
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 1172 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET)
Volume 10, Issue 03, March 2019, pp. 1172-1179. Article ID: IJMET_10_03_119
Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?JType=IJMET&VType=10&IType=3
ISSN Print: 0976-6340 and ISSN Online: 0976-6359
© IAEME Publication Scopus Indexed
THE EFFECT OF BUDGETARY
PARTICIPATION, DIFFICULTY LEVEL AND
ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ON THE
PERFORMANCE OF GOVERNMENT
OFFICIALS
Paulus Peka Hayon and Mohamad Ilham
Accounting Department, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Musamus,
Merauke, Indonesia
ABSTRACT
The performance of government officials is a reflection of the progress of a region.
The success of the performance of the regional government is interesting to note
because the regional government is an extension of the central government that runs
the government that has direct contact with the community in its area. This study aims
to determine the effect of budgeting participation, budget difficulty, and organizational
culture on the performance of government officials. This type of research is quantitative
research. The population in this study was government officials in the Tanah Miring
District of Merauke Regency. Sampling using the purpose sampling method that is
sampling with certain considerations. The data in this study were processed using SPSS
21 tools. The results of this study indicate that participation in budgeting had a
significant effect on the performance of government officials, while the level of difficulty
of the budget and organizational culture did not affect the performance of government
officials.
Keywords: Budgeting participation, Budget difficulties, Organizational culture,
Government official’s performance
Cite this Article Paulus Peka Hayon and Mohamad Ilham, the Effect of Budgetary
Participation, Difficulty Level and Organizational Culture on the Performance of
Government Officials, International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and
Technology, 10(3), 2019, pp. 1172-1178.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/issues.asp?JType=IJMET&VType=10&IType=3
1. INTRODUCTION
The policy of regional autonomy is basically directed at encouraging increased capacity of local
governments in providing services to the public more effectively and efficiently. The closeness
of government organizations at the regional level is expected to be better able to accept the

The Effect of Budgetary Participation, Difficulty Level and Organizational Culture on the
Performance of Government Officials
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 1173 editor@iaeme.com
people's real aspirations about what services are needed. Therefore, it is hoped that there will
be input obtained in the framework of development planning so that there is no gap between
the government development plans, both programs and budgets and the real needs of the
community (Silmilian, 2013).
As a public sector organization, local governments are required to have a performance that
is oriented to the interests of the community, and encourage the government to always be
responsive to its environmental guidance, by striving to provide the best services in a
transparent and quality manner and clear division of tasks to the government (Wulandari, 2013)
. Improving the performance of the public sector in this case the local government apparatus is
a comprehensive matter where the district and urban village as users of the budget will produce
different levels of performance according to their abilities and sense of responsibility.
According to Wahyudi (2005) in Wulandari (2013), argues that the performance of public
sector organizations in this case local government apparatus is the end result (output) of
organizations that are in accordance with organizational goals, transparent in accountability,
efficient in accordance with the wishes of users of information services, vision and the
organization's mission, quality, fair and organized using adequate facilities and infrastructure.
In general, performance (performance) is an illustration of the level of achievement of the
implementation of an activity / program / policy in realizing the goals, objectives, mission and
vision of the organization contained in the planning strategy of an organization (Mashum, at.all,
2006). Performance is often also used to refer to the achievement or success rate of individuals
and groups of individuals towards the achievement of targets that have been prepared
previously with certain criteria and indicators. Without any goals or targets, then the
achievements that are not obtained cannot be said to be performance because there is no
benchmark for the achievements that have been made so that the targets and benchmarks of the
expected outcomes are important in the performance appraisal process.
According to Fahmi (2011), argues that one way to see the progress of a performance in
one organization is to make an assessment of the organization. Assessments can be made to
employees and managers. The grading system is used the method that is considered to be most
appropriate to the form of the organization, because the misuse of the method will make the
assessment made unable to give the intended answer.
Maximum achievement of performance is influenced by various factors, including the
involvement of the organization in budgeting, the extent to which the level of budgetary
difficulties is structured and how the organization's culture in carrying out their respective
duties and obligations, organizational commitment, accounting control, reporting systems and
much more other factors.
According to Mashun at.all (2006), argues that the budget is a statement about the estimated
performance that will be achieved by an organization in a certain period expressed in monetary
terms. In public sector organizations the budget is an instrument of accountability for the
management of public funds and the implementation of programs financed with public money.
Budgeting in public sector organizations is an important activity because it is related to the
process of determining allocations and for each program and activity.
In the process of public sector budgeting, it starts from the budget preparation stage, the
budget ratification stage, and the budget implementation stage and the budget reporting and
evaluation stages (Purwanugaha at.al, 2012). The current development regarding budgeting is
done by approaching participation between superiors and subordinates. Budgeting with this
participation allows negotiations between managers as superiors and employees as
subordinates. Budgeting participation is a process where there is cooperation from all parties in
making decisions related to the budget that influence the activities of the organization in the

Paulus Peka Hayon and Mohamad Ilham
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 1174 editor@iaeme.com
future. Budgeting participation is a managerial approach that generally can improve managerial
performance. According to Adianto (2008), states that over the past four decades budgetary
participation and its influence on managerial performance have attracted the interest of several
researchers to conduct further research (Argyris 1952, Milani 1975, Kenis 1979, Brownell
1981, Brownell and Mclnnes 1986, Indriantoro 1993, Supomo 1998, Ardianto, 2008). Many
studies pay attention to the issue of budget participation, this is because participation is
considered to have consequences for the attitudes and behavior of organizational members
(Sinuraya 2009). Two reasons for this study are interesting because: 1) Participation is assessed
as a managerial approach that can improve organizational performance, 2) various studies that
examine the association between participation and outcome performance are conflicting
(Bronell, 1981).
The results of research conducted by Brownell (1982) and Brownell and McInness (1986)
show that there is a positive and significant relationship between budgetary participation and
the performance of the film manager (2013), with the results of the study finding that budgetary
participation has a positive effect on apparatus performance government.
In the budgeting process to produce a budget that is ready to be implemented so that it is
not too difficult for budget users. Not too difficult which means here is that it can be reached in
its implementation so that the prepared budget can be applied according to the budget and
according to the calendar set. According to Budiati (2005), states that the budgeting process is
relatively more difficult in uncertain environmental conditions because future events are
difficult to predict. This is related to the behavior of managers. The results of Hopwood's (1972)
study that manager behavior if judged based on the budget will have a negative impact, while
Otley (1978) suggests that managerial behavior if judged based on the budget will have a
positive impact.
The public demand for government performance lately is increasingly felt. The government
is required to provide services to the public that are timely, responsible and so on. The
government has also tried to meet these public demands. But not one hundred percent of the
public's demands have been fulfilled. This is thought to be influenced by organizational culture.
Fahmi (2011), that culture is the work of human creativity that is produced and has been used
as a part of the order of everyday life. A culture that is used and applied in life over a long
period of time will influence the pattern of formation of a society, such as the habit of diligent
work. This habit has an effect on the long term, namely the spirit of diligent work that must
occur until old age, and vice versa. Organizational culture is a habit that has lasted a long time
and is used and applied in the life of work activities as one of the drivers to improve the quality
of work of employees and company managers. Mustikawati's research (1999) shows that the
interaction of participation in budgeting with paternalistic culture has a significant influence on
improving managerial performance.
Based on the background of the problems described above, the researchers want to review
how the influence of budgetary participation, the level of difficulty of the budget, organizational
culture on the performance of the apparatus of the Tanah Miring District. Where currently the
Tanah Miring District is a district with several villages divided into two groups, namely local
villages and advanced villages.
2. METHODOLOGY
This research is a quantitative research that examines the relationship of several independent
variables on the dependent variable. The population in this study was the local government
apparatus in this case the apparatus in the office of the Tanah Miring District of Merauke
Regency. Sampling using the purpose sampling method that is sampling with certain
considerations (Sugiyono, 2014). The samples in this study were district heads, district
The Effect of Budgetary Participation, Difficulty Level and Organizational Culture on the
Performance of Government Officials
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 1175 editor@iaeme.com
secretaries, district treasurers, and village officials (village heads, village treasurers, village
secretaries) in the Tanah Miring District neighborhood, and all staff involved in the budgeting
process. The type of data in this study are primary data obtained through questionnaires
distributed with as many as 39 questionnaires. Data processed in this study using SPSS 21.0.
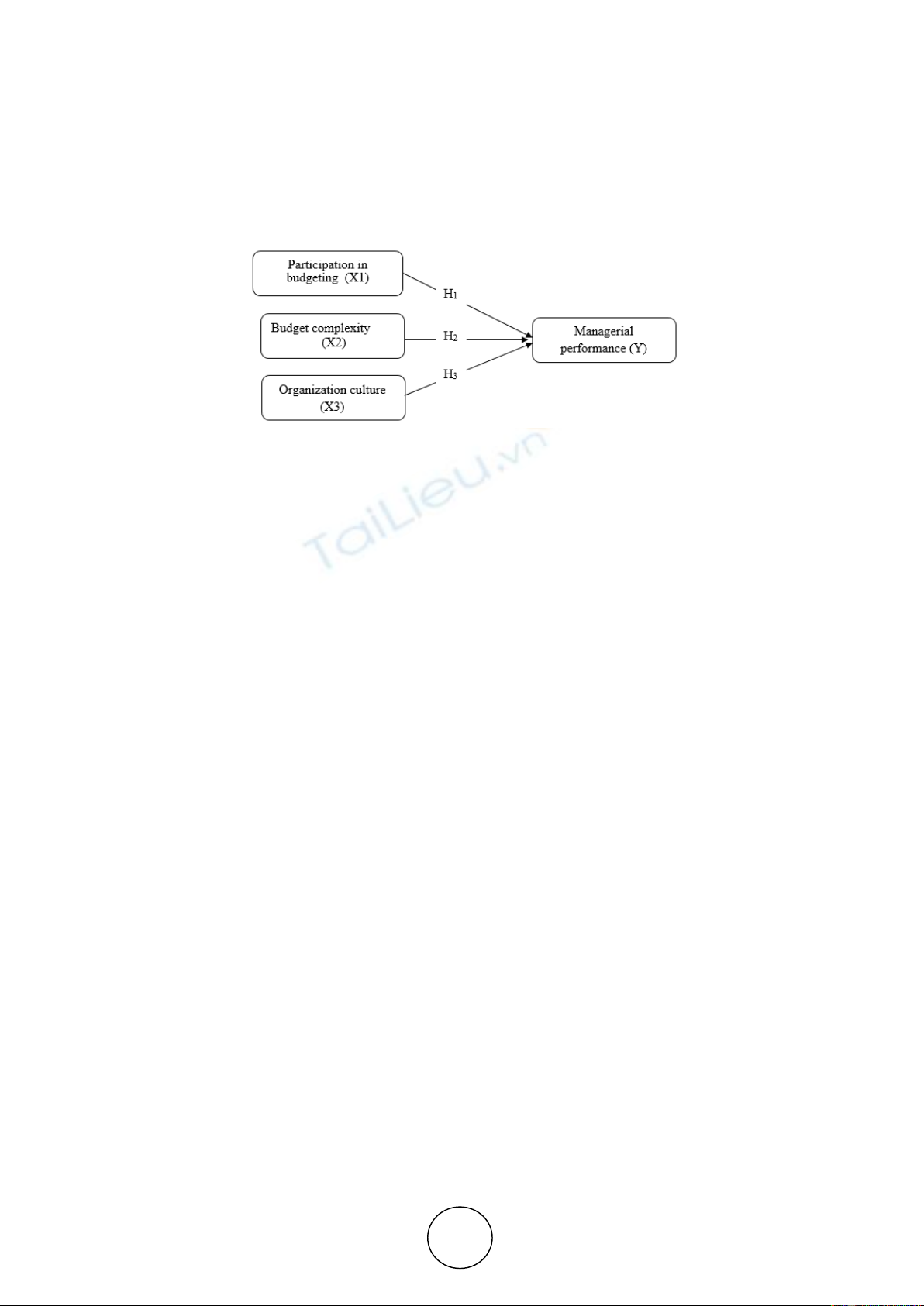
The research model is as follows (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Research model
Research Hypothesis:
H1: Budgeting participation (X1) has a significant positive effect on Government Apparatus
Performance (Y).
H2: The level of budget difficulties (X2) has a significant positive effect on Government
Apparatus Performance (Y).
H3: Organizational culture (X3) has a significant positive effect on the performance of
government apparatus (Y).
Variable measurement:
X1: Participation in budgeting uses 5 indicators, namely, involvement of subordinates,
opportunities given to subordinates, information provided, superiors involving subordinates,
superiors asking for opinions of subordinates, contributions of subordinates.
X2: The level of budget difficulties using indicators, namely problems in implementation,
can be achieved, sincerity in achieving them, expertise and knowledge.
X3: Organizational culture is measured using 4 indicators, namely compliance with
regulations, clarity of purpose, work is private property and nepotism.
Y: The performance of government officials is measured using indicators on this variable,
namely planning, investigation, coordination, evaluation, supervision, staff selection and
representation.
4. RESULTS
4.1. Data Quality Test
Before the data is processed, the data quality test is done first, the data quality test in this study
uses validity test and reliability test.
a. Validity test
A questionnaire is said to be valid if the question in the questionnaire is able to reveal what
will be measured by the questionnaire (Ghozali, 2011). Testing this validity uses the Pearson
correlation approach. If the correlation between scores of each question with a total score has a
significant level below 0.05 then the question item is said to be valid, and vice versa. Based on
the results of data processing, it is known that all items in this study were declared valid.
b. Reliability test
Paulus Peka Hayon and Mohamad Ilham
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 1176 editor@iaeme.com
According to Ghozali (2011) Reliability test is a tool to measure a questionnaire which is
an indicator of a variable or construct. A questionnaire is said to be reliable or reliable if the
respondent's answers are consistently stable over time. To test this reliability produces a
cronbach alpha value. A variable is said to be reliable if it gives an alpha cronbach value> 0.69.
Based on the results of data processing, it is known that all variables in this study are declared
reliable.
4.2. Regression Analysis Results
After testing the quality of the data regression analysis was carried out. The results of the
regression analysis in this study are presented in the following table 1.
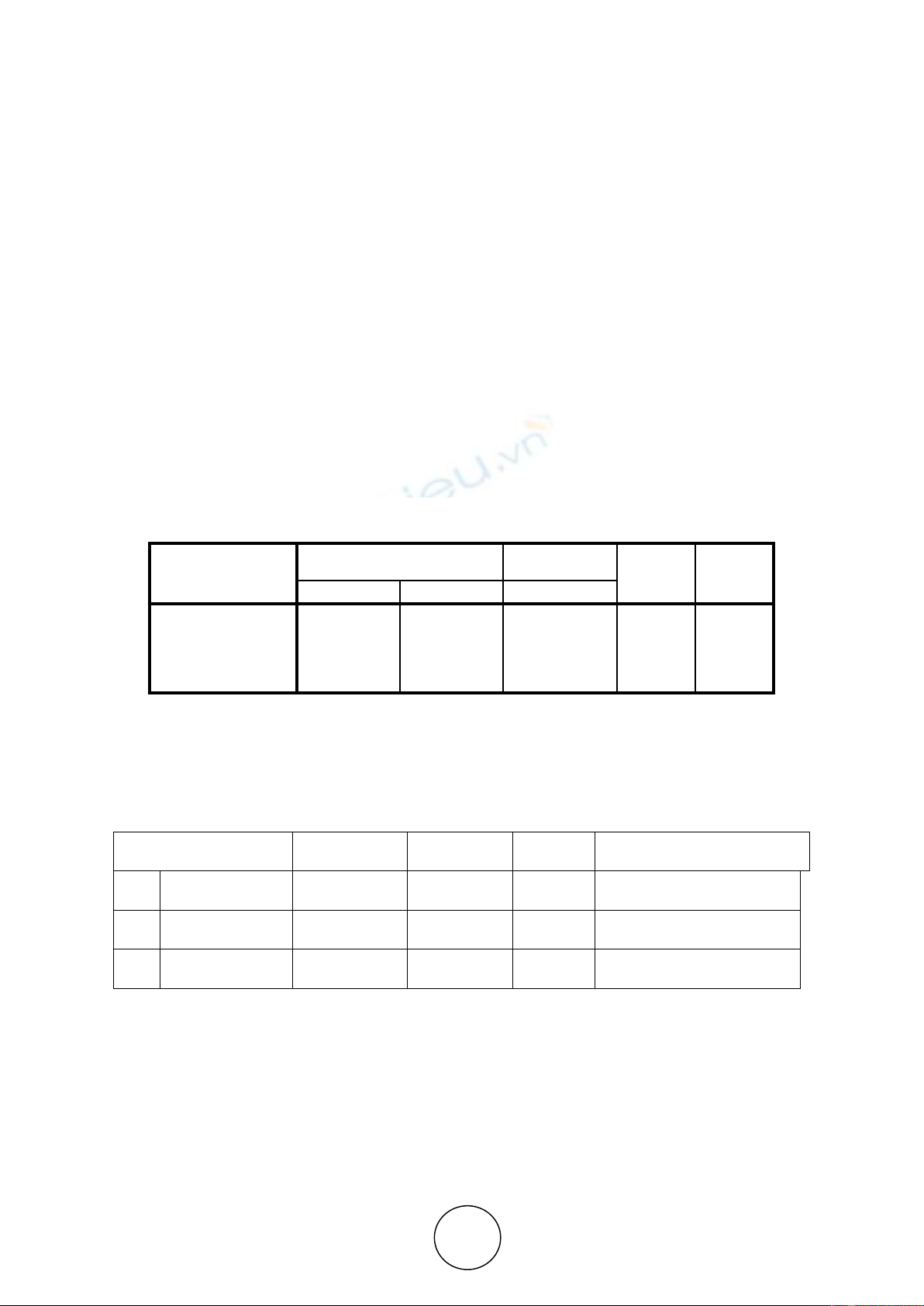
The results of multiple regression analysis obtained from the results of calculations through
SPSS can be seen in Table 1. From the table we can see that the constant value is 8,333, the
regression coefficient value X1 is 0,816, X2 regression coefficient value is -0,201 and X3
regression coefficient of 0.023 so that the equation is obtained:
Y= 8.833+ 0.816X1 +-0.201X2 +0.023X3
Table 1. Multiple Regression Analysis
Coefficientsa
Model
Unstandardized Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t
Sig.
B
Std. Error
Beta
1
(Constant)
8.833
3.606
2.450
.019
X1
.816
.186
.773
4.387
.000
X2
-.201
.257
-.116
-.780
.440
X3
.023
.094
.037
.247
.806
From the above equation it is known that the constant value is 8,833, which means that
when budgetary participation, budget difficulty, and organizational culture are zero, the
performance value of the government apparatus is 8,833.
Table 2. Summary of Hypothesis Testing Results
Hypothesis
Coefficient
t-count
Sig.
Remark
H1 : X1 → Y
0,816
4,387
0,000
Significant positive
H2 : X2 → Y
-0,201
-0,780
0,440
Not Significant negative
H3 : X3 → Y
0,023
0,247
0,806
Not Significant positive
5. DISCUSSION
5.1. Effects of Budgetary Participation
The results of data analysis are known that t-count obtained for 4.387 greater than the value of
t-table with a significant level of 0.000, where this value is smaller than the significant level of
5%. In accordance with the basis of decision making, it can be concluded that partially
participation in budgeting has a significant effect on the performance of government officials
or in other words that the first hypothesis is accepted.






![Tài liệu bồi dưỡng lưu trữ viên chính (Hạng III) theo tiêu chuẩn chức danh: [Chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2021/20211020/caphesuadathemduong/135x160/5031634703055.jpg)







![Văn hóa công vụ: Tài liệu những vấn đề chung [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250821/vyvy108@gmail.com/135x160/70301755829982.jpg)


![Tài liệu Nhập môn tội phạm học [chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250803/sea2che@gmail.com/135x160/20461754291783.jpg)








