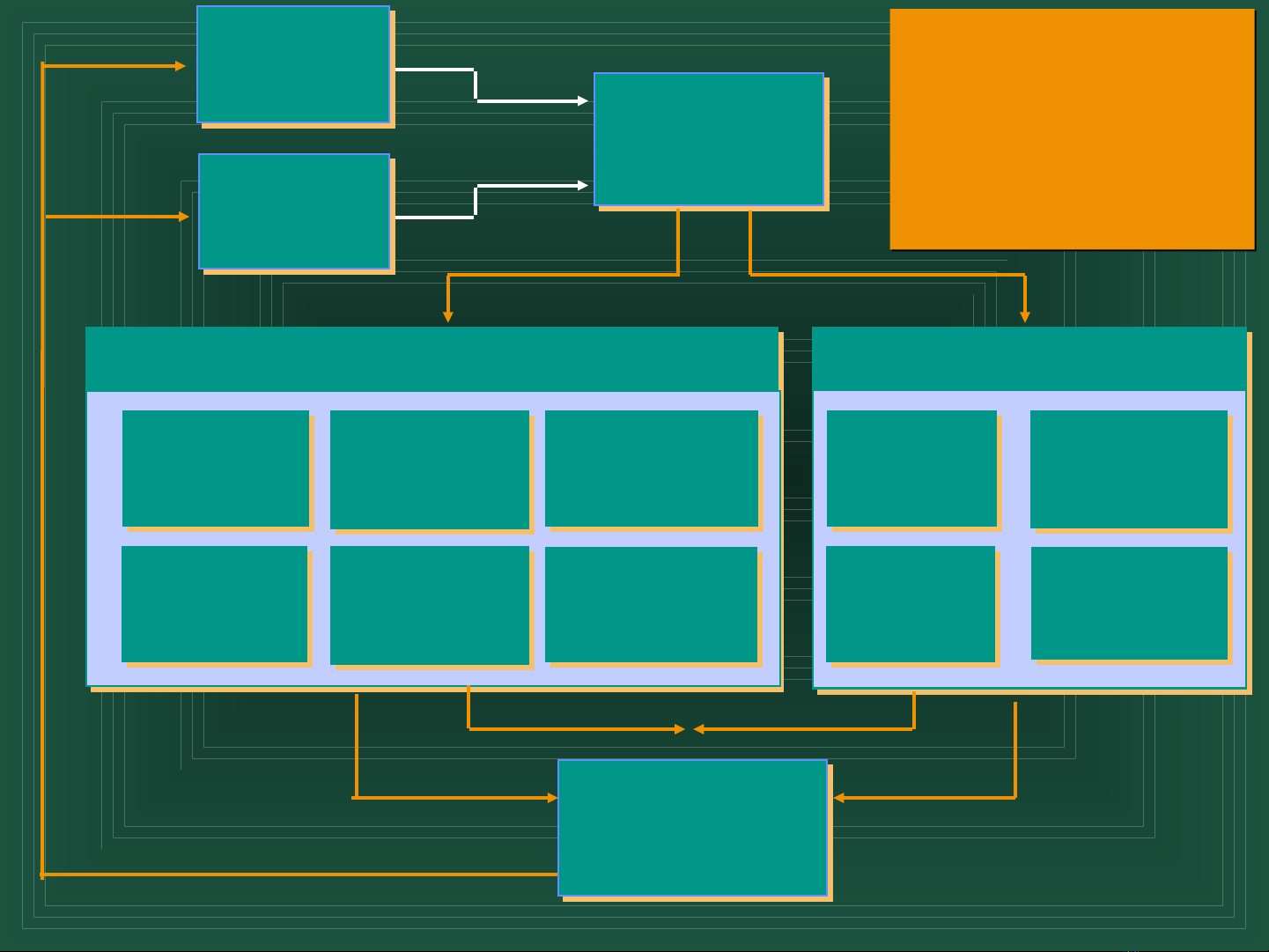
The Strategic Management Process
The Strategic Management Process
Involves the full set of:
Involves the full set of:
Actions
Actions
Commitments
Commitments Decisions
Decisions
Ch1
The Strategic
The Strategic
Management
Management
Process
Process
The Strategic
The Strategic
Management
Management
Process
Process
Chapter 3
Internal
Environment
Chapter 2
External
Environment
Strategic Intent
Strategic Mission
Strategy Formulation Strategy Implementation
Chapter 4
Business-Level
Strategy
Chapter 5
Competitive
Dynamics
Chapter 6
Corporate-Level
Strategy
Chapter 8
International
Strategy
Chapter 9
Cooperative
Strategies
Chapter 7
Acquisitions &
Restructuring
Chapter 10
Corporate
Governance
Chapter 11
Structure
& Control
Chapter 12
Strategic
Leadership
Chapter 13
Entrepreneurship
& Innovation
Strategic
Inputs
Feedback
Strategic
Outcomes
Strategic
Strategic
Actions
Actions
Strategic
Competitiveness
Above Average
Returns
Ch1
Chapter One: Key Themes
Chapter One: Key Themes
•Industrial Organization Model
Industrial Organization Model
•Resource-Based Model
Resource-Based Model
Challenge of Strategic Management
Challenge of Strategic Management
Changing Competitive Landscape
Changing Competitive Landscape
Two Models of Superior Profitability
Two Models of Superior Profitability
Key Stakeholder Groups


























