
Chapter
Two
External
Analysis:
The
Identification of
Opportunities
and Threats

Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2 | 2
External Analysis requires an assessment of:
Industry environment in which company operates
•Competitive structure of industry
•Competitive position of the company
•Competitiveness and position of major rivals
The country or national environments
in which company competes
The wider socioeconomic or macroenvironment
that may affect the company and its industry
•Social
•Government
• Legal
• International
• Technological
External Analysis
The purpose of external analysis is to identify
the strategic opportunities and threats in the
organization’s operating environment that
will affect how it pursues its mission.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2 | 3
External Analysis:
Opportunities and Threats
Analyzing the dynamics of the industry in which
an organization competes to help identify:
Opportunities
Conditions in the
environment that a
company can take
advantage of to
become more
profitable
Threats
Conditions in the
environment that
endanger the integrity
and profitability of the
company’s business
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2 | 4
Industry Analysis:
Defining an Industry
Industry
•A group of companies offering products or services that are
close substitutes for each other and that satisfy the same
basic customer needs
•Industry boundaries may change as customer needs evolve
and technology changes
Sector
•A group of closely related industries
Market Segments
•Distinct groups of customers within an industry
•Can be differentiated from each other with distinct attributes
and specific demands
Industry analysis begins by focusing on
the overall industry – before
considering market segment or sector-level issues
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2 | 5
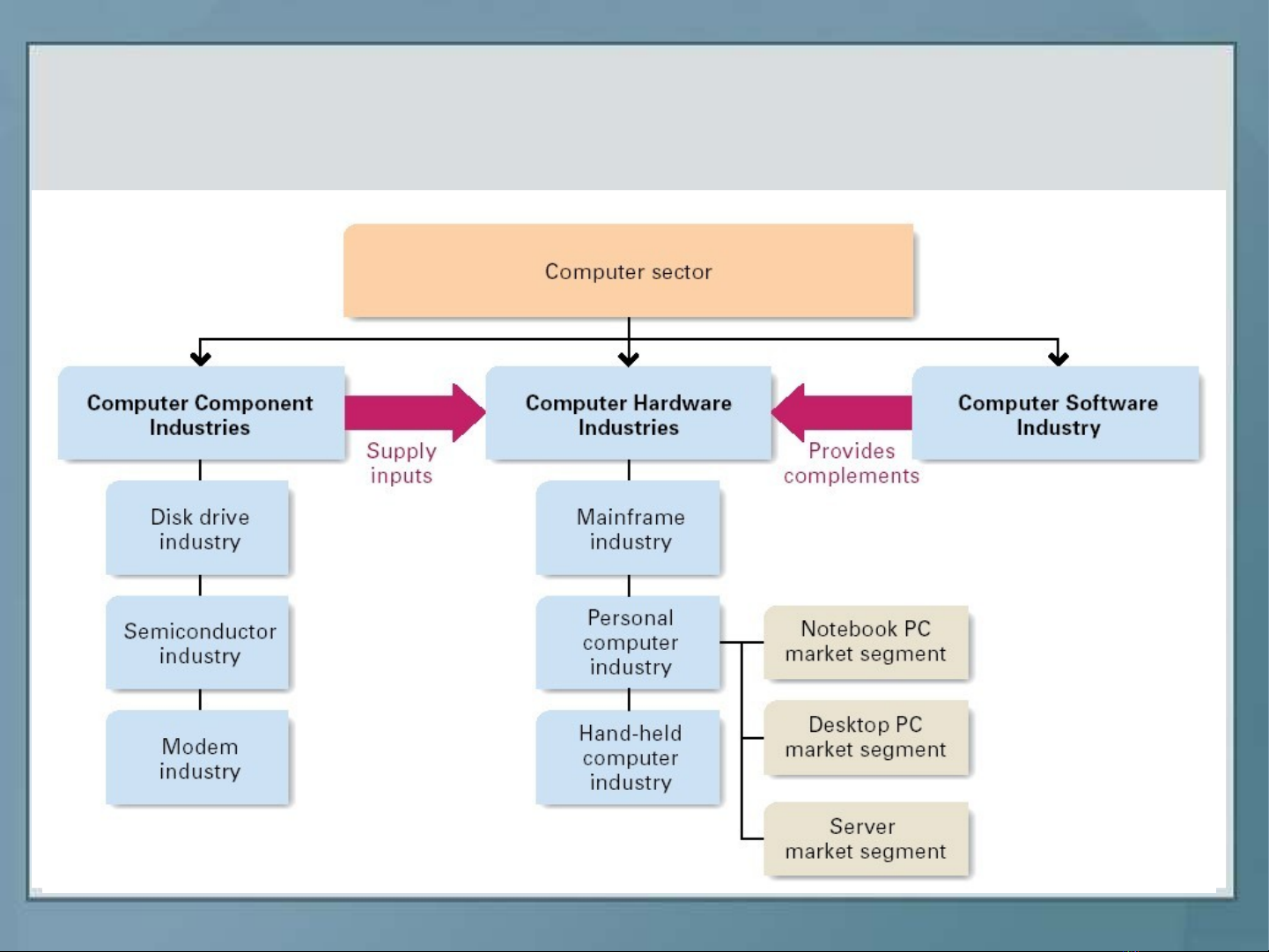
The Computer Sector: Industries
and Market Segments
Figure 2.1


![Tài liệu học tập Quản trị chất lượng [mới nhất/chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250717/vijiraiya/135x160/577_tai-lieu-hoc-tap-quan-tri-chat-luong.jpg)





![Tài liệu học tập Quản trị chất lượng Phần 2: [Thêm mô tả cụ thể về nội dung phần 2]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2023/20231110/caongulam/135x160/1804834663.jpg)
![Tài liệu học tập Quản trị chất lượng Phần 1: [Mô tả chi tiết nội dung tài liệu]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2023/20231110/caongulam/135x160/1081892989.jpg)
















