
Tập 18 Số 5-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
67
VIETNAMESE CURRENT E-COMMERCE AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR HUMAN
RESOURCES TRAINING IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS
Phan Thi Thuy1, Le Vu Thuy Dung2
Received Date: 23/07/2024; Revised Date: 12/09/2024; Accepted for Publication: 30/09/2024
ABSTRACT
E-commerce has developed rapidly worldwide over the past two decades, and Vietnam is now
experiencing its first decade of significant growth. This study aims to assess the current state of
E-commerce (EC) development and the demand for human resources by Vietnamese enterprises. The
study also identifies opportunities for human resource training activities in educational institutions,
particularly through formal training programs. Data from the Department of E-commerce and Digital
Economy and the Vietnam E-commerce Association (2021-2023), and various previous reports and
studies is based to analyse. Using descriptive statistical methods, the study reveals that the development
and application of EC in enterprises, is diverse and has been continuously increasing over the years.
However, enterprises face a shortage of high-tech personnel. Futhermore, human resource training in
educational institutions remain limited. This situation, thus, presents an opportunity to expand training
programs and courses to better meet the needs of society and enterprises.
Keywords: e-commerce, human resources, educational institutions, Vietnam.
1. INTRODUCTION
Digital platforms are keys in the context of
e-commerce and the digital economy. By reducing
search and transaction costs, digital platform-
based businesses facilitate the connection of assets
and services with users more efficiently. In other
words, enterprises can avoid the costs associated
with construction and operation; reduce marketing
expenses through direct access to a large customer
base; decrease human resource investment costs;
and enhance service quality. This also creates
opportunities for businesses to participate in major
e-commerce platforms (Nguyen Nhat Tan, 2024).
In the digital economy, e-commerce is a key driver
for economic development, providing extensive
economic benefits to all countries (Rahayu and
Day, 2017; Terzi, 2011). By utilizing e-commerce
and other digital platforms, products, and services
are transacted more effectively between buyers
and sellers, enhancing product visibility. In other
words, e-commerce positively impacts the business
sector by fostering macroeconomic growth and
labor market expansion (Singh, 2008).
Currently, e-commerce is expanding in scale,
quantity, and access market, encompassing
not only large enterprises but also small and
medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) (OECD, 2019).
According to a report by Wearesocial, the number
of Internet users and participants in e-commerce
globally has shown a rapid increase from 2019
to 2023, with over 5 billion users in 2023 and
an average Internet usage time of 6 hours and 37
minutes (Wearesocial, 2023). Vietnam also is one
of the most promising e-commerce markets in
ASEAN, with an average Internet usage time of 6
hours and 23 minutes, ranking sixth globally. The
scale of Vietnam’s Internet economy ranks third in
Southeast Asia, following Indonesia and Thailand,
with a value of USD 30 billion in 2023, which is
predicted to increase to USD 43 billion by 2025
(iDEA, 2023).
However, this growth has led to significant
challenges in finding human resources with high
technology expertise. This real situation creates a
essential demand for human resources in the digital
economy, particularly in e-commerce, especially
formally trained personnel from educational
institutions. In recent years, e-commerce training
has received greater attention, such as 47% of
institutions offering e-commerce courses. By the
end of 2025, the government goal for half of all
higher education institutions to offer e-commerce
training. This will help businesses adapt to the
digital age (Vietnamese Government, 2020). The
government has issued policies to encourage
e-commerce education. These policies include
supporting e-commerce cources in universities,
promoting online learning methods, and
developing resources for e-commerce research
(Vietnamese Government, 2020). However,
achieving numerical targets for training programs
is feasible while the quality of e-commerce human
1Faculty of Economics, Tay Nguyen University;
2Import-Export & Trading Department, Simexco DakLak;
Corresponding author: Phan Thi Thuy; Tel: 0935346969; Email: ptthuy@ttn.edu.vn

Tập 18 Số 5-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
68
resource training warrants considerable discussion
(VECOM, 2023). Consequently, enterprises are
facing great challenges in finding personnel with
technology expertise (high-tech). For instance,
these enterprises are willing to pay high salaries
and attractive benefits to find highly qualified
high-tech workers.
This paper aims to (1) understand the
development of e-commerce amongin Vietnamese
enterprises; (2) assess the challenges of human
resources for e-commerce; and (3) explore the
opportunities for higher education institutions to
provide professional, high-quality training to meet
societal and business needs.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Materials
Overview of E-commerce
Electronic commerce, commonly written as
E-Commerce, refers to the trading of products
or services using computer networks (Jain et al.,
2021). It encompasses the process of business
trading with other businesses and the formulation
of internal processes using electronic links (Kütz,
2016). Essentially, E-commerce is a business
model where commercial activities are conducted
via electronic networks, particularly the Internet
(Uni Commerce Global Union, 2019).
Types and forms of E commerce
E-commerce encompasses various types and
forms.
- Based on the relationships between
participating parties, the e-commerce includes
(1) Business-to-business (B2B); (2) Business-
to-consumer (B2C); (3) Consumer-to-consumer
(C2C); and (4) Business-to-administration (B2A).
- Based on the type of enterprises, the
e-commerce is divided into (1) Pure players
(enterprises that sell exclusively or primarily via
the Internet); (2) Platform sellers (entities that
provide online marketplaces for external vendors);
and (3) Omni-channel players (businesses that
integrate physical stores with online platforms
to deliver a seamless marketing and centralized
management experience (Uni Commerce Global
Union, 2019).
E-commerce has revolutionized many aspects
of business, including how sales, purchases, and
transactions with customers and suppliers (Achrol
and Kotler, 1999; MacGregor and Vrazalic, 2005).
Three core concepts of the nature of e-commerce:
(1) Transaction Management: Online technologies
and computer networks enable efficient and cost-
effective transaction processing; (2) Business
Process Optimization: E-commerce facilitates the
redesigning of business processes into streamlined,
interconnected activities using online tools and
networks, maximizing efficiency and effectiveness;
(3) Remote Work Enablement: Information
technologies and networks empower employees
to telecommute or telework, fostering flexible
work arrangements, distributed workforces, and
improved productivity.
2.2. Methods
This study employs a descriptive statistics
to analyze datasets. Specifically, authors
collect secondary data from the Department
of E-commerce and Digital Economy and the
Vietnam E-commerce Association from 2021 to
2023. This data helps to insight an overview of
current development of EC.
Beside that, data from educational report of
VECOM during 2021-2024, which informed
the informationa about the human resources and
e-commerce education in educational institutions.
Additionally, materials are sourced from
databases including Scopus, Google Scholar,
Web of Science, and Oficial report, thesises and
paperson the research topic. Keywords such as
“e-commerce,” “human resources,” “professional
and high-quality human resources,” and “education
institutions” are used to search for relevant articles,
which are then selected, compared, synthesized,
and statistically analyzed.
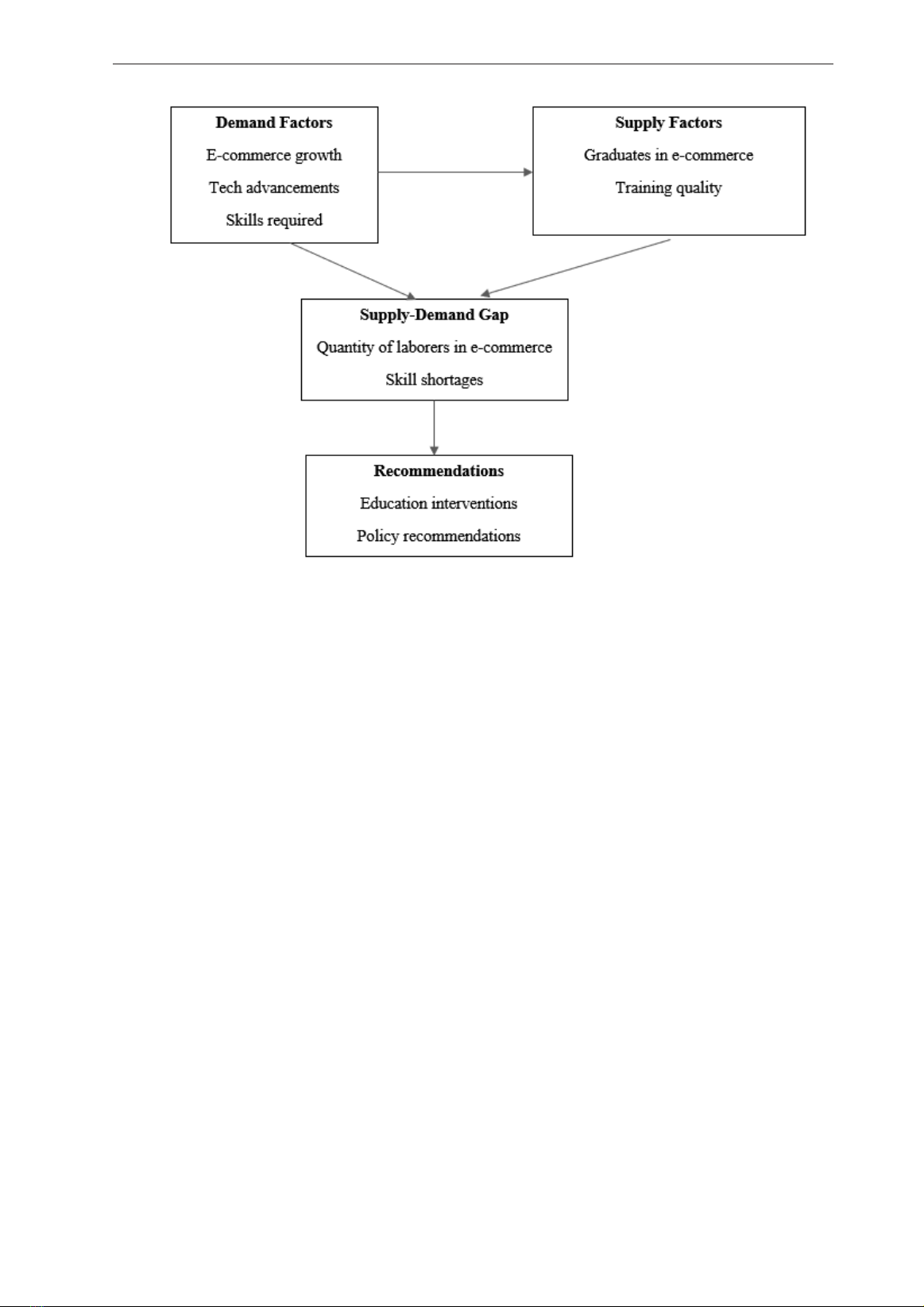
Analytical framework:
The demand-supply framework provides a
structured approach to assessing both current and
future human resource needs in the e-commerce
sector. This approach enables the analysis of the
demand for workers in the e-commerce market and
the supply of trained personnel from educational
institutions.
Tập 18 Số 5-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
69
Figure 1. The demand-supply progress of EC in the study
Source: Suggested by the authors, 2024
From many previous studies of the demand-
supply conceptual framework and the demand
and supply labor markets, authors draw a
demand -supply progress for EC in this study
(Bell, 1981; Esper et al., 2010; Panitchpakdi,
1977; Toutkoushian et al., 2016). The aim is to
identify the demand of EC’s human resources
(depending on EC’s current situation) and
supply of EC’s laborers (graduated laborers
from educational institutions). From that, a gap
of supply-demand is determined before giving
the recommendations.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1. The e-commerce development in Vietnamese
digital economy
Vietnam is now one of the top three fastest-
growing e-commerce markets in Southeast Asia.
In recent years, Vietnam has made significant
strides, becoming one of the fastest-growing
e-commerce markets globally, with an annual
growth rate of 35% (VECOM, 2023). These
results emphasize the increasingly vital role of
e-commerce as a key component of the digital
economy in Vietnam.
For instance, in 2023, the retail e-commerce
market size increased by approximately
25% compared to 2022. Vietnam’s largest
e-commerce platforms are expected to continue
their robust growth in 2024, accounted for VND
310 trillion (US$12.5 billion) of with revenue
and sales volume, representing a 35% increase
from 2023 (VECOM, 2023). This growth
offers numerous benefits, including economic
development, technological advancement,
better use of human resources, lower production
costs, increased international trade, and more
accurate information sharing between buyers
and sellers. However, as noted by Hue et al.
(2024), and Minh et al.(2022), despite the
strengths and advantages of EC, there are
several major obstacles remain unchanged,
leading to its reduced competativeness.
Therefore, in addition to recommendations for
enterprises’ efforts, government policies and
human resources play an important factor for
development of Vietnammese E (Choi & Mai,
2018, Nhung et al., 2024). It implied that the
development and critical role of e-commerce
highlight the opportunities for training high-
quality human resources in this field (Nguyễn
Bích Lâm, 2021).
Tập 18 Số 5-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
70
According to the Vietnam E-commerce report
2023, the scale of Vietnam’s B2C e-commerce
market has experienced an average annual growth
rate of 20%-30%. Vietnam’s B2C e-commerce
revenue is estimated at USD 20.5 billion in 2023,
reflecting a growth rate of 25%, an increase of 5%
compared to 2022 (E-commerce report, 2023).
E-commerce is enabling consumers to shop in
international markets via the Internet, transforming
them into “global consumers.” Specifically, in
2023, Vietnam had 61 million online shoppers,
out of nearly 80% of the population using the
Internet, with an estimated per capita shopping
value of USD 336. Among the various channels,
e-commerce platforms remain the most popular for
online shopping. Retail sales of goods constitute
the highest proportion of all online revenue
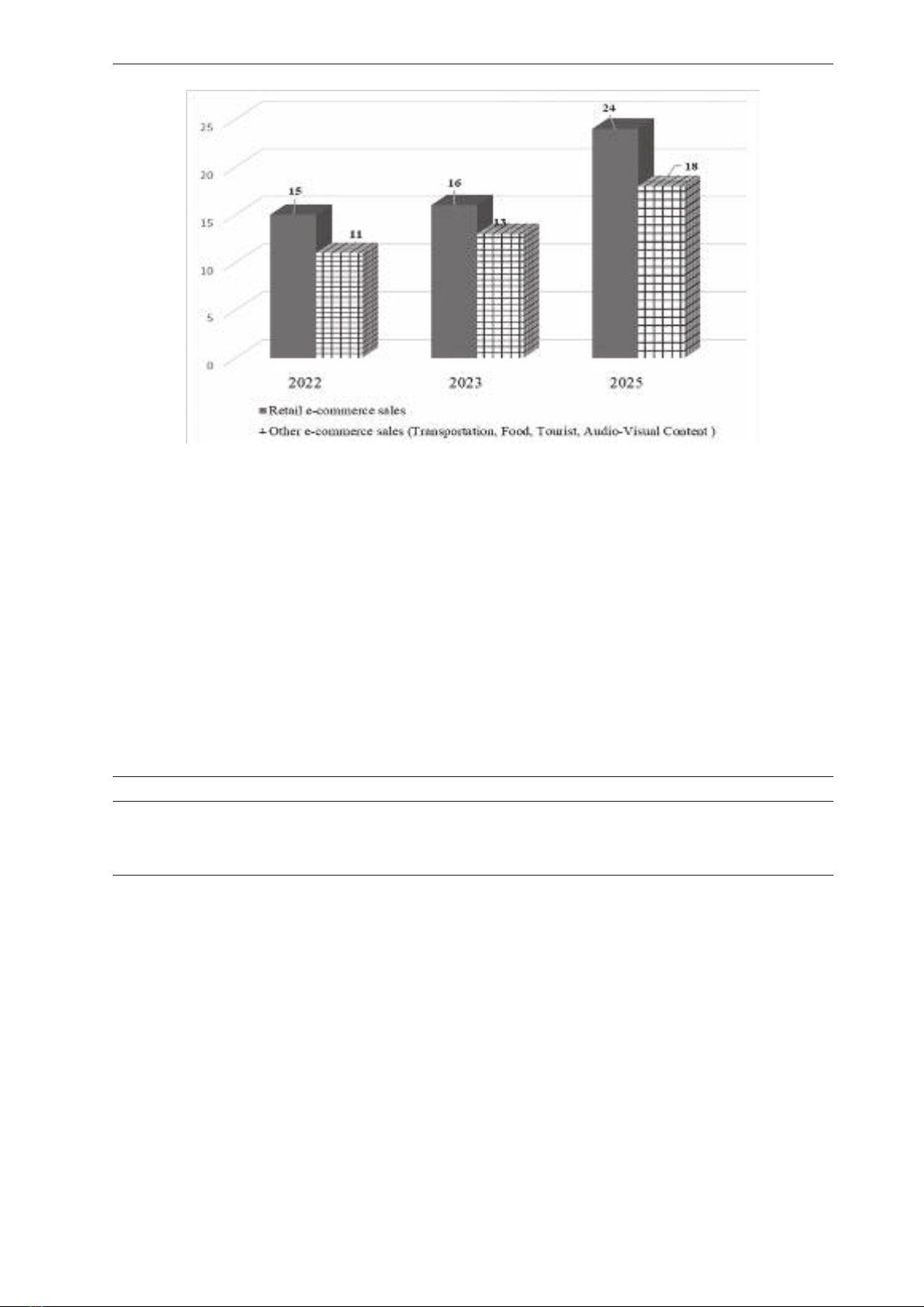
activities in Vietnam (Figure 2). These figures
indicate that the e-commerce sector continues to
grow robustly at a rate exceeding 25%, reaching a
market scale of over USD 20 billion. This growth
rate is expected to be sustained over the three-year
period from 2023 to 2025.
Figure 2. Revenue growth in Vietnam in 2022, 2023 and the forecast for 2025 (Billion USD)
Source: iDEA, 2023
Table 1. The Vietnamese participant in E-commerce
Items 2021 2022 2023
Online shoppers (Thousand people) 54,6 57 61
Ratio of Internet users (%) 73 73,2 78,6
E-commerce gross merchandise value (per person) 251 288 336
Source: iDEA, 2023
This trend motivates enterprises to integrate
e-commerce into their business operations,
underscoring that e-commerce in business is both
a current and future development trajectory aimed
at meeting consumer demands. Consequently,
establishing websites or selecting platforms for
business purposes is crucial for enterprises.
In reality, enterprises are effectively capitalizing
on Vietnamese consumer trends by variety of
platforms. This includes e-commerce platforms
such as Shopee and Lazada, which accounted
for 57% of in 2022. Notably, enterprises are
increasingly leveraging social medias (Facebook,
Tiktok, Zalo, Viber, WhatsApp, and Skype) for
sales, replacing traditional email communication.
Moreover, mobile apps had shown substantial
growth, comprising 22% of transactions in 2022
(Figure 3). The widespread use, convenience, and
speed of social media sales enable businesses to
more easily introduce and deliver their products
to both domestic and international customers.
Statistics show that 62% of enterprises has over
half their workforce regularly uses this tool to
interact with customers (VECOME, 2021). In
2020, the proportion of businesses participating
in e-commerce platforms reached 23% (Statista,
2022).

Tập 18 Số 5-2024, Tạp chí Khoa học Tây Nguyên
71
3.2. The e-commerce human resources in
Vietnamese enterprises
According to the World Bank (2018), the
employment trends in Vietnam will be quite
diverse in the coming years. In the digital context,
it will lead to new types of jobs and employment,
altering the nature and conditions of work,
changing skill requirements, and impacting the
labor market as well as labor distribution (United
Nations Conference on Trade and Development,
2017).
Regarding EC, E-commerce requires human
resources with specialized skills and knowledge.
These include understanding technology,
regulations, and online business practices.
Employees should be skilled in both business
and technology, always learning about new
developments, and staying ahead of emerging
business opportunities.
In the other words, human resources require
systematic training, progressing from basic
to advanced levels corresponding to specific
positions, tasks, and specialized fields. However,
the situation shows that the e-commerce human
resources are facing a severe shortage, which was
highlighted by previous studies (Dung & Tu, 2018;
Nhung, 2023; Nhung et al., 2024).
Figure 3. The percentage of online market share via platforms in 2023
Source: iDEA, 2023
Table 2. The human resources of e-commerce in Vietnamese enterprises (%)
Items 2021 2022 2023
(1) 22 35 -
(2) 32 - -
(3) - 64 65
(1) E-commerce specialist in enterprises; (2) Enterprises facing difficulties in recruiting skilled
e-commerce and technology workers; (3) Enterprises prioritize hiring personnel trained in e-commerce
Source: iDEA, 2023
Table 2 indicates that the proportion of
enterprises with dedicated e-commerce specialists
was 22% in 2021 and 35 % in 2022, respectively.
Concurrently, from 32% to 65 % of enterprises
has facing difficulties in recruiting e-commerce
personnel during 2021 - 2023.
Moreover, enterprises need to diversify
their human resources when participating in
the e-commerce market. In other words, most
enterprises faced challenges in recruitment
of workers, who lack skills such as database
management, marketing, and online payment
implementation. Clearly, the shortage of
e-commerce human resources is driving the
recruitment demand and providing significant
employment opportunities for the Vietnamese
workforce (VECOM, 2023).
This presentation implied that there is an
opportunity for educational institutions to focus
on training human resources in this field to meet
the needs of society and businesses.



![Đề thi Giao tiếp trong kinh doanh học kì 3 năm 2021-2022 có đáp án [kèm đề thi]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250409/gaupanda086/135x160/5071744187387.jpg)






















