Ch ng 4ươ
Đ T BI N NHI M SĂC THỘ Ế Ễ Ể

N i dung chínhộ
1. Đ t bi n c u trúc NSTộ ế ấ
–L p đo nặ ạ
–M t đo nấ ạ
–Đ o đo nả ạ
–Chuy n đo nể ạ
1. Đ t bi n s l ng NSTộ ế ố ượ
–Đa b i hoáộ
–L ch b i hoáBB t ho t c a NST Xệ ộ ấ ạ ủ
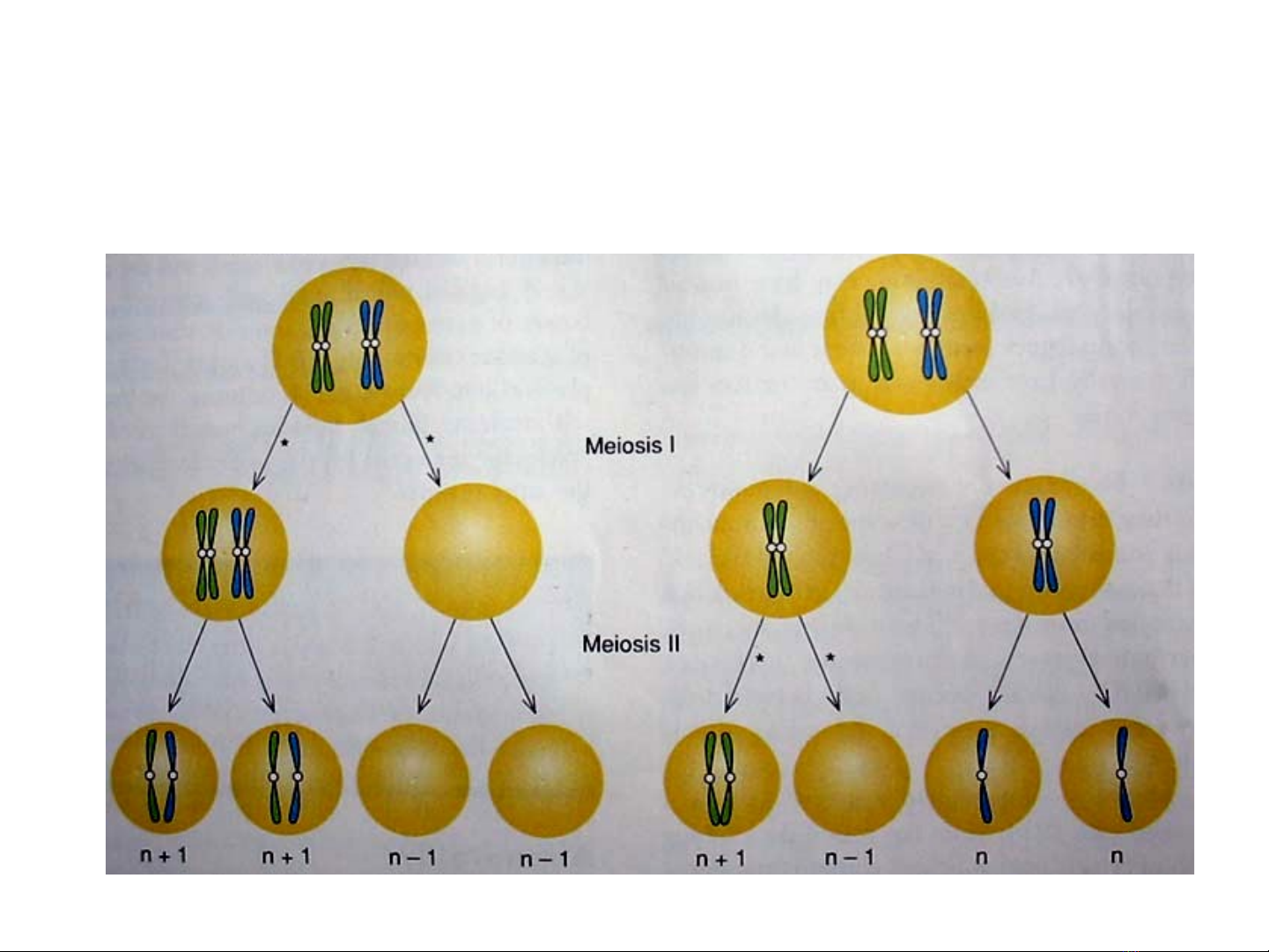
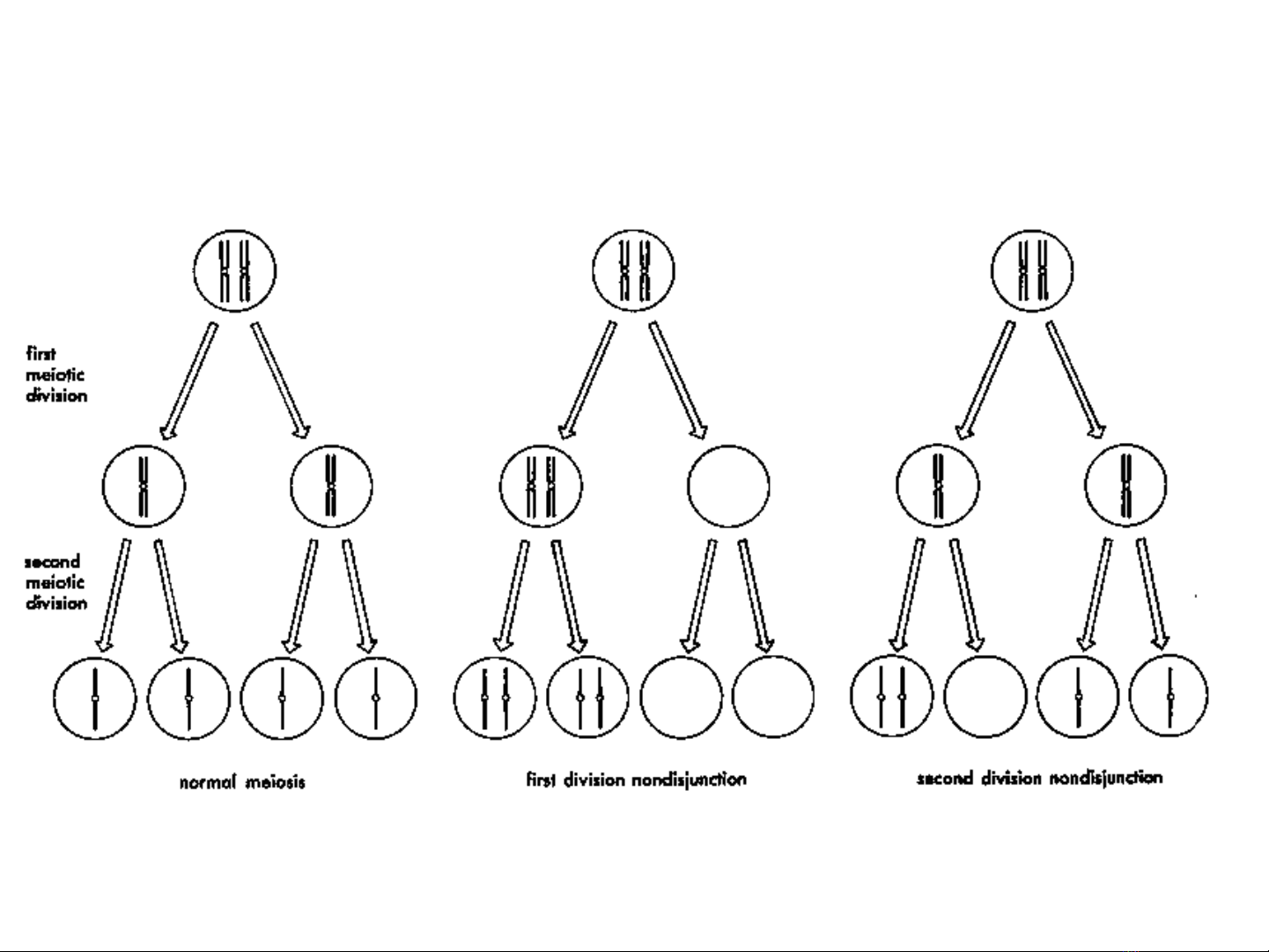
Hi n t ng l ch b i (aneuploidy)ệ ượ ệ ộ
•Nguyên nhân và c chơ ế
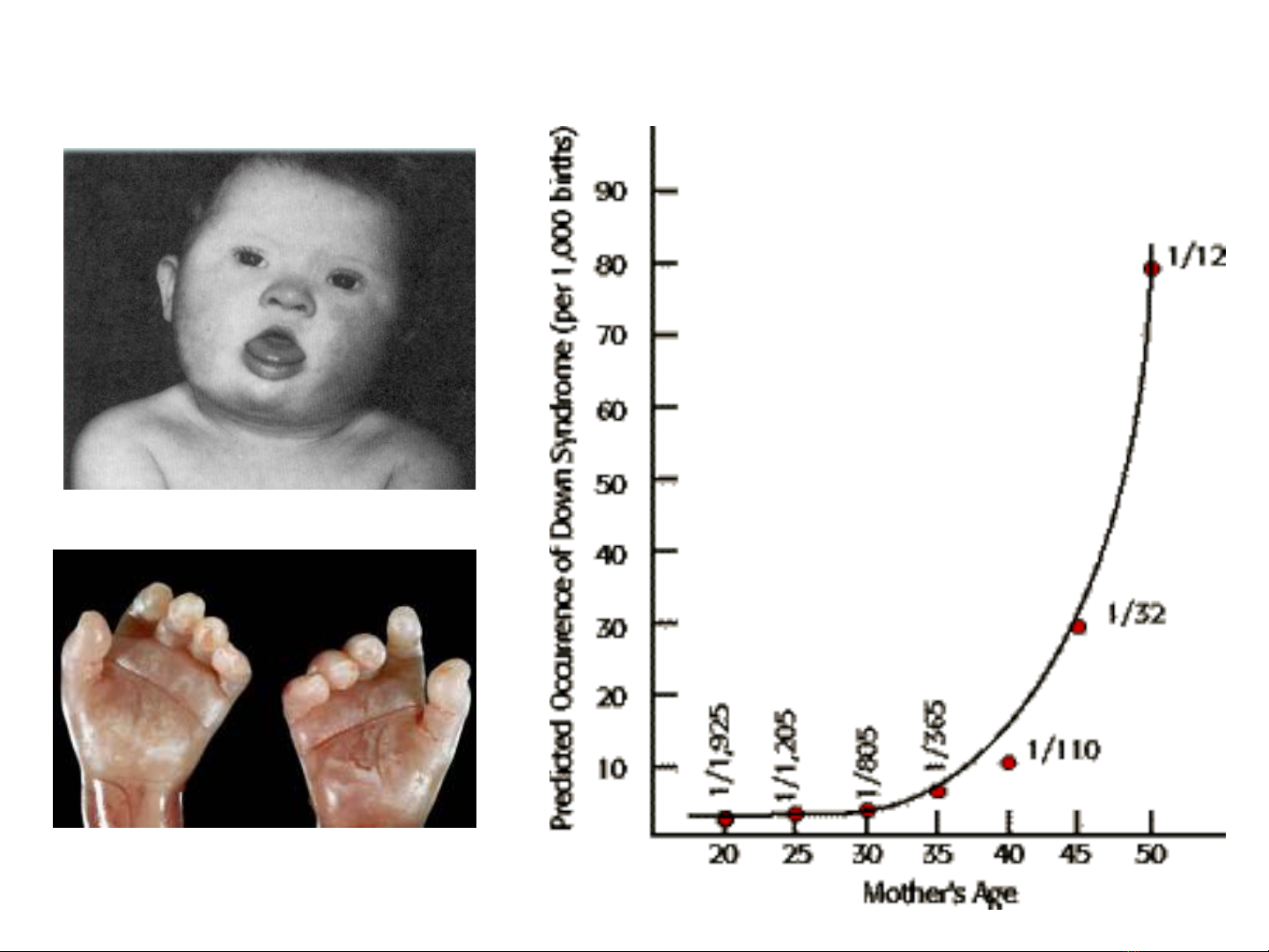
Hi n t ng l ch b i ng iệ ượ ệ ộ ở ườ



![Bài giảng Kỹ thuật DNA và công nghệ sinh học [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2022/20220110/trollhunters/135x160/9101641828200.jpg)








![Giáo trình Vi sinh vật học môi trường Phần 1: [Thêm thông tin chi tiết nếu có để tối ưu SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251015/khanhchi0906/135x160/45461768548101.jpg)





![Bài giảng Sinh học đại cương: Sinh thái học [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250812/oursky02/135x160/99371768295754.jpg)



![Đề cương ôn tập cuối kì môn Sinh học tế bào [Năm học mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260106/hoang52006/135x160/1251767755234.jpg)

![Cẩm Nang An Toàn Sinh Học Phòng Xét Nghiệm (Ấn Bản 4) [Mới Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251225/tangtuy08/135x160/61761766722917.jpg)